Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: Biowarfare and Bioterrorism
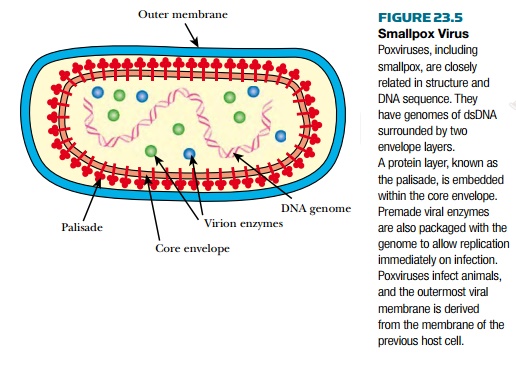
Smallpox Virus
SMALLPOX
VIRUS
Smallpox virus is a member of the
poxvirus family. These are large viruses that contain double-stranded DNA (
Fig. 23.5 ). Poxviruses are the most complex animal viruses and are so large
they may just be seen with a light microscope. They measure approximately 0.4 by
0.2 microns, compared to 1.0 by 0.5 microns for bacteria such as E. coli .
Unlike other animal DNA viruses, which all replicate inside the cell nucleus,
poxviruses replicate their dsDNA in the cytoplasm of the host cell. They build
subcellular factories known as inclusion bodies, inside which virus particles
are manufactured. Poxviruses have 185,000 nucleotides encoding 150 to 200
genes, about the same number as the T4 family of complex bacterial viruses.
Variola virus infects only humans, which allowed its eradication
by the World Health Organization, a task completed by 1980. Smallpox is highly
infectious and exists as two variants, Variola major with a fatality
rate of 30% to 40% and Variola minor with a fatality rate of around 1%.
The two differ by about 2% of their base sequence. Vaccinia virus is a
related but very mild poxvirus which is used as a live vaccine. Immunity is
effective against several closely related poxviruses including smallpox and
monkeypox.
For an industrial nation, the preparation of large amounts of a virus whose particles are fairly stable and long-lived, such as smallpox, is feasible. For a Third World nation, it might be possible. A suggested terrorist scenario is that suicidal volunteers would be deliberately infected and then travel to densely populated target areas. They would deliberately mingle with as many people as possible, by attending mass events and traveling the subways in large cities.
Related Topics