Nomenclature, Methods of preparation, Physical and Chemical properties - Alkyl Isocyanides (Carbylamines) | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Organic Nitrogen Compounds
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Organic Nitrogen Compounds
Alkyl Isocyanides (Carbylamines)
Alkyl Isocyanides (Carbylamines)
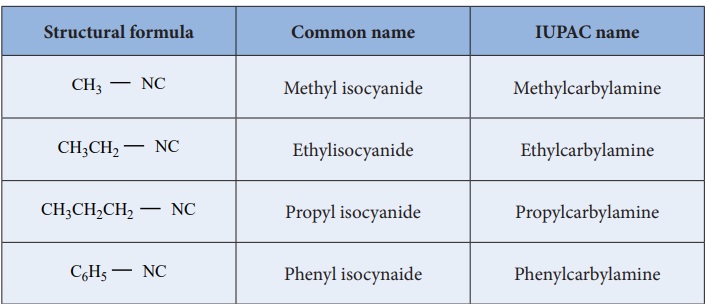
Nomenclature of isocyanides
They are commonly named as Alkyl isocyanides. The IUPAC system names
them as alkylcarbylamines
Table : Nomenclature of alkylisocyanides
Methods of preparation of isocyanides
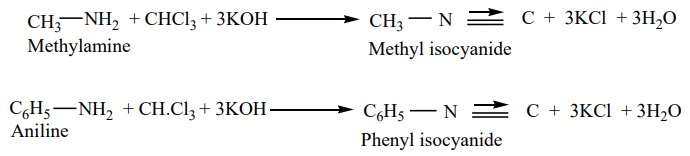
1. From primary amines (carbylamines reaction)
Both aromatic as well as aliphatic amines on treatment with CHCl3
in the presence of KOH give carbylamines
2. From alkyl halides
Ethyl bromide on heating with ethanolic solution of AgCN give ethyl isocyanide as major product and ethyl cyanide as minor product.
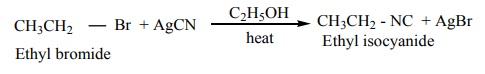
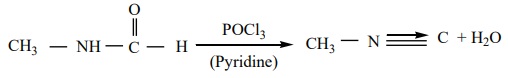
3. From N – alkyl formamide. By reaction with POCl3 in pyridine.
Properties of isocyanides
Physics properties
• They are colourless, highly unpleasant smelling volatile liquids and
are much more poisonous than the cyanides.
• They are only slightly soluble in water but are soluble in organic
solvents.
• They are relatively less polar than alkyl cyanides. Thus, their
melting point and boiling point are lower than cyanides.
Chemical properties
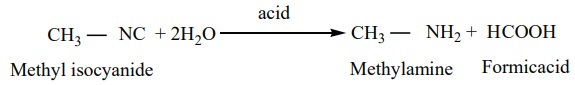
1. Hydrolysis: Alkyl
isocyanides are not hydrolysed by alkalies. However they are hydrolysed with dilute mineral acids to give
primary amines and formic acids.
2. Reduction: When reduced catalytically (or) by nascent hydrogen, they give secondary amines.
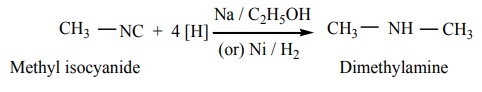
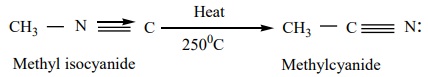
3. Isomerisation:
When
Alkyl isocyanides and heated at 250ºC, they
change into the more stable,
isomeric cyanides
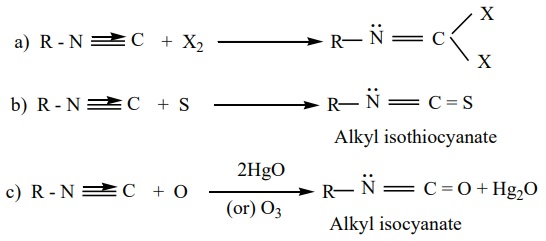
4. Addition
reaction. Alkyl isocyanides add on halogen, sulphur, and oxygen to form the corresponding addition compounds.
Related Topics