Organic Nitrogen Compounds | Chemistry - Short answer Questions | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Organic Nitrogen Compounds
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Organic Nitrogen Compounds
Short answer Questions
Organic Nitrogen Compounds | Chemistry
Short answer Questions
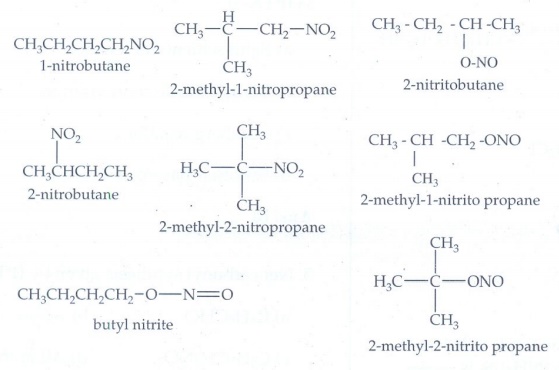
1. Write down the possible isomers of the C4 H9NO2 give their IUPAC names
2. There are two isomers with the formula CH3NO2 . How will you distinguish between them?
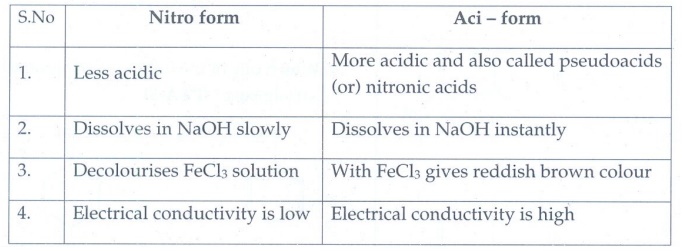
Nitro form
1.
Less acidic
2.
Dissolves in NaOH slowly
3.
Decolourises FeCl3 solution
4.
Electrical conductivity is low
Aci – form
1.
More acidic and also called pseudoacids (or) nitronic acids
2.
Dissolves in NaOH instantly
3.
With FeCl3 gives reddish brown colour
4.
Electrical conductivity is high
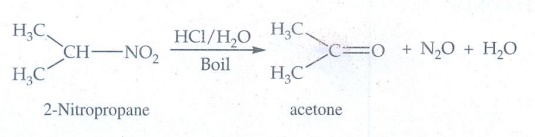
3. What happens when
i. 2 – Nitropropane boiled with HCl
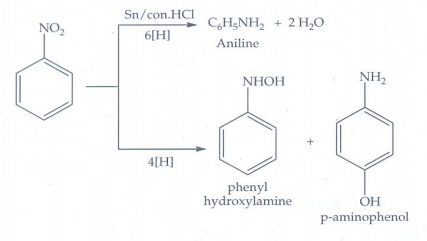
ii. Nitrobenzene undergo electrolytic-reduction in strongly acidic medium.
iii. Oxidation of tert – butylamine with KMnO4
iv. Oxidation of acetoneoxime with trifluoroperoxy acetic acid.
i) 2 - Nitropropane boiled with
HCl
When
2 - Nitropropane boiled with HCl gives acetone.
ii. Nitrobenzene electrolytic
reduction in strongly acidic medium.
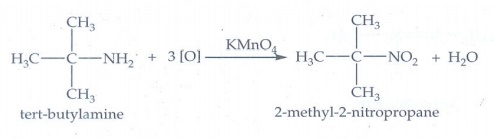
iii. Oxidation of tert -
butylamine with KMnO4
tert
- butyl amine is oxidised with aqueous KMnO4 give tert - nitro
alkanes.
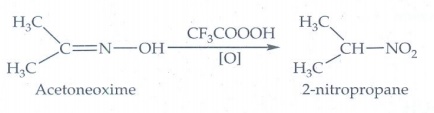
iv. Oxidation of acetoneoxime
with trifluoroperoxy acetic acid.
Oxidation
of acetoneoxime with trifluoroperoxy acetic acid gives 2 - nitropropane.
