Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 1 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
Muscular system
Muscular system
A brand or bundle of fibrous tissue in a human body that has the
ability to contract, producing movement in or maintaining the position of parts
of the body.
The muscular system has three different types of muscles
1.
Cardiac muscle
2.
Skeletal muscle
3.
Smooth muscle
Cardiac muscles are striated muscles only found in the
heart. Cardiac muscles works involuntarily without the control of a person.The
cells found in cardiac muscle are the myocardiocytes which contract the
myocardium.
Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, that enables
the skeletal structures to move. These muscles are also controlled by the
nervous system and the majority of skeletal muscles are attached to the bones
of the body with tendons to enable body movement.
Smooth muscles are non striated and involuntary muscles. Muscles
that control the movements and actions of the internal organs and systems of
the body like peristalsis.
Role of muscular system
·
Voluntary movement with the skeletal muscles
·
Involuntary actions with the smooth muscles
·
Involuntary contractions and relaxation of the heart with the
cardiac muscles
Abduction: Movement away from the centre of the body.
Adduction: Movement towards the middle of the body
Flexion: Bending movement of a joint or muscle
Hyperflexion: The flexion of a joint that is beyond what it normally
should do, for example, can occur with a traumatic car crash when the head is
forced to the chest, or flexed, beyond what it normally should do.
Extension: Normal straightening movement of a joint or muscle.
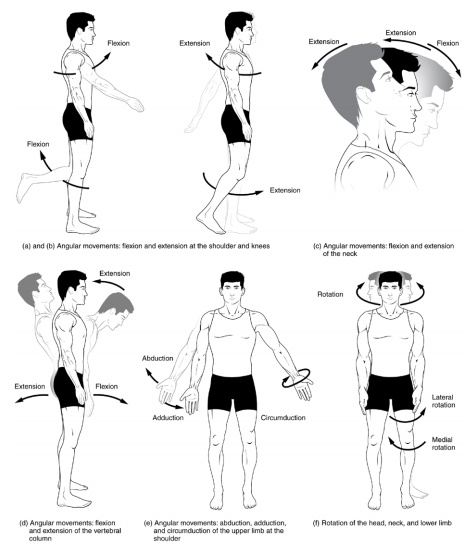
Hyperextension: Extension of a joint is beyond what it
normally should do, for example, can occur with a traumatic car crash when the
head is forced backwards, or extended, beyond what it normally should do.
Rotation: Circular movement of a joint or muscle that allows the body
part to move in a circular manner.
External rotation: Muscular and joint movement that entails
both circular movement and also movement away from the center of the body.
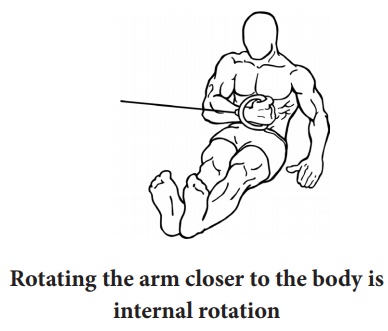
Rotating the arm closer to the body is internal rotation
Internal rotation: Muscular and joint movement that entails
both circular movement and also movement towards the center of the body.
·
Circumduction: The muscular and joint movement that entails complete
3600 movement
·
Inversion: The turning of a joint inward
·
Eversion: The turning of a joint outward
·
Plantar flexion: Movement of the foot downward
·
Dorsiflexion: Movement of the foot upward
Cartilage
Cartilage is an important structural component of the body. It is
less hard than bones and more flexible than bones and helps in articulations It
protects the ends of the bone. It is found in elbows , knees and ankle.
Tendons
A tendon is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that usually
connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding tension. It is made up
of collagen.
Ligaments
A ligament is a short band of tough, flexible fibrous tissues,
tissues that connects bones to bone to form a joint. It also maintain position
of the organs.
Joints
Joint or articulation is the connection made between bones in the
body which link the skeletal system into a functional whole.
Types of Moveable Joints
·
Hinge joint, e.g. interphalangeal joints – fingers and toes.
·
Ball and socket joint, e.g. hip and shoulder joints
·
Pivot joint, e.g. atlantoaxial joint between the atlas and axis – neck
·
Gliding joint (“Condyloid” joint), e.g. between
radius, scaphoid and lunate bones – wrist.
Structural and functional
Structural (binding tissue)
·
Fibrous joint - joint by connective tissue.
·
Cartilage joint - joint by cartilage
·
Synovial joint - not directly joined.
·
Facet joint - between two vertebrae.
Functional (movement)
·
Synarthrosis means no mobility (skull)
·
Amphiarthrosis means slight mobility (vertebrae)
·
Diarthrosis means freely movable (knee)
Fascia
A fascia is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily
collagen, beneath the skin that attaches, stabilize, enclose and separates
muscles and other internal organs.
It is classified as
·
Superficial fascia
·
Deep fascial fascia
·
Visceral fascia
·
Parietal fascia.
Diseases related to the bone
·
Arthritis
·
Rheumatoid arthritis
·
Osteoporosis
·
Osteoarthritis
·
Osteomyelitis
·
Fractures
Functions of musculo skeletal system
The human skeleton and the skeletal system perform several
functions.
1.
The protection of the vital organs of the body
2.
The support of the human body which gives it its form and
stability
3.
Body movement
4.
Control of metabolic functions like the calcium and calcium
storage as well as iron metabolism and iron storage in the bone marrow
5.
Hematopoiesis, the production of red blood cells in the bone
marrow of bones.
Related Topics