Chapter: 11th Home Science : Chapter 9 : Personality Development and Life Coping Skills
Coping Mechanism
COPING MECHANISM
Coping Mechanisms can also be described as
“Survival Skills”. They are strategies that people use in order to deal with
stresses, pain and natural changes that we experi-ence in life.
Coping involves managing taxing circumstances,
expending effort to solve life’s problems and seeking to master or reduce
stress.
We experience a range of emotions through out our lives. Some good, some not so good. Our behaviors are usually a result of how we handle our emotions. If we are able to handle our emotions positively behavior will be positive.
1. Coping with Depression
Depression is an emotional state of low mood
and aversion to activity that can affect a persons thoughts, behavior,
feel-ings and sense of well being. Depression is an illness characterized by
persistent sad-ness and a loss of interest in activities that you normally
enjoy, accompanied by an inability to carry out daily activities, for at least
two weeks.
Cause of Depression
Depression is more than just feeling down.
Research tells us that the other factors contribute to onset of depression
include genetics, changes in hormone levels, cer-tain medical conditions,
stress, grief or difficult life circumstances.

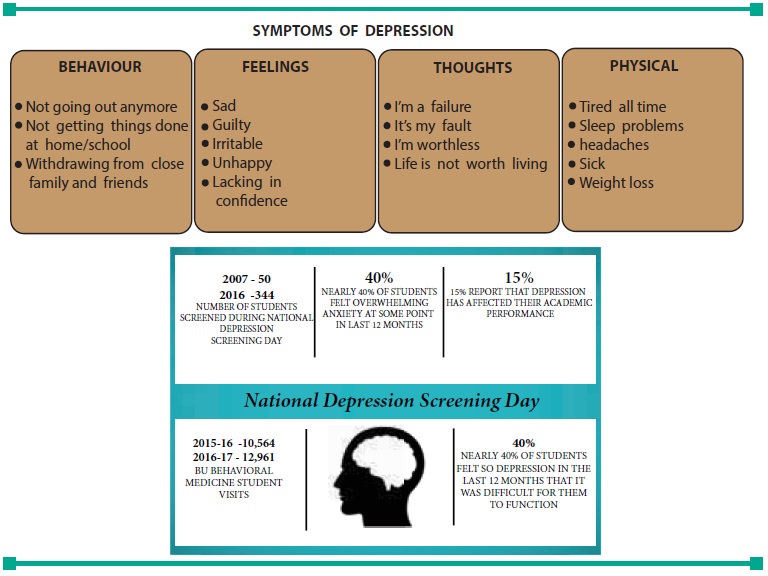
Symptoms of Depression
A depressed person will experience any of the
following symptoms.
WHO reports that 7.5% Indians suffer from mental dis-orders. Around 4.5% of India’s
population suffer from depression, 38 million Indians suffer from anxiety
disorders.

Steps to overcome Depression
·
Break tasks down into small steps
·
Focus on your positive experiences
·
Avoid isolation by connecting with people.
·
Find a hobby and exercise daily.
·
Use self relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises
·
Engage in voluntary activities to keep you active
·
Set realistic goals challenge negative thoughts
·
Improve diet and also take Omega 3 supplement
·
Have a regular sleep time.
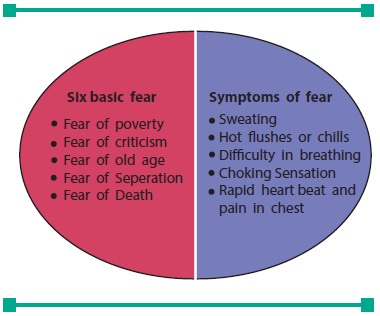
2. Coping with Fear
Fear is an unpleasant emotion that is
pre-programmed into animals and humans as an instinctual response to potential
danger. Fear is the emotion we experi-ence when the automatic nervous system
releases adrenaline energizing the system for fight or flight.
“Fear is discrimination
learning. It provides us with information as to what object is dangerous and
what delightful.
The common fears expressed in babyhood include those related to loud noise, animals, dark room, high places, being alone, pain and strange person places and objects. Older children have fears related to self or status. They are afraid of facilitating, being ridiculed and of being “different”.
Types of Fear
·
Fear of Failure
·
Fear of Judgment
·
Fear of Success
·
Fear of Speaking
·
Fear of not being able to make a living
·
Fear of Rejection
·
Fear of losing everything
·
Fear of people and public places
Aware techniques for overcoming Fear
A-
Accept the Fear
W - Watch the Fear
A - Act normal
R-
Repeat the steps
E -
Expect the best
3. Shyness
Shyness is a psychological state that causes a person to feel discomfort in social situ-ations in ways that interfere with enjoy-ment or that cause avoidance of social contacts altogether.
American Psychological Association (APA-2012) defined Shyness as the ten-dency to feel awkward, worried or tense during social encounters, especially with unfamiliar people.