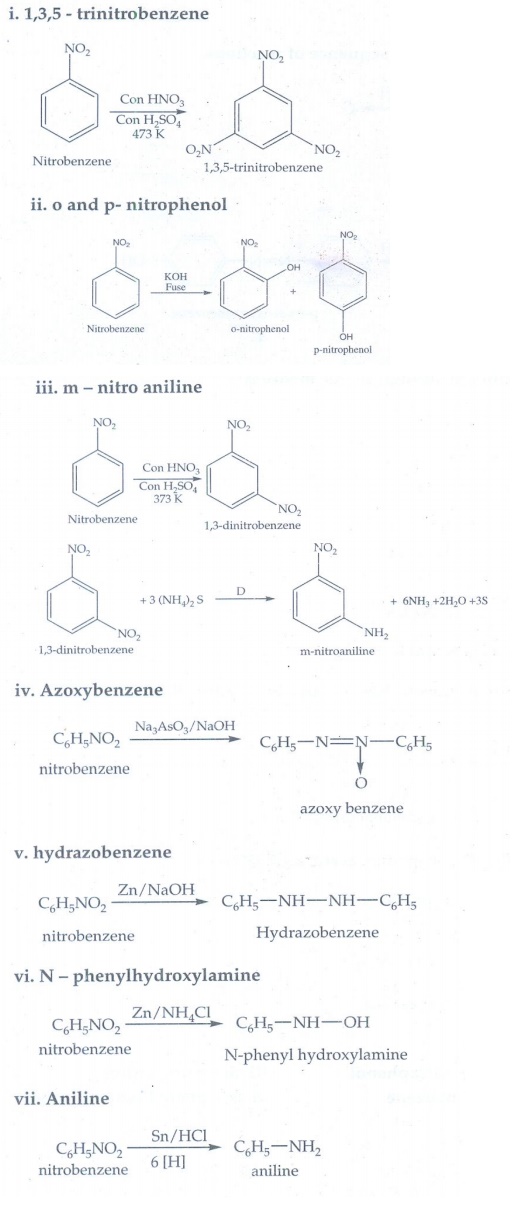
4. How will you convert nitrobenzene into
i. 1,3,5 - trinitrobenzene
ii. o and p- nitrophenol
iii. m – nitro aniline
iv. azoxybenzene
v. hydrozobenzene
vi. N – phenylhydroxylamine
vii. Aniline
Answer:
5. Identify compounds A,B and C in the following sequence of reactions.
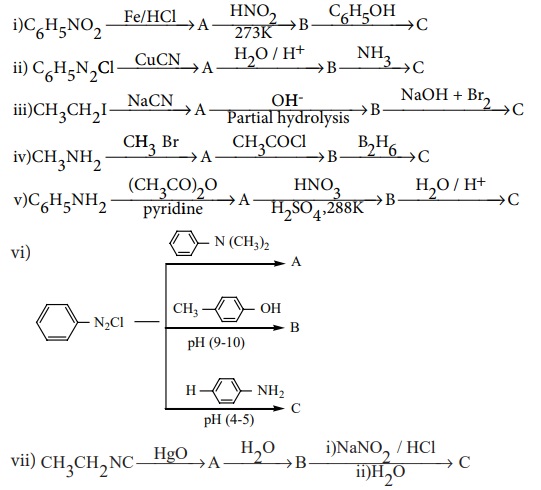
Answer:
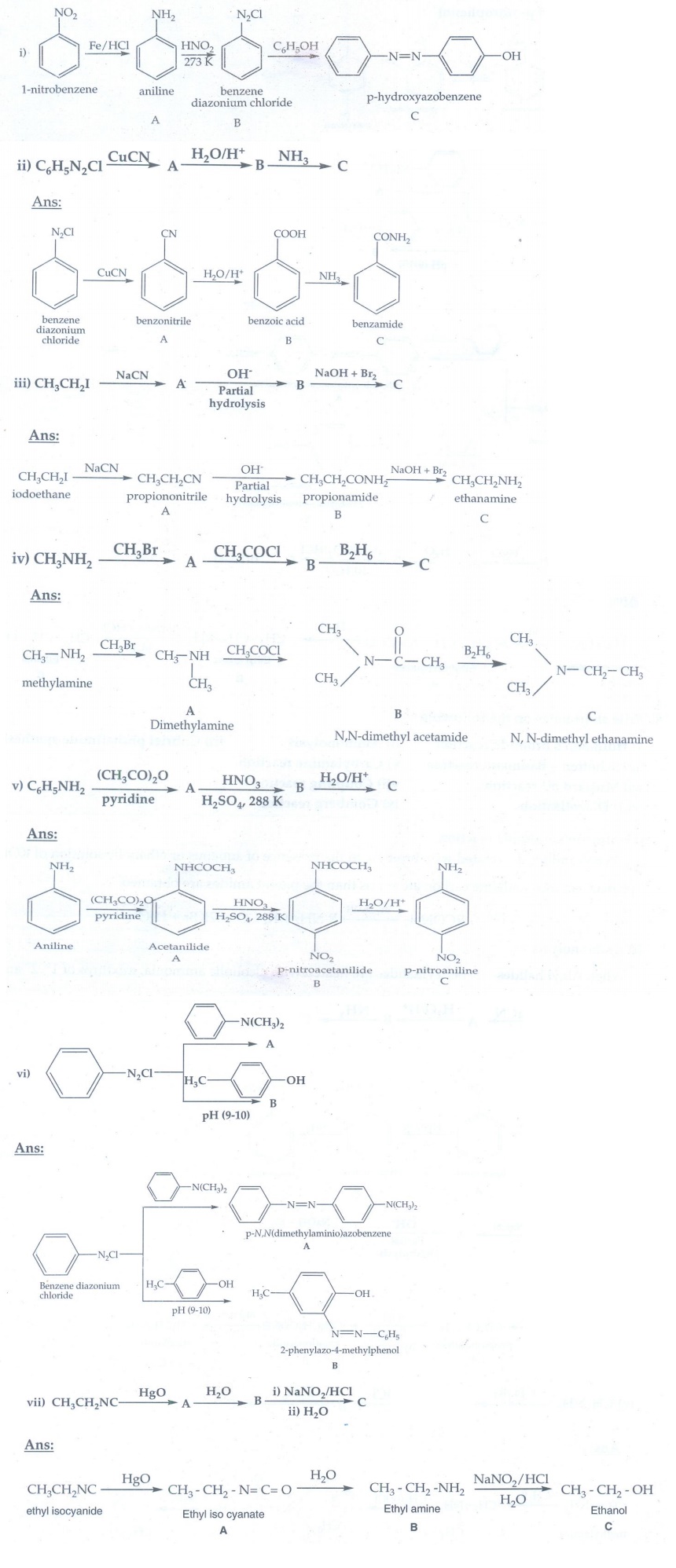
6. Write short notes on the following
i. Hofmann’s bromide reaction
ii. Ammonolysis
iii. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
iv. Schotten – Baumann reaction
v. Carbylamine reaction
vi. Mustard oil reaction
vii. Coupling reaction
viii. Diazotisation
ix. Gomberg reaction
i) Hofmann's bromide reaction
When
amides are treated with bromine in the presence of aqueous or ethanolic
solution of KOH, primary amines with one carbon atom less than the parent
amides are obtained.
RCONH2
—- Br2/KOH→ R NH2 + K2 CO3 +
2KBr + H2O
ii) Ammonolysis
When
Alkyl halides (or) benzylhalides are heated with alcoholic ammonia, mixtures of
