Nomenclature, Methods of preparation, Physical and Chemical properties - Cyanides | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Organic Nitrogen Compounds
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Organic Nitrogen Compounds
Cyanides
CYANIDES
Introduction
These are the derivatives of hydrocyanic acid (HCN), and is known to
exist in two tautomeric forms
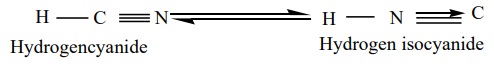
Two types of alkyl derivatives can be obtained. Those derived by
replacement of H – atom of hydrogen cyanide by the alkyl groups are known as
alkyl cyanides (R-C ≡ N). and
those obtained by the replacement of H – atom of hydrogen isocyanide are known
as alkyl isocyanides (R-N ![]() C)
C)
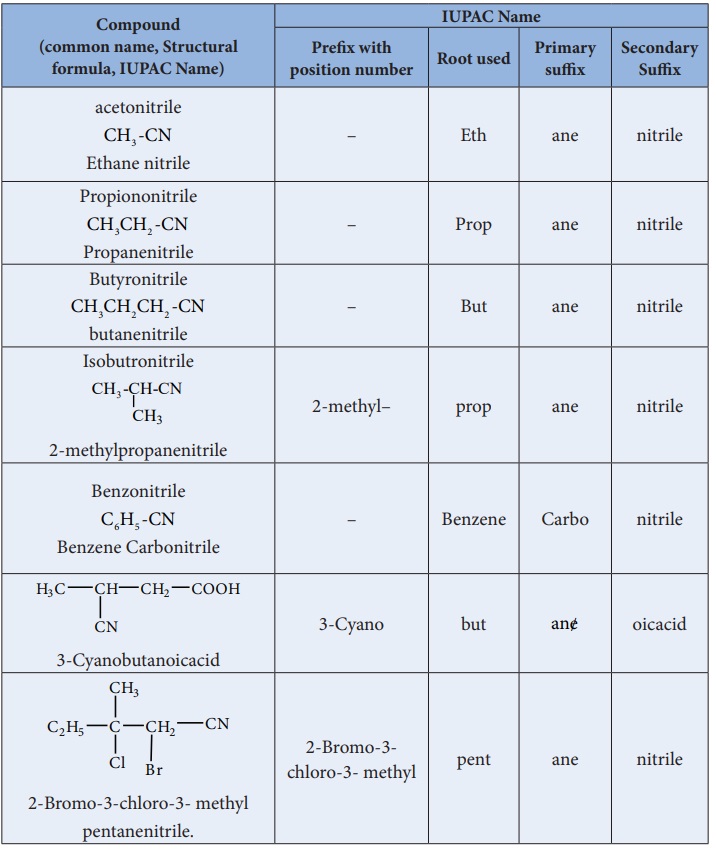
In IUPAC system, alkyl cyanides are named as “alkanenitriles” whereas
aryl cyanides as “ arenecarbonitrile”.
Table : Nomenclature of cyanides
Methods of preparation of cyanides
1) From alkyl halides
When alkyl halides are treated in the solution NaCN (or) KCN , alkyl
cyanides are obtained. In this reaction a new carbon – carbon bond is formed.
Example

Aryl cyanide cannot be prepared in this method because of their less
reactivity towards nucleophilic substitution. Aryl cyanides are prepared using
Sandmeyers reactions.
2) By dehydration of primary amides and aldoximes with P2 O5

3) By dehydration of ammonium carboxylates with P2 O5
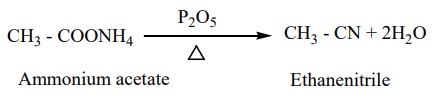
This method suitable for large scale preparation of alkyl cyanides.
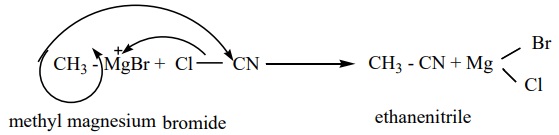
4) From Grignard reagent
Methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with cyanogen chloride (Cl - CN) forms
ethanenitrile.
Properties Of Cyanides
Physical Properties
The lower members (up to C14 ) are colourless liquids with a
strong characteristic sweet smell. The higher members are crystalline solids,
They are moderately soluble in water but freely souble in organic solvents.
They are poisonous.
They have higher boiling points than analogous acetylenes due to their
high dipole moments.
Chemical properties
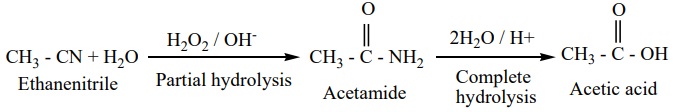
1. Hydrolysis
On boiling with alkali (or) a dilute mineral acid, the cyanides are
hydrolysed to give carboxylic acids.
For
example
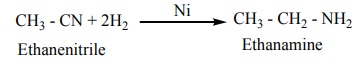
2. Reduction
On reduction with LiAlH4 (or) Ni / H2 , alkyl
cyanides yields primary amines.
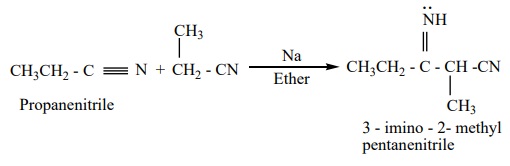
3. Condensation reaction
a) Thorpe
nitrile condensation
Self condensation of two molecules of alkyl nitrile (containing a–H atom)
in the presence of sodium to form iminonitrile.
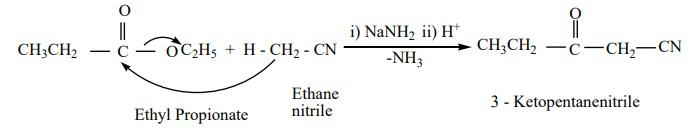
b) The nitriles containing α-
hydrogen also undergo condensation with esters in the presence of sodamide in
ether to form ketonitriles. This reaction is known as “ Levine and Hauser”
acetylation
This reaction involves replacement of ethoxy (OC2 H5
)group by methylnitrile (- CH2CN) group and is called as
cyanomethylation reaction.
Related Topics