Mapping Skills | Geography - Remote Sensing as a Source of Map Data | 9th Social Science : Geography: Mapping Skills
Chapter: 9th Social Science : Geography: Mapping Skills
Remote Sensing as a Source of Map Data
REMOTE
SENSING AS A SOURCE OF MAP DATA
Remote Sensing refers
to the observation and measurement of earthly objects
without touching them.
‘Remote’
means far away and ‘Sensing’ means observing or collecting information. Remote sensing
means acquiring information
of things/places from a distance,
using a variety of tools and methods.
Remote sensing has
a long history, dating back from the use of cameras
carried by balloons and pigeons in the 18th and 19th centuries. During the 20th century, airborne photographs
and satellite remote sensing developed swiftly.
1. Aerial photography
Aerial photography refers to the technique of obtaining information about places or objects or phenomena
with the help of
photographs taken using cameras mounted
on low flying birds, balloons,
helicopters, aeroplanes and drones.
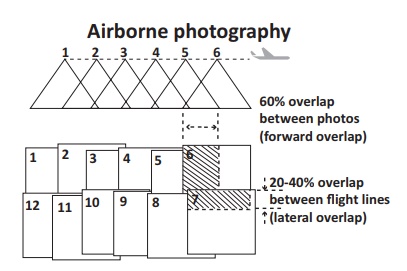
The aerial photographs
are captured continuously with a time gap of 10-30 seconds at a fixed height. Each photo will have a slight overlap of the area in the
preceding photo. By making a mosaic of all the photos
excluding the overlapping
areas, a stereoscopic (3D) image of the study area can be produced.

Nowadays you might have
seen drones
being used for photography during grand occasions such as conferences, weddings, etc.
2. Satellite Remote Sensing
Satellite remote sensing is the science of collecting data about an object
or area from artificial
satellites orbiting the
Earth. The term ‘satellite imagery’ refers
to digitally transmitted images of the satellites.
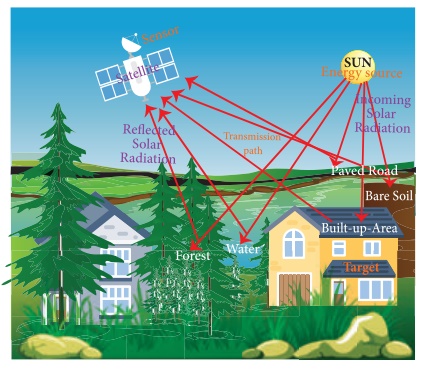
Components of remote sensing
Energy source
Transmission path
Target
Sensor
3. Process of remote sensing
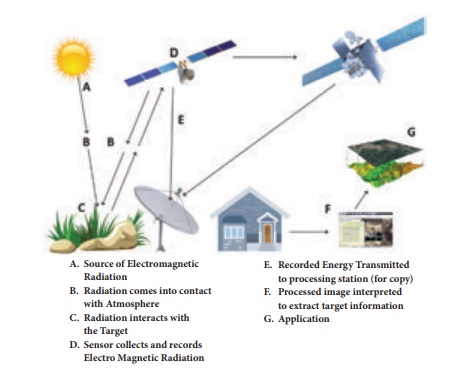
(A) The EMR (Electro Magnetic
Radiation) or solar radiation is the primary source of energy for remote
sensing.
(B) Sunlight travels from the sun
through the atmosphere, before it reaches the earth surface. In the atmosphere,
the sun's rays are not obstructed by any object.
(C) When solar radiation falls on the earth's surface, some of its
energy is absorbed. While some is transmitted through the surface, the rest is
reflected. Surfaces naturally emit radiation in the form of heat. The reflected
energy travels from the earth surface back to space.
(D) Sensors in the
satellite record the reflected and emitted radiation. Each surface/object
possesses a characteristic spectral signature, a unique pattern
of reflecting sunlight.
(E) The energy
recorded by the sensor has to be transmitted to a ground
station where the data are processed
into an image.
(F) The processed image is interpreted either visually by human interpreters or by computer aided techniques called digital
image processing to identify and distinguish between the different spectral signatures to get information
about objects/places.
(G) Finally, we understand and apply the extracted information in mapping the area or assist in solving
the particular problem.
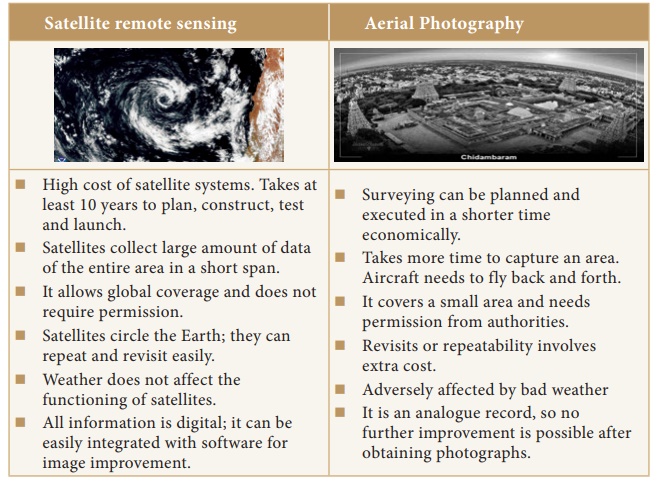
Satellite remote sensing