1°, 2° and 3° amines and quaternary ammonium salts are obtained.
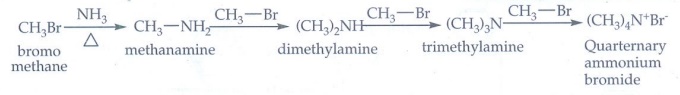
iii) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
Phthalimide
on treatment with ethanolic KOH forms potassium salt of phthalimide which on
heating with alkyl halide followed by alkaline hydrolysis gives primary amine.
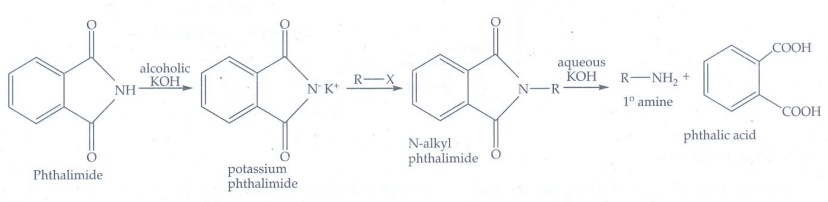
iv) Schotten - Baumann reaction
Aniline
reacts with benzoyl chloride in the presence of NaOH to give N -phenyl
benzamide.

v) Carbylamine reaction
Aliphatic
(or) aromatic primary amines react with chloroform and alcoholic KOH to give
isocyanides (carbylamines), which has an unpleasant smell. This test used to
identify the primary amines.
C2H5 - NH2 [Ethylamine] + CHCl3 [Chloroform] + 3K0H → C2H5
- NC [Ethyl isocyanide] + 3KCl +
3H2O

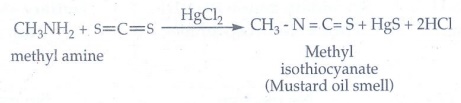
vi) Mustard oil reaction
When
primary amines are treated with carbon disulphide (CS2), N -
alkyldithio carbonic acid is formed which on subsequent treatment with HgCl2,
give an alkyl isothiocyanate.
