Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves - Sky Wave Propagation | 12th Physics : UNIT 10b : Communication Systems
Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 10b : Communication Systems
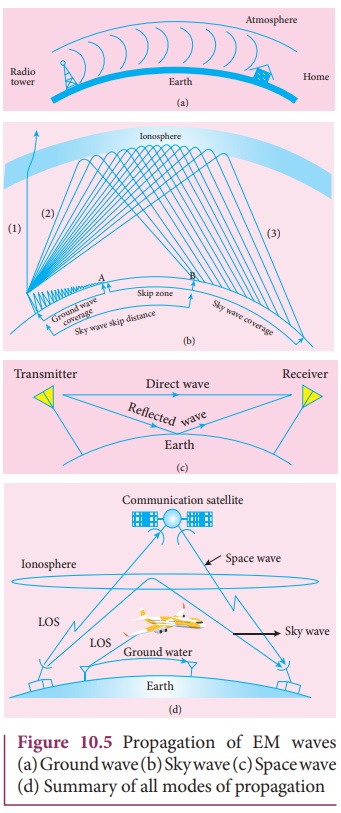
Sky Wave Propagation
SKY WAVE PROPAGATION
The mode of propagation in which the electromagnetic waves
radiated from an antenna, directed upwards at large angles, gets reflected by
the ionosphere back to earth is called sky wave propagation or ionospheric
propagation. The corresponding waves are called sky waves (Figure 10.5(b)).
The frequency range of EM waves in
this mode of propagation is 3 to 30 MHz. EM waves of frequency more than 30 MHz
can easily penetrate through the ionosphere and does not undergo reflection. It
is used for short wave broadcast services. Medium and high frequencies are for
long-distance radio communication. Extremely long- distance communication is
also possible as the radio waves can undergo multiple reflections between the
earth and the ionosphere. A single reflection helps the radio waves to travel a
distance of approximately 4000 km.
Ionosphere acts as a reflecting
surface. It is at a distance of approximately 50 km and spreads up to 400 km above
the Earth surface. Due to the absorption of ultraviolet rays, cosmic ray, and
other high energy radiations like α, β rays from sun, the air molecules in the
ionosphere get ionized. This produces charged ions and these ions provide a
reflecting medium for the reflection of radio waves or communication waves back
to Earth within the permitted frequency range. The phenomenon of bending the
radio waves back to earth is nothing but the total internal reflection.
This is the reason why the EM waves
are transmitted at a critical angle to ensure that the waves undergo total
reflection and reaches the ground without escaping into space.
The shortest distance between the transmitter and the point of
reception of the sky wave along the surface is called as the skip distance shown in Figure 10.5(b).
The electromagnetic waves are transmitted from the ground at
particular angles. When the angle of emission increases, the reception of
ground waves decreases. At one point, there will be no reception due to ground
waves and marked as A in the Figure
10.5(b).
If the angle of emission is
increased further, the reception of sky waves starts at point B in the Figure
10.5(b). There is a zone (in between A
and B) where there is no reception of electromagnetic waves neither ground nor
sky, called as skip zone or skip area.
The higher the frequency, higher is
the skip distance and for a frequency less than the critical frequency, skip
distance is zero.
Related Topics