Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Organic Nitrogen Compounds
General methods of preparation Amines
General methods of preparation Amines
Aliphatic and aromatic amines are prepared by the following methods.
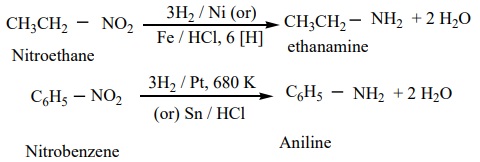
1) From nitro compounds
Reduction of Nitro compounds using H2 / Ni (or) Sn / HCl or Pd/H2 gives primary amines.
2) From nitriles
a) Reduction of alkyl or aryl cyanides with H2 /Ni (or) LiAlH4 (or) Na / C2H5OH gives primary amines. The reduction reaction in which Na / C2 H5OH is used as a reducing agent is called mendius reaction
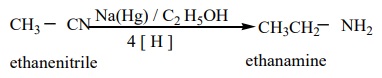
b) Reduction of isocyanides with sodium amalgam / C2 H5OH gives secondary amines
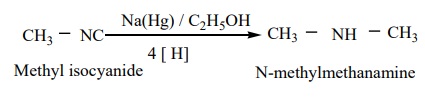
3) From amides
a) Reduction of amides with LiAlH4 gives amines
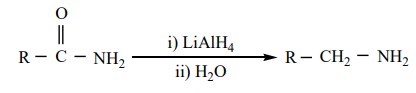
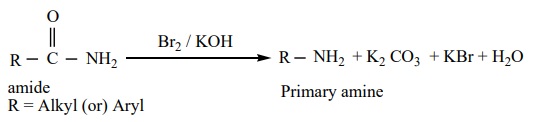
b) Hoffmann’s degradation reaction
When Amides are treated with bromine in the presence of aqueous or ethanolic solution of KOH, primary amines with one carbon atom less than the parent amides are obtained.
Example:
4) From alkyl halides
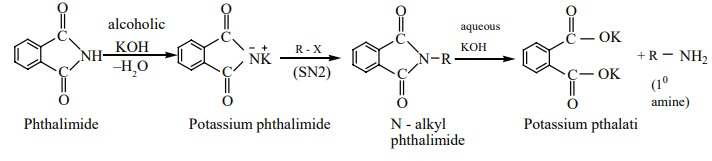
a) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
Gabriel synthesis is used for the preparation of Aliphatic primary amines. Phthalimide on treatment with ethanolic KOH forms potassium salt of phthalimide which on heating with alkyl halide followed by alkaline hydrolysis gives primary amine. Aniline cannot be prepared by this method because the arylhalides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide
b) Hoffmann’s ammonolysis
When Alkyl halides (or) benzylhalides are heated with alcoholic ammonia in a sealed tube, mixtures of 1º, 2º and 3º amines and quaternary ammonium salts are obtained.
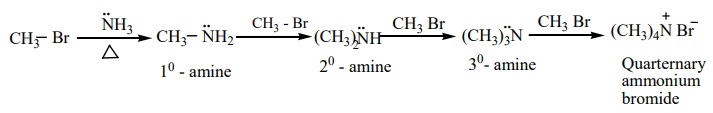
This is a nucleophilic substitution , the halide ion of alkyl halide is substituted by the -NH2 group. The product primary amine so formed can also has a tendency to act as a nucleophile and hence if excess alkyl halide is taken, further nucleophilic substitution takes place leading to the formation of quarternary ammonium salt. However, if the process is carried out with excess ammonia, primary amine is obtained as the major product.
The order of reactivity of alkylhalides with amines.
RI > RBr > RCl
c) Alkyl halide can also be converted to primary amine by treating it with sodium azide (NaN3 ) followed by the reduction using lithium aluminium hydride.
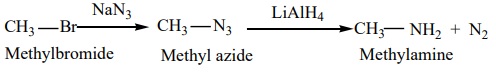
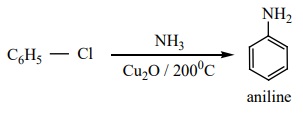
d) Preparation of aniline from chlorobenzene
When chlorobenzene is heated with alcoholic ammonia, aniline is obtained.
5) Ammonolysis of hydroxyl compounds
a) when vapour of an alcohol and ammonia are passed over alumina, W2 O5 (or) silica at 4000C, all types of amines are formed. This method is called Sabatier – Mailhe method.
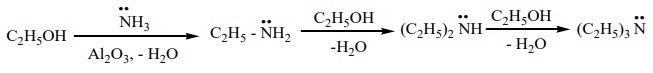
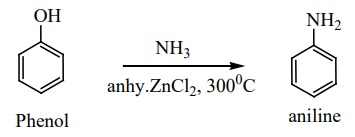
b) Phenol reacts with ammonia at 3000C in the presence of anhydrous ZnCl2 to give aniline
Related Topics