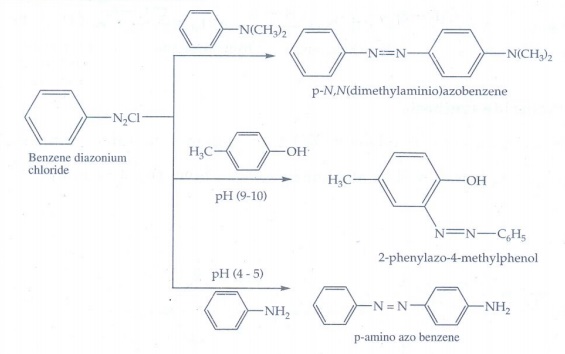
vii) Coupling reaction
Benzene
diazonium chloride reacts with electron rich aromatic compounds like phenol,
aniline to form brightly coloured azo compounds. Coupling generally occurs at
the para position. If para position is occupied then coupling occurs at the
ortho position. Coupling tendency is enhanced if an electron donating group is
present at the para - position to N2+ C𝑙− group.
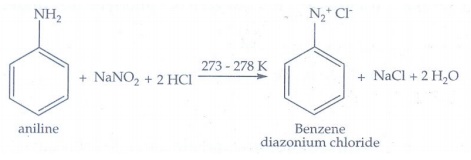
viii) Diazotisation
Aniline
reacts with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperature (273 - 278
K) to give benzene diazonium chloride which is stable for a short time and
slowly decompose even at low temperatures.
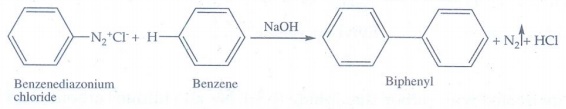
ix) Gomberg reaction
Benzene
diazonium chloride reacts with benzene in the presence of sodium hydroxide to
give biphenyl.
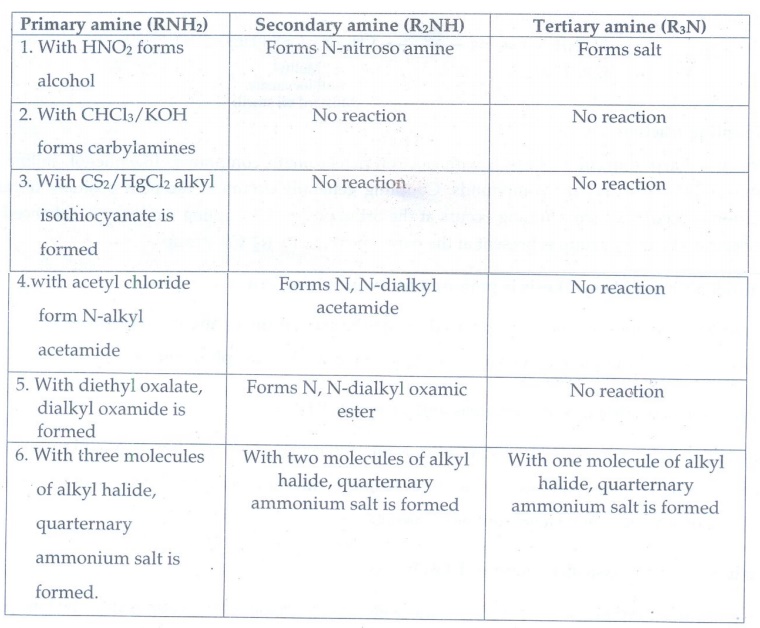
7. How will you distinguish between primary secondary and tertiary alphatic amines.
8. Account for the following
i. Aniline does not undergo Friedel – Crafts reaction
ii. Diazonium salts of aromatic amines are more stable than those of aliphatic amines
iii. pKb of aniline is more than that of methylamine
iv. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is preferred for synthesising primary amines.
v. Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not
vi. Amines are more basic than amides
vii. Although amino group is o – and p – directing in aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions, aniline on nitration gives a substantial amount of m – nitroaniline.
i. Aniline does not undergo
Friedel - Crafts reaction.
Aniline
does not undergo Friedel - Crafts reaction (alkylation and acetylation).
Aniline is basic in nature and it donates its lone pair to the lewis acid AlCl3
to form an adduct which inhibits further the electrophilic substitution
reaction
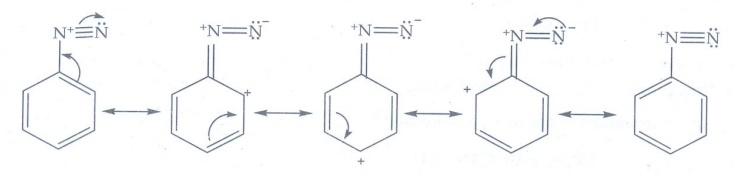
ii. Diazonium salts of aromatic
amines are more stable than those of aliphatic amines
Diazonium
salts of aromatic amines are more stable. This is due to the dispersal of the
positive charge over the benzene ring
iii) pKb of aniline is
more than that of methylamine
The
lone pair of electrons on the N atom present in the aniline is involved
delocalized over the benzene ring. Therefore lone pair of electron on the
nitrogen atom is not available for donation.
