Definition, Factors influencing, Types of Self Esteem - Self Esteem | 11th Home Science : Chapter 9 : Personality Development and Life Coping Skills
Chapter: 11th Home Science : Chapter 9 : Personality Development and Life Coping Skills
Self Esteem
SELF ESTEEM
Self-esteem is the personal value, self-respect and self
-worth that an individul places on themselves
1. Definition
“Self Esteem is the satisfaction or dissatis-faction with
oneself ” (James – 1980)
“Self-esteem is the judgment or opinion we
hold about ourselves. It’s the extent to which we perceive ourselves to be
worthwhile and capable human beings.” (Coopersmith, 1967)

2. Factors influencing Self Esteem
Self esteem or self image of adolescents is
based on six domains as shown in figure 2.
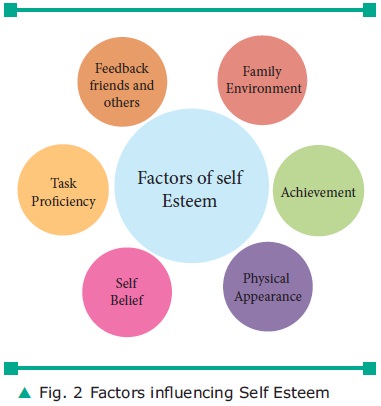
Family Environment
Family is the first school for an individ-ual.
A childs life is mainly influenced by the family environment; it is the primary
source of social development. Each family is different from the other, as it is
com-posed of different members. Each varies in its social and economic
conditions with different background
Achievement
Academic achievement and achievement of one’s
goals related to their hobbies play a crucial role in forming a positive,
healthy view of the self.
Physical Appearance
Physical characteristics such as hair, fig-ure,
height weight, skin colour may also influence the self-esteem of an individual
Self Belief
A person who has high confidence levels may
learn things quickly, trust that they can complete tasks to a good standard and
this subsequently may boost their self esteem.
Task Proficiency
This includes the skills required for per-forming tasks and the ability to complete the task. Task proficiency influences the personality of an individual
Feedback Friends and others
Positive & Negative messages and feedback
from friends and others may boost or break an individual’s self-esteem.
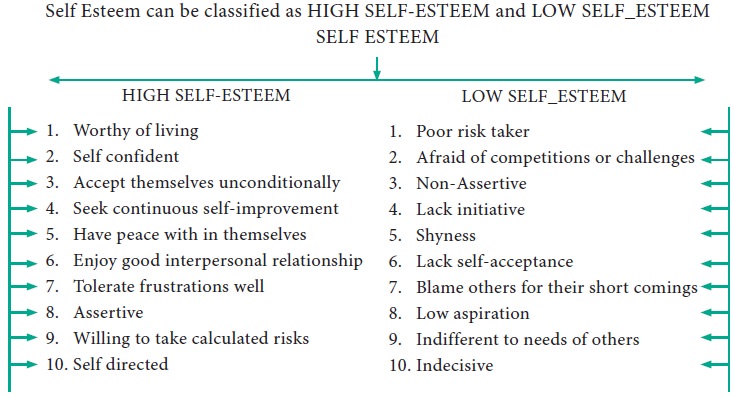
3. Types of Self-Esteem
High Self-Esteem – Feeling positively about yourself, your actions and your future.
Low Self-Esteem – Feeling negatively about yourself, your actions and your future.

4. Motivation
The Word motivation comes from the Latin word
‘motum’ which means ‘move’, ‘motor’, and ‘motion’. That is ‘to put into action
or to move’.

Definition
Motivation is defined as “Acts that arouse,
sustain and direct behaviour.
·
It helps to sustain the attention in one’s efforts or task
·
Restlessness to achieve the goal stops after the goal is reached
A continuous flow in shape of a cycle named
motivational cycle is explained in figure 3.
Need
A need is lack or deficit of some neces-sity.
It’s a state of physical deprivation that
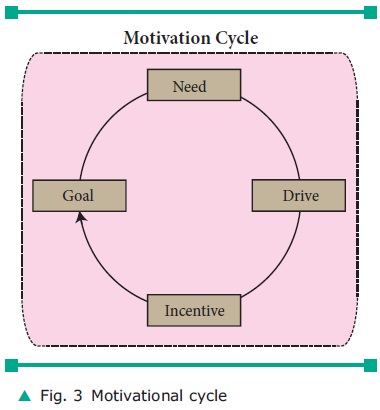
The tension caused when the
person is deprived of basic neces-sities of life as food, water, and sleep,
causes imbalance. For any goal directed
behavior, need is the first condition or stimulating factor.
Drive
Need leads to drive, which is the second step
towards achieving goal. Drive can be defined as the state of tension or arousal
produced by need. It is the state of height-ened tension leading to restless
activity and preparatory behaviour. For instance, when person is hungry and/or
thirsty, he seeks to reduce this drive by eating and/or drinking.
Incentive
Environment that activates, directs, and
maintains behaviour is called incentive. It can be anything as long as it has
either positive or negative value in motivating behaviour. For example:
behaviour like eating food is an incentive that reduces the drive of the person
caused by the need to fulfill his hunger. The reduction of behav-iour then cuts
off and restores balance in an organism.
Goal
The reduction of tension in the body can be
considered as the goal of any motivated behaviour. Let’s go back to the example
of a hungry man. A hungry man eats food, and his body restores to a balanced
condition. This then reduces the tension. This reduc-tion of tension as a
result of an energized activity is called goal. Once the goal has been
completed, the organism is again ready for another goal-motivated behaviour.
Principles of Motivation
Maslow’s Theory of Motivation

Maslow describes how motivation devel-ops
stage by stage from purely physiolog-ical drives to complex social purpose, as
described in the figure presented below:

Physiological needs: The basic physi-ological
desires are food, water, shelter, etc., They are the most basic and
fun-damental human needs.
Safety Needs: It arises on account
of future expectations. For example, in-surance against future,
keeping a bank balance, investing in LIC.
Love and Belongingness Needs: Need for affection, praise, warmth, accep-tance, approval,
affiliation.
Self-Esteem Needs: Need for achieve-ment,
status, self-respect, self-confidence, feelings of strength and adequacy.
Achievement Needs: Needs for
un-derstanding implies knowledge of re-lationships, process, the integration of
knowledge into broad structure etc. thus achievement needs are related to
intellectual domination and cognitive competencies.
Aesthetic needs: This is concerned with appreciation of order and beauty. One whose lower order
needs are ful-ly satisfied or known that he need not bother about them, derives
pleasure in beauty and nature.
Self-Actualization Needs: Need for self-fulfillment, self-expression, ful-fillment of
potentialities, working out one’s own mental personality.
Related Topics