Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 6 : Respiration
Respiratory volumes and capacities
Respiratory
volumes and capacities
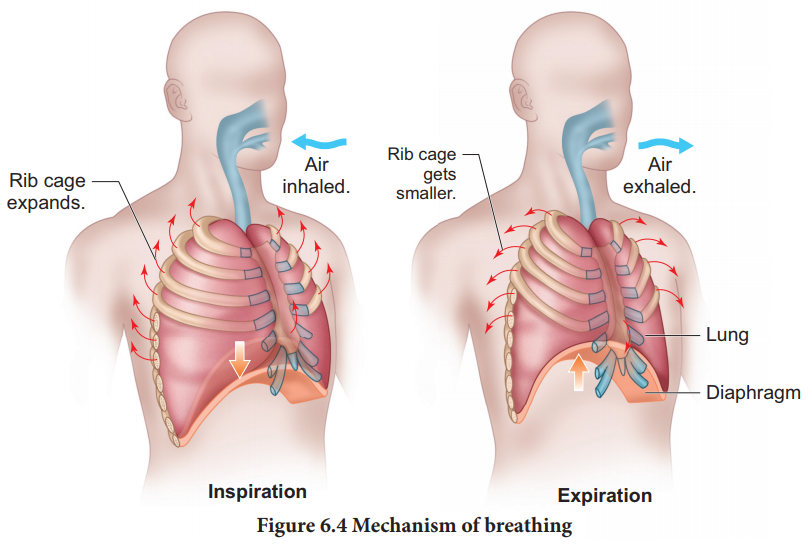
The volume of air present in various phases of respiration is denoted as Respiratory volumes.
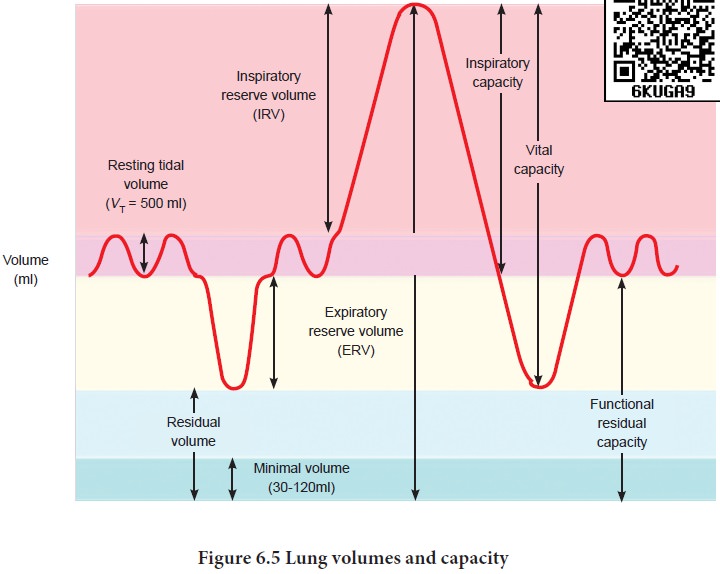
Respiratory volumes: (Figure 6.5)
• Tidal Volume (TV) Tidal
volume is the amount of air inspired or expired with each normal breath. It is approximately 500 mL., i.e. a normal human
adult can inspire or expire approximately 6000 to 8000mL of air per minute.
During vigorous exercise, the tidal volume is about 4–10 times higher.
•
Inspiratory
Reserve volume (IRV) Additional volume of air a person can inspire by forceful inspiration is
called Inspiratory Reserve Volume. The normal value is 2500–3000 mL.
•
Expiratory
Reserve volume (ERV) Additional volume of air a person can forcefully exhale by forceful
expiration is called Expiratory Reserve Volume. The normal value is 1000–1100
mL.
•
Residual
Volume (RV) The volume of air remaining in the lungs after a forceful expiration. It is
approximately 1100–1200 mL.
Respiratory capacities:
•
Vital
capacity (VC) the maximum volume of air that can be moved out during a single breath following a
maximal inspiration. A person first inspires maximally then expires maximally.
VC=ERV+TV+IRV
•
Inspiratory
capacity (IC) The total volume of air a person can inhale after normal expiration. It includes
tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume. IC=TV+IRV
•
Expiratory
capacity (EC) The total volume of air a person can exhale after normal inspiration. It
includes tidal volume and expiratory reserve volume. EC=TV+ERV
•
Total
Lung Capacity (TLC) The total volume of air which the lungs can accommodate after forced
inspiration is called Total Lung Capacity. This includes- the vital capacity
and the residual volume. It is approximately 6000mL. TLC=VC+RV
•
Minute
Respiratory Volume The amount of air that moves into the respiratory passage per minute is
called minute respiratory volume.
Normal TV
= 500mL; Normal respiratory rate = 12 times/minute
Therefore,
minute respiratory- volume = 6 Litres/minute (for a -normal healthy man).
Dead space
Some of
the inspired air never reaches the gas exchange areas but fills the respiratory
passages where exchange of gases does not occur. This air is called dead space.
Dead
space is not involved in gaseous exchange. It amounts to approximately 150mL.
Related Topics