Whereas
in methylamine due to +1 effect, the lone pair of electrons are available for
donation and shows higher basicity than aniline.
Smaller
the value of pKb, stronger is the base. Methylamine is strong base
than aniline. Hence pKb of aniline is more than that of methylamine.
iv) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
is preferred for synthesising primary amines.
Gabriel
phthalimide synthesis is preferred for synthesizing primary amines. It involves
SN2 nucleophilic substitution of alkyl halide by the
anion formed by the phthalimide.
v) Ethylamine is soluble in water
whereas aniline is not
When
Ethylamine was added to water, it forms intermolecular Hydrogen bonding with
water and therefore soluble water. Aniline does not form H-bond with water to a
very large extent due to the presence of aromatic ring. Hence aniline is
insoluble.
vi) Amines are more basic than
amides
The
carbonyl group present in the amide draws electron from the -NH2
group results the lone pair of electron on the nitrogen atom of -NH2
group is less available for donation and the basicity decreased. The lone pair
of electrons on the amine is easily available to act as a base. Hence amines
are more basic than amides.
vii) Although amino group is o -
and p - directing in aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions, aniline on
nitration gives a substantial amount of m - nitroaniline.
Direct
nitration of aniline gives o and p - nitro aniline. In a strong acid medium
aniline is protonated to form anilinium ion which is m - directing and hence m
- nitro aniline is also formed
9. Arrange the following
i. In increasing order of solubility in water, C6 H5NH2 ,(C2H5 )2NH,C2 H5NH2
ii. In increasing order of basic strength
a) aniline, p- toludine and p – nitroaniline
b) C6 H5 NH2 ,C6 H5 NHCH3 ,C6 H5 NH2 ,p-Cl-C6 H4 -NH2
iii. In decreasing order of basic strength in gas phase
(C2 H5 )NH2 ,(C2H5 )NH, ( C2H5 )3 N and NH3
iv. In increasing order of boiling point
C6H5OH, (CH3)2NH, C2H5NH2
v. In decreasing order of the pKb values
C2 H5NH2 , C6H5 NHCH3 ,(C2 H5 )2 NH and CH3NH2
vi. Increasing order of basic strength