Causes of shyness
·
Less Chances to meet people or less interaction with them.
·
Insecurity / lack of confidence.
·
Overprotection.
·
Criticizing / criticism of – child in front of others
Symptoms of Shyness
·
Blushing (cheeks turn red), feeling anxious
·
Heart beats fast
·
Sweating
·
Feeling mind has gone blank
·
Trembling
·
headache
4. Loneliness
Loneliness is a complex and usually unpleasant
emotional response to isola-tion. Loneliness typically includes anxious
feelings about a lack of connection or com-munication with other beings, both
in the present and extending into the future.

Symptoms of Loneliness
·
Physical Symptoms - aches and pains
·
Mental health conditions - increased risk of depression,
anxiety, panic attacks
·
Low Energy - tiredness or lack of motivation
Causes of Loneliness
·
Lack of social skills
·
Lack of interest in other people
·
Lack of empathy
·
High self criticism
·
Failure to disclose information about themselves
·
Lack of sense of community
Coping with Loneliness
·
Think about what is making you lonely.
·
Talk freely
·
Take time to develop personal inter-ests that you may not have
had time for before.
·
Make new connections
·
Try a new recreational activity. Exer-cise and physical activity
will increase your energy and help you to feel better about yourself.
·
Work on developing relationships with others. Avoid impulsive,
desperate and clingy behaviours that tend to drive others away.
·
Work on your listening and communi-cation skills.
·
Present a positive image.
5. Coping with Anger
Anger is a normal, usually healthy emo-tion.
But when it turns destructive it can affect the very quality of our lives.
Anger can be caused by external events, for instance getting angry with your friend or colleague
and internal which is often triggered by unhappy memories or by worrying and
brooding.

Causes of Anger
Anger can be triggered due to many
fac-tors as given below:
·
Rejection by parents
·
Rejection by peers
·
Lower levels of academic achievements
·
More mental health intervention
What happens in your body
when you get angry?
(i). Your heart pounds
(ii). Your
breathing changes
(iii). Your
muscles get tense
(iv). Your
face gets red
(v). There’s
a knot in your stomach
(vi). There’s
a lump in your throat
(vii).
Release of the hormone Adrenaline
Anger is a difficult feeling. When
you’re angry, you might do bad things that you wouldn’t do if you were happy.
But did you know that it’s normal to feel angry from time to time? It happens
to everyone
6. Verbal Abuse
Verbal abuse is a way of attacking (or)
negatively defining another person using words or silence – as a weapon. It can
take a variety of forms ranging from loud rants to passive – aggressive remark

