Chapter: Essentials of Psychiatry: Somatoform Disorders
Somatoform Disorders: Epidemiology, Treatment
Epidemiology
In view of the vicissitudes of diagnostic approaches and the re-cency of
the current somatoform disorder grouping, it is not sur-prising that estimates
of the frequency of this group of disorders in the general population as well
as in clinical settings are incon-sistent if not nonexistent. Yet, existing
data seem to indicate that such problems are indeed common and account for a
major pro-portion of clinical services, especially in primary care settings.
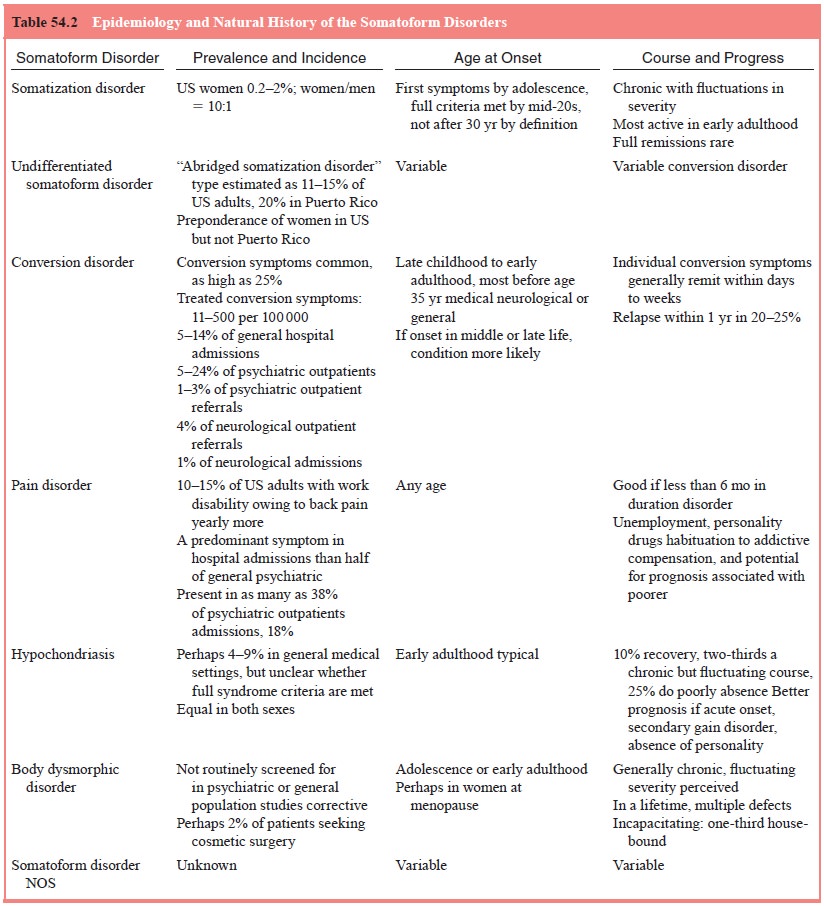
Table 54.2 summarizes what is known about the epidemi-ology of these
disorders.
In
consideration of the substantial frequency of somato-form disorders in
nonpsychiatric settings, instruments have been designed to aid primary care
physicians in diagnosing psychiat-ric conditions. The Primary Care Evaluation
of Mental Disorders (PRIME-MD) (Spitzer et al., 1994) includes somatoform
items in its screening questionnaire and in its physician education guide. The
DSM-IV Primary Care Edition (DSM-IV-PC) includes an “unex-plained physical
symptoms” algorithm among the nine it included to address the most common
psychiatric symptom groups presenting in primary care settings (American
Psychiatric Association, 1995).
The epidemiology of the specific somatoform disorders is discussed
individually in following sections.
Treatment
Whereas specific somatoform disorders indicate specific treat-ment
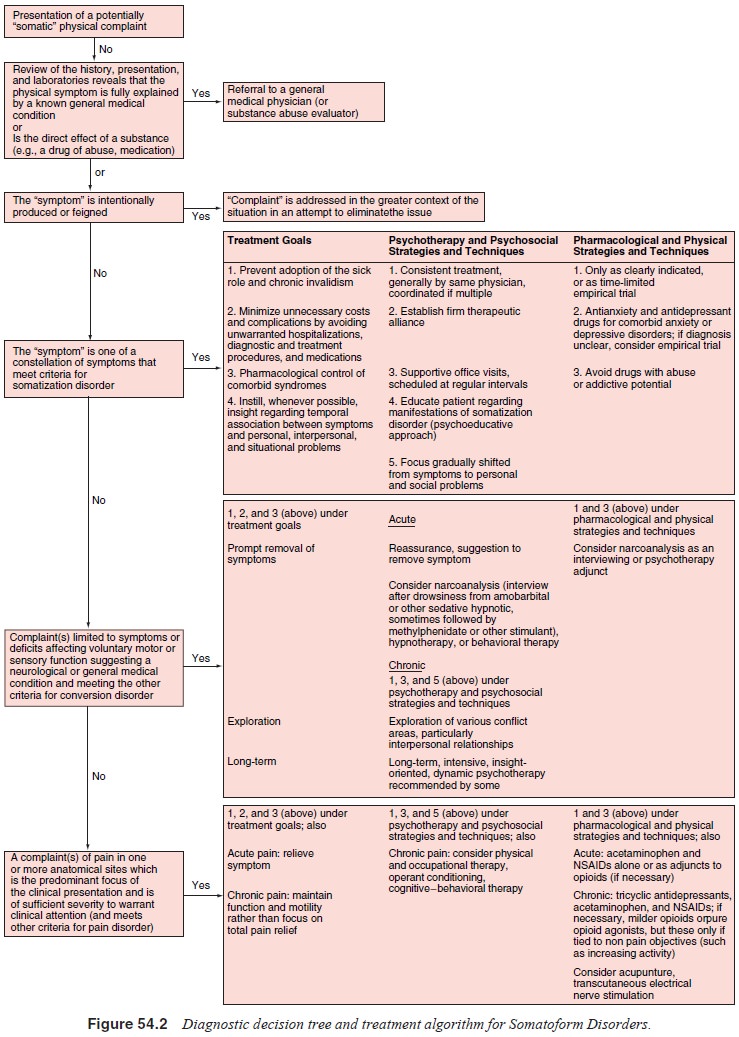
approaches, some general guidelines apply to the somato-form disorders as a
whole (Figure 54.2 and Table 54.2). Thera-peutic goals include 1) as an
overriding goal, prevention of the adoption of the sick role and chronic
invalidism; 2) minimiza-tion of unnecessary costs and complications by avoiding
unwar-ranted hospitalizations, diagnostic and treatment procedures, and
medications (especially those of an addictive potential); and 3) effective
treatment of comorbid psychiatric disorders, such as depressive and anxiety
syndromes. The three general treatment strategies include 1) consistent
treatment, generally by the same physician, with careful coordination if multiple
physicians are in-volved; 2) supportive office visits, scheduled at regular
intervals rather than in response to symptoms; and 3) a gradual shift in focus
from symptoms to an emphasis on personal and interper-sonal problems.
Related Topics