Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 6 : Respiration
Exchange of gases in Human Respiration
Exchange of
gases
The
primary site for the exchange of gases is the alveoli. The uptake of O2
and the release of CO2 occur between the blood and tissues by simple
diffusion driven by partial pressure gradient of O2 and CO2.
-Partial pressure is the pressure
contributed by an individual gas in a mixture of -gases. It is represented as pO2
for -oxygen and pCO2 for carbon–
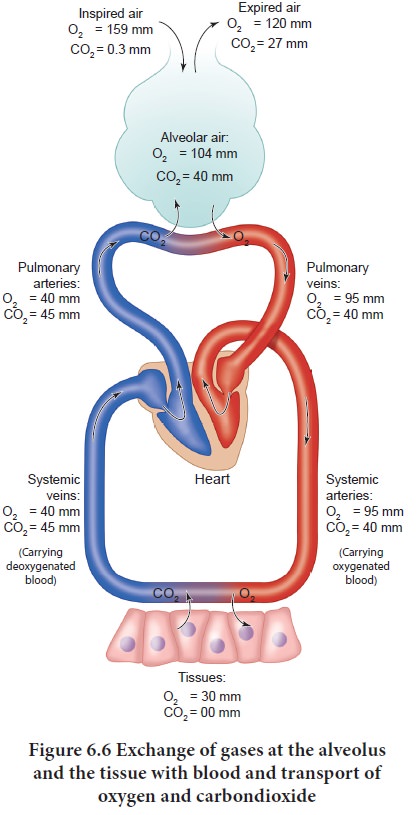
Due to pressure gradients, O2 from the alveoli enters into the blood
and reaches the tissues. CO2 enters into the blood from the tissues
and reaches alveoli for elimination. As the solubility of CO2 is
20–25 times higher than that of O2, the partial pressure of CO2
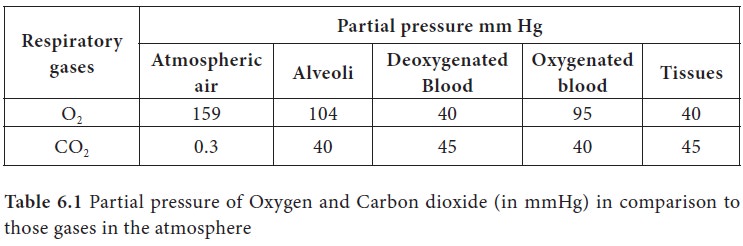
is much higher than that of O2 (Tab.6.1 and Figure 6.6).
Respiratory pigments
Haemoglobin
Haemoglobin
belongs to the class of conjugated protein. The iron containing pigment portion
haem constitutes only 4% and the rest colourless protein of the histone class
globin. Haemoglobin has a molecular weight of 68,000 and contains four atoms of
iron, each of which can combine with a molecule of oxygen.
Methaemoglobin
If the iron component of the haem moieties is in the ferric state, than the normal ferrous state, it is called methaemoglobin. Methaemoglobin does not bind O2. Normally RBC contains less than 1% methaemoglobin.
Related Topics