C6 H5NH2 ,C6H5 N(CH3 )2 ,(C2H5 )2 NH and CH3 NH2
vii. In decreasing order of basic strength
i. In increasing order of
solubility in water, C6H5NH2 ,(C2H5)2NH,C2H5NH2
C6H5NH2
< (C2H5)2NH < C2H5NH2
ii. In increasing order of basic
strength
a) aniline, p- toluidine and p -
nitroaniline
p
- nitroaniline < aniline< p- toluidine
b) C6H5NH2,C6H5NHCH3
,p-Cl-C6H4 -NH2
p-Cl-C6H4
-NH2 < C6H5NH2 < C6H5NHCH3
,
iii. In decreasing order of basic
strength in gas phase
C2H5NH2,
(C2H5)2NH,( C2H5)3
N and NH3
(C2H5)3N
> (C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2
> NH3
iv. In increasing order of
boiling point
C6H5OH, (CH3)2NH,
C2H5NH2
(CH3)2NH
< C2H5NH2 < C6H5OH
v. In decreasing order of the pKb
values C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3,
(C2H5)2NH and CH3NH2
C6H5NHCH3
< CH3NH2 < C2H5NH2
< (C2H5)2NH
vi. Increasing order of basic
strength
C6H5NH2,
C6H5N(CH3)2, (C2H5)2
NH and CH3NH2
C6H5NH2
< C6H5N(CH3)2 <CH3NH2<(C2H5)2
NH
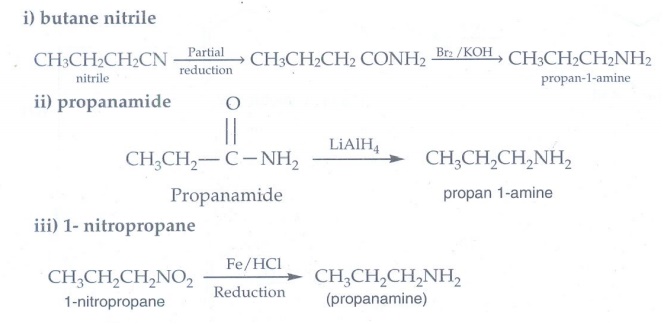
10. How will you prepare propan – 1- amine from
i) butane nitrile ii) propanamide ii) 1- nitropropane
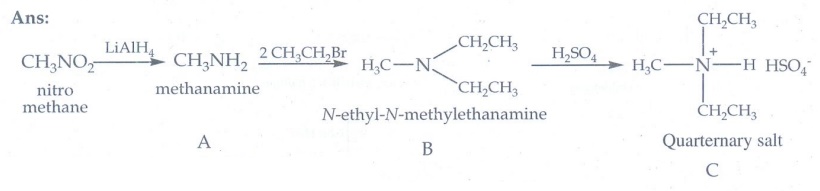
11. Identify A,B,and C
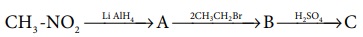
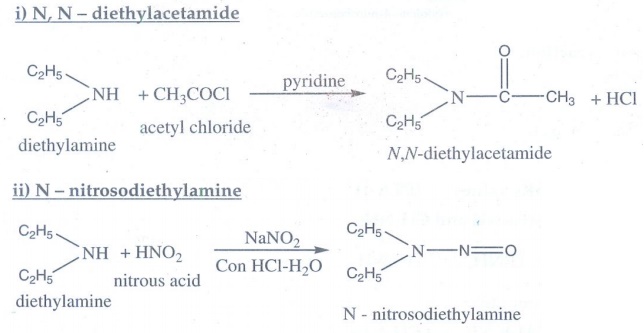
12. How will you convert diethylamine into
i) N, N – diethylacetamide ii) N – nitrosodiethylamine
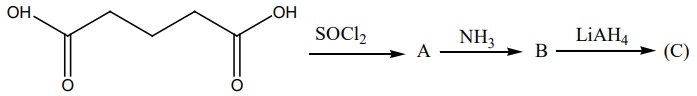
13. Identify A,B and C

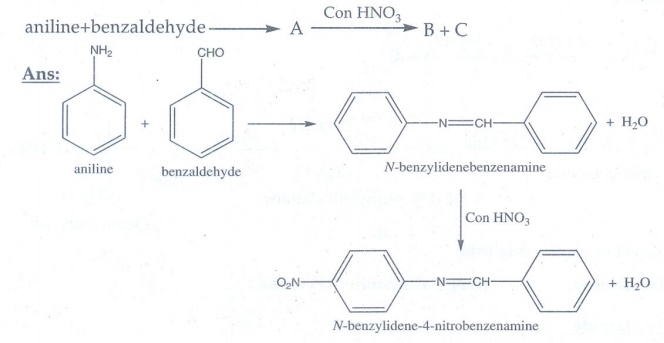
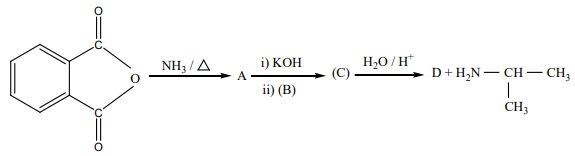
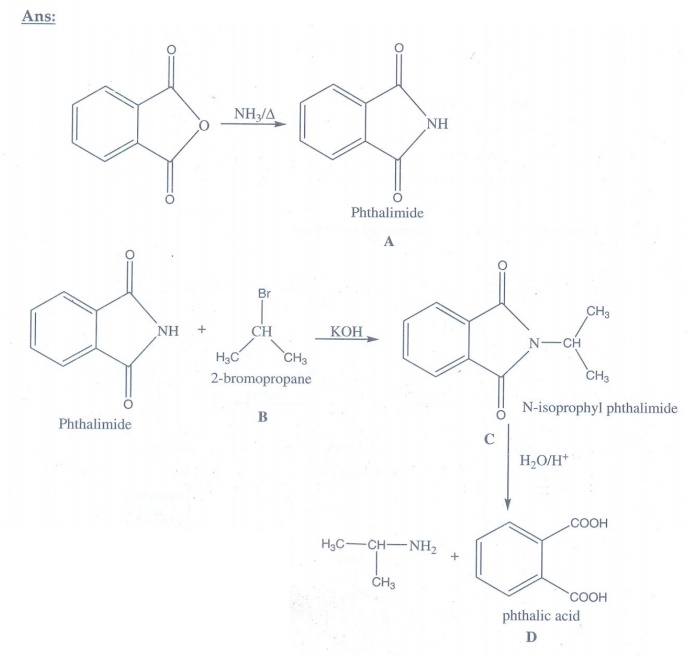
14. Identify A,B,C and D
15. Complete the following reaction
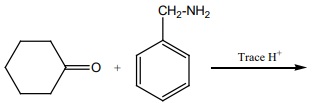
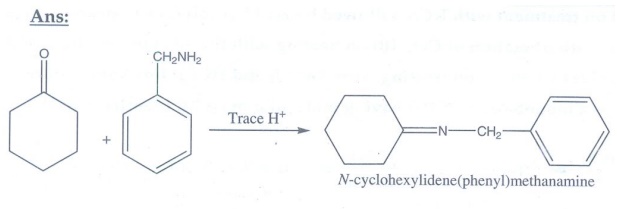
16. Predict A,B,C and D for the following reaction
17. A dibromo derivative (A) on treatment with KCN followed by acid hydrolysis and heating gives a monobasic acid (B) along with liberation of CO2 . (B) on heating with liquid ammonia followed by treating with Br2 /KOH gives (c) which on treating with NaNO2 and HCl at low temperature followed by oxidation gives a monobasic acid (D) having molecular mass 74. Identify A to D.
