Chapter: Biology of Disease: Disorders of the Gastrointestinal Tract, Pancreas, Liver and Gall Bladder
Small Intestine and Homeostasis
THE SMALL INTESTINE AND
HOMEOSTASIS
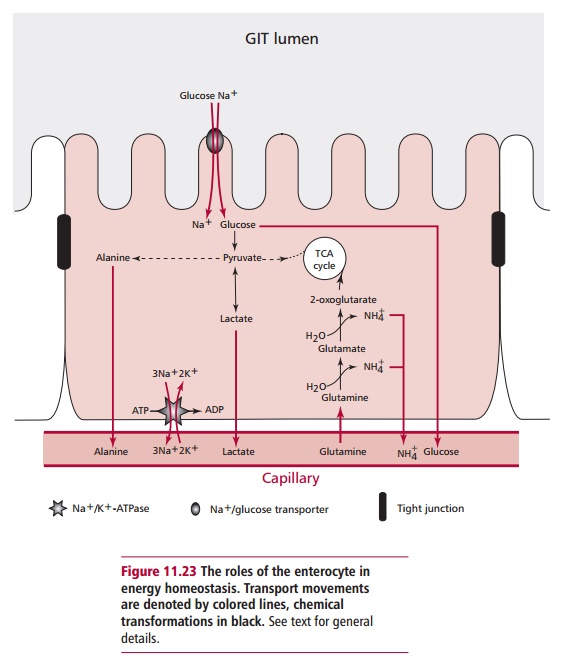
Within enterocytes a portion of the monosaccharides
absorbed are converted to lactate by glycolysis. Excess nonessential amino
acids, especially glutamine, are used to synthesize alanine and ammonia (Figure 11.23). These products are then
delivered to the liver in the hepatic portal vein. Converting some of the
absorbed nutrients to lactate and alanine reduces the metabolic load on the
liver because it can easily regenerate pyruvate from them. Pyruvate is a
versa-tile liver metabolite; it is a substrate for the TCA cycle, allowing the
formation of ATP during oxidative phosphorylation but it can be used for the
biosynthe-sis of glucose and glycogen, ketone bodies, fatty acids and all but two
of the nonessential fatty acids and cholesterol. The GIT is a significant
contributor to nutrient homeostasis both during and after nutrient absorption
because the formation of lactate and alanine continues even when absorption
ceases.
Related Topics