Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 1 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
Gastro Intestinal System
Gastro
Intestinal System
Introduction
The alimentary canal, is a continuous hollow tube from the mouth
to the rectum. The alimentary canal along with the associated organs like the
salivary glands, liver, pancreas and the gallbladder is called the digestive or
gastrointestinal system. The primary role of the digestive system is to supply
blood stream with nutrients that can be used by the body for its fuel, energy
and fluid needs.
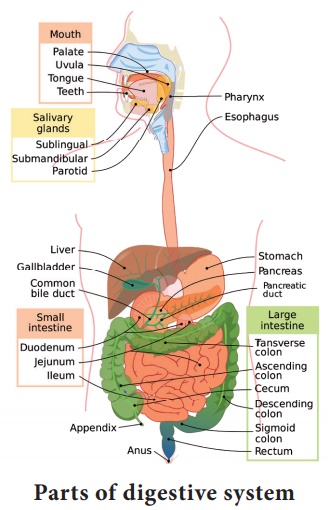
The organs that contribute to digestion are the tongue, salivary
glands, the liver, the gallbladder, and the pancreas. The gallbladder and the
pancreas secrete and deposit bile and digestive enzymes, respectively through
the common bile duct to the duodenum of the small intestine.
Mouth
The cheeks,tongue and palate frame the mouth, which is also called
oral cavity .its boundaries are defined by the lips, cheeks, soft palate and
epiglottis. It is divided in to two sections.
They are
·
The vestibule- the area between the cheeks and the teeth.
·
The oral cavity- filled by the tongue
The mouth is the opening through which the person ingests food and
fluids. Incisors, canines, premolar and molars are the types of teeth helps in
mastication
Tongue
Tongue is one among the five sensory organ. It is a muscular
structure used for moving food in the mouth and to swallow fluid and food.
Taste buds are found on the upper surface of the tongue and the salivary
glands.
Salivary glands
Salivary glands produce saliva which contains the digestive enzyme
amylase. Amylase digests and breaks down starch into glucose and maltose.
Pharynx
The pharynx receives air from the nares or the mouth and it also
receives food from the mouth. When people say that their food has gone down the
wrong pipe, they are experiencing an abnormal small amount of food moving from
the pharynx to the trachea.
Epiglottis
The epiglottis is the flap like projection in the back of the
mouth attached to the larynx. It goes up during breathing to allow the air to
enter into the trachea and it moves down during the swallowing of food and
drinking fluids to allow the food to enter the oesophagus.
Oesophagus
The oesophagus is a long straight hollow structure that starts at
the pharynx and ends at the stomach. The upper portion of the oesophagus has
skeletal muscles and the lower portion has smooth muscles. Oesophagus has a
sphincter at the top of pharynx end and it has a sphincter at the bottom of the
stomach which prevent food from flowing back into the pharynx from oesophagus
and backing up from the stomach into the oesophagus. The primary role of the oesophagus
is peristalsis, wave like movements that move and propel food and fluids along
the digestive tract with the help of muscles.
Stomach
The stomach is a hollow organ on the left side of the abdomen that
collects and processes food and fluids. The stomach has the fundus, body and
antrum. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes, such as pepsin, hydrochloric
acid and gastric acid to facilitate the digestive process. As the food and
fluids are processed in the stomach, a partially digested chyme is formed.
Pepsin digests proteins; and hydrochloric acid provides the pH of acidity that
is necessary for digestion. Minimal absorption of water soluble vitamins and
some medications such as aspirin takes places at stomach.
Liver
The liver is an abdominal organ and gland on the right side of the
abdominal cavity and near the center of the body. The liver produces bile which
is then transported to the gallbladder through the common bile duct and then to
the small intestine. Bile is used for the breakdown and digestion of fats.
Small Intestine
The chyme from the stomach is mostly absorbed in the small
intestine as usable minerals and nutrients. The small intestine also receives
bile and the pancreatic enzymes from the bile ducts. These pancreatic enzymes
break down carbohydrates, fats and proteins for absorption. The small intestine
is also a hollow abdominal tube that connects to the stomach at its upper end
and to the large intestine at its lower end which sphincter prevents back flow.
The three parts of the small intestine are the duodenum, jejunum
and ileum
Iron is absorbed in the duodenum, jejunum absorbs all of the
products of digestion and the ileum absorbs any remaining nutrients that has
left behind.
Large Intestine
The large intestine is involved in the absorption of water and the
removal of by products of digestion through defecation. The two major parts of
the large intestine are the cecum and sigmoid colon.
The caecum is connected to the appendix which has an unknown role
and the colon absorbs water and propels waste to the rectum.
Rectum
The rectum is a part of the lower gastro intestinal tract. It is a
continuation of a sigmoid colon and connects to the anus. The key role of the
rectum is to act as a storehouse for feces.
Anus
The anus is the last part of the digestive tract. The lining of
the upper anus is specialized to detect rectal contents. It knows whether the
contents are liquid, gas or solid.
The stages of digestion are:
Mastication
Digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication(chewing)
aided by teeth, a form of mechanical digestion.
Saliva secreted by the salivary glands which contains the
following:
Salivary Amylase - Starts the digestion of starch
Mucus - Lubricates the food
Hydrogen carbonate - Maintains the ideal condition of PH (Alkaline)
for Amylase to work
Digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into
small water-soluble food molecules. So that they can be absorbed into the
watery blood plasma. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is divided into
mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the
stepwise physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. In
chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body
can use.
Absorption
95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine.
Water and minerals are reabsorbed by the colon .
Diseases related to digestive system
·
Poisonings
·
Diarrhea
·
Constipation
·
Diverticulitis
·
Gastric Eosophageal Reflux Disorder (GERD)
·
Peptic ulcers
·
Cholelithiasis
·
Cirrhosis of liver
·
Hepatitis
·
Colitis
·
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
·
Cancer
Related Topics