Solution:
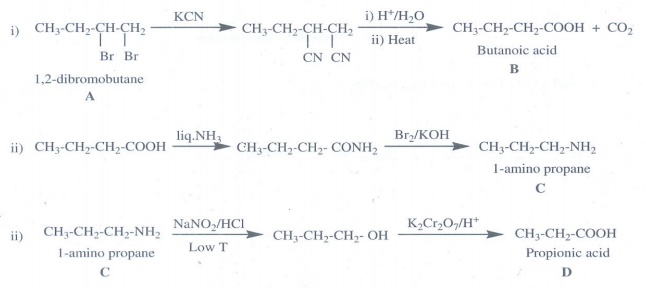
Answer:
A
- 1, 2 - dibromobutane
B
- Butanoic acid
C
- 1-amino propane
D - Propionic acid [Molecular mass 74]
18. Identify A to E in the following sequence of reactions.
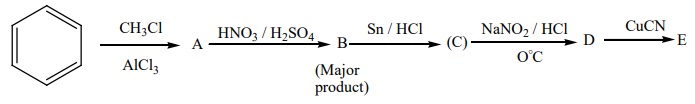
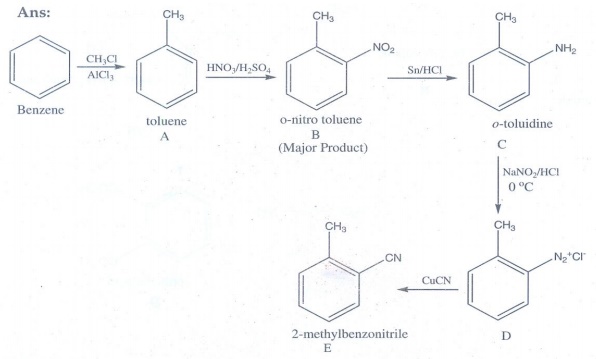
EVALUATE YOURSELF:
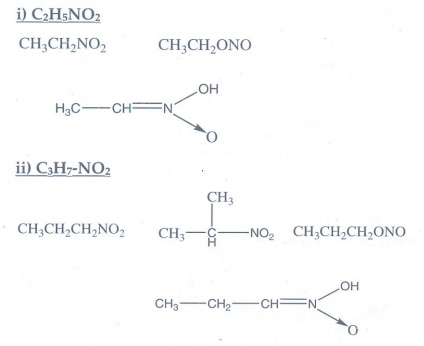
1. Write all
possible isomers for the following compounds.
i) C2H5NO2
ii) C3H7-NO2
2. Find out the
product of the following reactions.
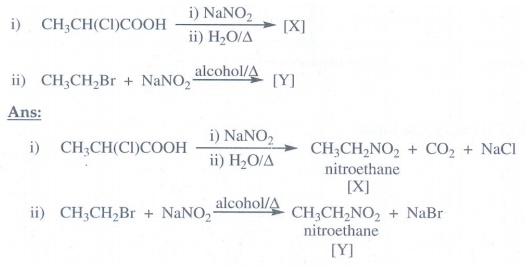
3. Predict the
major product that would be obtained on nitration of the following compunds.