Types of Abuse Physical abuse
Intentional infliction of bodily harm or
injury on another person
What is Verbal Abuse?
Verbal abuse occurs when someone uses language, either spoken or written, to cause harm to an individual.
Emotional abuse
·
Verbal abuse
·
Using words to mistreat or injure another person
Stalking
Repeated following, harassment or threat-ening
on an individual to frighten or cause him or her harm
Effects of Verbal Abuse
·
Can effect one’s self image psychologi-cal and emotional ways
·
Leads to low self esteem, fear depres-sion, bad eating habits,
sleeping prob-lems and irritability
·
Can cause students to fail school due to fear,
·
Substance abuse, or in very extreme cases, death !
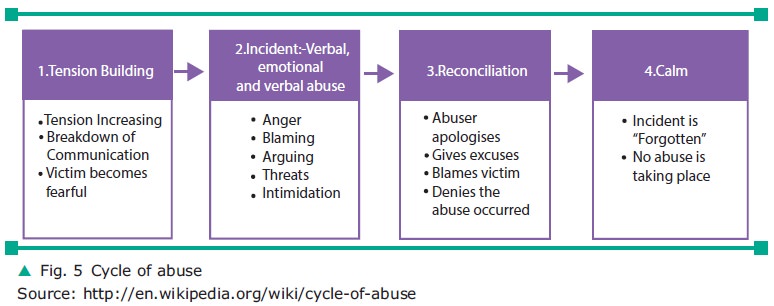
The cycle usually goes in the follow-ing order
as shown in figure 5 and will repeat until the conflict is stopped, aban-doning
the relationship or some form of intervention.
Cycle of Abuse
4. Helpful Tips for Overcoming Verbal Abuse
Tip 1: Stop the Cycle: When Someone abuses (either verbally or physically), it usually becomes a
cycle. Verbal abuse has to be stopped is to break that cycle
Tip 2: Leave the situation: The verbal abuse can be stopped by just walking away from the situation
without saying anything.
Tip 3: Report it to the higher Authorities: Verbal abuse at home, school or any other places should be
reported to some trust worthy adult, head of the institution or any social
group that will address the situation
“It’s important for everyone – young or old, male or female, – to learn how to stop
verbal abuse. No individual should accept that sort of attack from anyone, not
even from their own parents.
7. Failure
Failure is a lack of success in achieving
something especially in relation to a par-ticular activity.

Definition
Making mistakes does not mean you’re a
failure. It just means you’re trying and learning in life
Example of an Effect and cause of failure
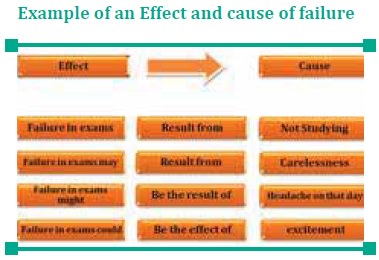
How to Overcome failure
The following nine powerful habits
will enable an individual to cope with failure
·
Just accept how you feel
·
Remember you are not a failure just because of a set back
·
Be constructive
·
Find Inspiration
·
Move forward
·
Take action plan
·
Improve you self esteem
Tips
to overcome failure
is shown in figure. 6
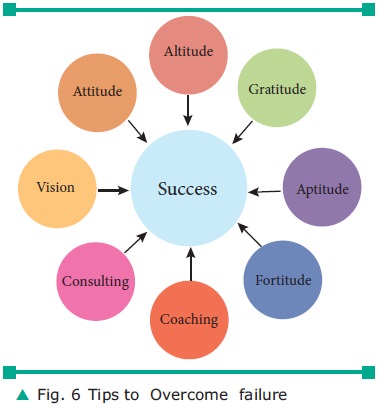
Vision- think positive of the situation you
face, Attitude- have a relaxed attitude, Altitude- Aim high to achieve,
Gratitude- Be greatful for the situation, Aptitude- be ready to learn from that
situation, Fortitude-ability to withstand adversity (unfavourable fortune),
Coaching- prepare yourself to overcome worst situation also, Consulting-
discuss with trust-able persons.These tips will lead to success.
8. Criticism
Criticism is defined as negative com-mentary
about something or someone.
Criticism is the practice of judging the
merits and faults of something.

People who accept criticism are the one’s who are genuinely interested in self improvement.
Types of Criticism
·
Factual Criticism
Criticism can be factual, pointing out right
and wrong facts.
Example: No, it is Tuesday, not
Monday
·
Evaluating criticism
Criticism can also be evaluative, point-ing
out good and bad. This is trickier, as it assumes the critic’s values are
similar or superior to those of the crit-icized person.
Example: Don’t look at me like
that !

Related Topics