Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 1 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
Reproductive System
Reproductive System
The role of the male and female reproductive system is to
procreate and to provide sexual gratification to the person.
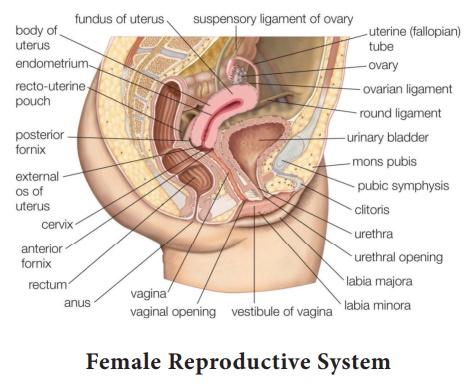
Female reproductive system
The female reproductive system is made up of the internal and
external sex organs that function in reproduction of new offspring. The female
reproductive system is immature at birth and develops to maturity at puberty
and able to produce gametes, and to carry a foetus to full term.
Parts of Female Reproductive System.
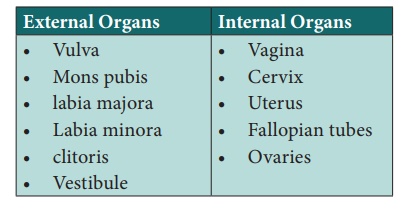
External Organs
Vulva
The vulva is the external part of the female genitalia. It
protects the woman’s sexual organs urethra, vestibule, and vagina.
Mons Pubis
The mons pubis is a pad of fat lying in front of the symphysis
pubis where pubic hair develops with puberty.
Labia majora
The labia majora are two thick folds which form the sides of the
vulva.
Labia minora
The labia minora lies just inside the labia majora and surround
the openings to the vagina and urethra.
The Clitoris
The clitoris lies above the vagina is covered with a protective
cover or hood.
Vestibule
It is a small space or cavity at the beginning of a vaginal canal.
Internal Organs
Vagina
The Vagina is an elastic, muscular canal that extends from the
vulva to the cervix. The vaginal canal travels upwards and backwards between
the urethra at the front and the rectum at the back.
The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a membrane
called the hymen. It joins the internal and external female reproductive organs
and protects against infection by a moist secretion.
Cervix
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus. The lower narrow
portion where it joins with the upper part of the vagina. The cervix is usually
2-3 cm long and roughly cylindrical in shape which changes during pregnancy. As
labour progresses, the cervix becomes softer and shorter, beings to dilate and
facilitate normal labour.
Uterus
The uterus is a pear shaped muscular organ and the major female
reproductive organ. It provides mechanical protection, nutritional support, and
removal of the waste for developing embryo and fetus.
It has three layers, they are perimetrium, myometrium and
endometrium.
Major functions are to accept a fertilized ovum which becomes
implanted into the endometrium, and menstruation.
The fallopian tube
The fallopian tubes are two tubes leading from the ovaries in to
the uterus. They enable the passage of ovum from the ovaries to the uterus.
Different segments are interstitial, isthmus, ampulla, infundibulum and
fimbriae. Fertilization takes place in the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
Ovaries
The ovaries are considered as the female gonade. Each ovary is
whitish in colour and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus. It
secretes estrogen, testosterone, Inhibin and progesterone. These hormones are
responsible to maintain menstrual cycle, pregnancy and development of breast.
Functions of the female reproductive system
·
To produce ovum.
·
To protect and nourish fertilized egg until it is fully developed.
·
To give birth.
·
Menstruation.
·
To have sexual intercourse.
Diseases related female reproductive system
·
Breast cancer
·
Cervical cancer
·
Ovarian cancer
·
Poly cystic ovarian disorder
·
Menorrhagia
·
Fibroids
Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system consists of internal and external
organs.
The external organs
·
Penis
·
Scrotum
The Penis
The tip of the penis is protected with foreskin. The penis
enlarges and becomes erect with sexual excitation because there is a rich
supply of blood.
The Scrotum
The scrotum lies bilaterally behind the penis. The scrotal sac
holds and protects the testes.
The internal organs are the
• Testes
• Epididymis
• Vas deferens
• Seminal vesicles
• Ejaculatory ducts
• Prostate gland
• Urethra
Testes
The testicles, or testes, lie bilaterally to the penis in the
scrotum. The testes are endocrine glands and gonads.
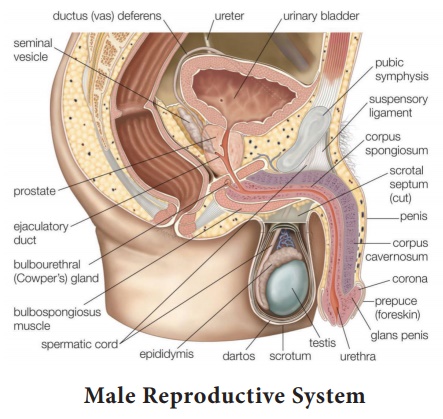
Epididymis
The epididymis is the connecting tube between the testes and the
vas deferens which stores, transports and matures the sperm from the testes.
The epididymis has three parts such as, the head, body and tail.
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens moves the mature sperm from the epididymis to the
ejaculatory ducts and then to the urethra for ejaculation.
Seminal Vesicles
The seminal vesicles are the pair of glands which attach to the
vas deferens near and under the bladder. It produces a fructose substance that
provides the sperm with the energy it needs to locomote and move through the
male reproductive tract.
Prostate
The prostate is an exocrine gland which secretes an alkaline fluid
that preserves the life of the sperm when it hits the acidic female vagina.
Ejaculatory Ducts
The pair of ejaculatory ducts forms the union of the vas deferens
and the seminal vesicles. Sperm enters the ejaculatory ducts from the vas
deferens.
Urethra
The urethra is an organ common for both reproductive system and
urinary system.
The primary male reproductive hormones are
Follicle stimulating hormone which produces sperm
(spermatogenesis).
Luteinizing hormone which produces testosterone.
Testosterone which leads to the development of primary and
secondary sexual characteristics during puberty.
Disease related to reproductive system
• Prostate cancer
• Testicular cancer
• Gynecomastia
• Erectile dysfunction
• Varicocele
• Hydrocele.
Related Topics