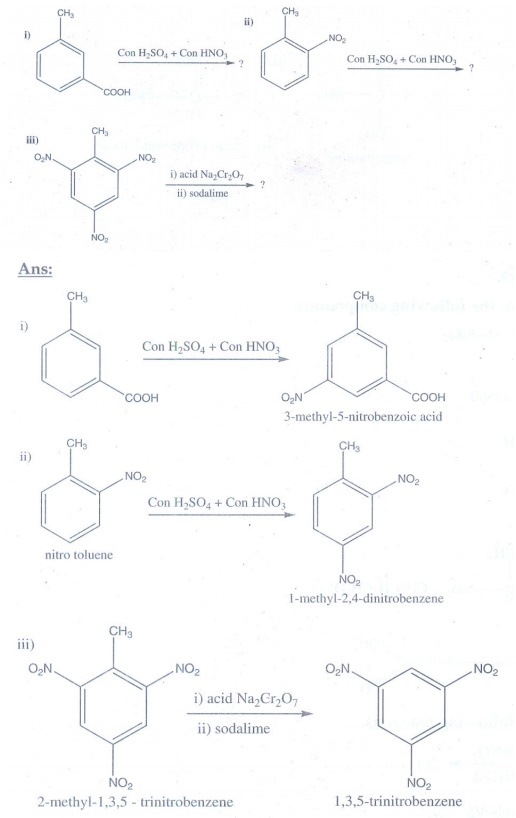
4. Draw the
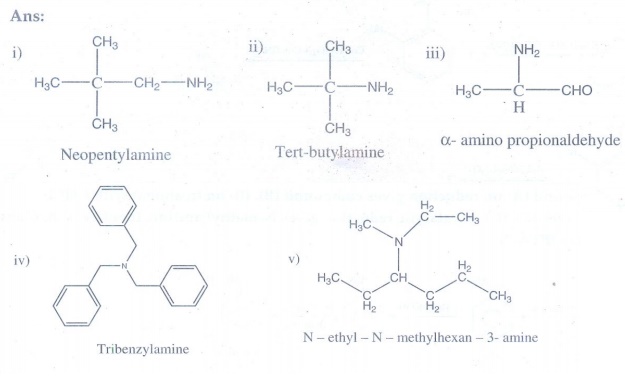
structure of the following compounds
i. Neopentylamine
ii. Tert -
butylamine
iii. α- amino
propionaldehyde
iv. Tribenzylamine
v. N - ethyl - N -
methylhexan - 3- amine.
Answer:
5. Give the correct
IUPAC names for the following amines
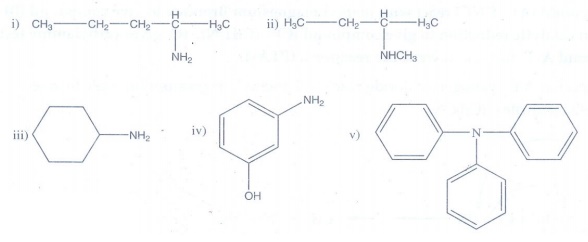
Answer:
(i)
pentan-2-amine
(ii)
N-methylbutan-2-amine
(iii)
cyclohexanamine
(iv)
3-aminophenol
(v) N, N, N - triphenyl amine
NITRO COMPOUNDS
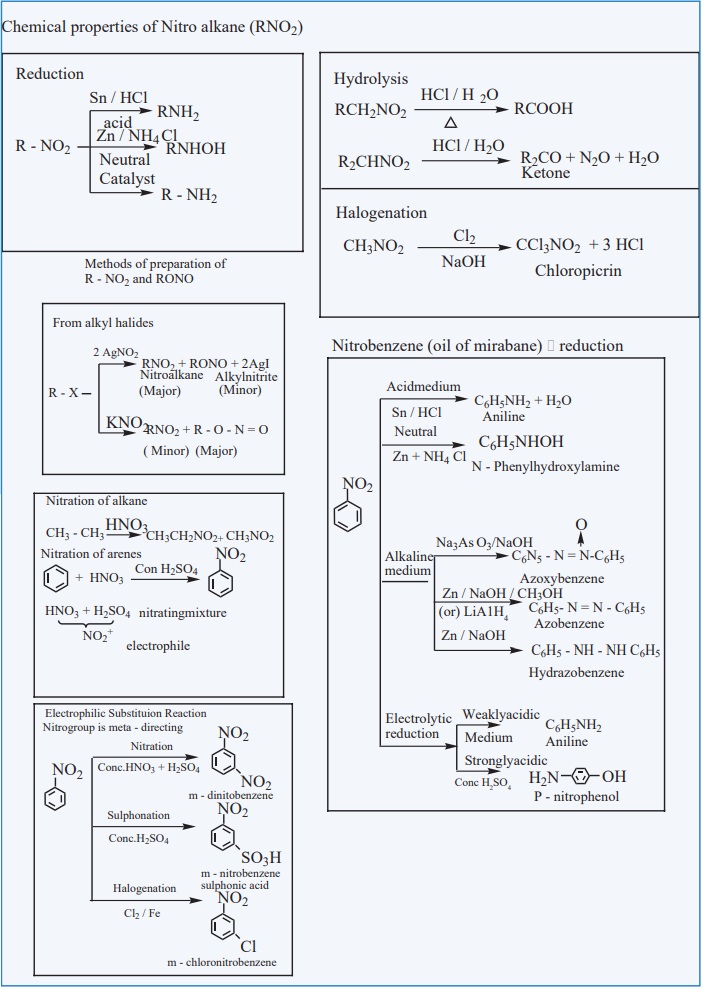
Related Topics