·
High
cost of satellite systems. Takes at least 10 years to plan, construct, test and
launch.
·
Satellites
collect large amount of data of the entire area in a short span.
·
It
allows global coverage and does not require permission.
·
Satellites
circle the Earth; they can repeat and revisit easily.
·
Weather
does not affect the functioning of satellites.
·
All
information is digital; it can be easily integrated with software for image
improvement.
Aerial Photography

·
Surveying
can be planned and executed in a shorter time economically.
·
Takes
more time to capture an area. Aircraft needs to fly back and forth.
·
It
covers a small area and needs permission from authorities.
·
Revisits
or repeatability involves extra cost.
·
Adversely
affected by bad weather
·
It is
an analogue record, so no further improvement is possible after obtaining
photographs.
Advantages of Remote sensing
It is the only practical way to obtain data
from inaccessible regions,
e.g. Antarctica, Amazon forest.
It helps
in constructing cheap base maps in the absence of detailed
land surveys.
It detects the spread of natural
calamities such as flood, forest fire and volcanic eruption, so that immediate rescue operations and planning can be carried
out.
Disadvantages of Remote sensing
It is difficult to prepare large scale maps from obtained
satellite data.
The technique
is very expensive
for small areas requiring one time analysis.
Remote sensing and Disaster Management
Remote sensing technology is highly used in disaster management
to study the effects of earthquakes, tsunamis, cyclones, volcanic eruption,
floods and wildfires.
Recent usage of Remote Sensing device in India and Malaysia
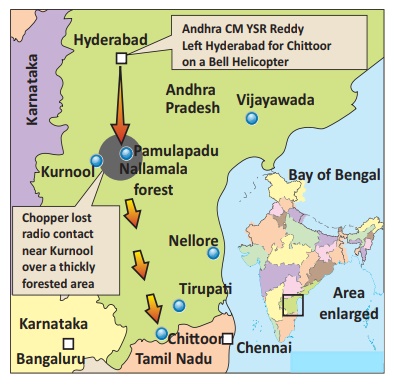
The whereabouts of the former Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister Y.S.
Rajasekhara Reddy remained uncertain, after a helicopter carrying him went
missing over a dense forest area prompting a continuing massive search
operation on September 3rd, 2009. Low flying Air craft of the National Remote
Sensing Agency has taken 41 imagery photographs of Nallamala forest area where
the search operations were undergone to pick metal signals. ISRO processed the
photographs in Hyderabad.
Overview of remote sensing application for search of missing Malaysia Airline MH370
This Boeing Commercial Airplane had disappeared on 8 March 2014
with 237 passengers onboard from Kuala Lumpur to Beijing. Numerous satellite
images from diverse times, day and night, were used for the search for the
missing flight. It became the most expensive search in aviation history, relying
mostly on analysis of data from the Inmarsat (British satellite) to look into
the airplane, flight data recorder and cockpit voice recorder, as well as the
possible path. Search for oil slicks or debris or a piece of wing from MH370
with satellite image processing using ENVI software was done by thousands of
volunteers. After analyzing the 23 March 2014 satellite imagery, two weeks
after MH370 disappeared, 12 objects in the ocean classifying as "probably
man-made", were found to suspect the burst of the flight. The
communications between Flight 370 and the satellite communication network
relayed by the Inmarsat-3 F1 satellite provided significant clues to the
location of Flight 370. The search goes on with no confirmed results yet.
The preliminary data is retrieved from
satellites like LANDSAT,
CARTOSAT, OCEANSAT, etc. Fire and flood details can be extracted
and delivered to relevant authorities within two hours of satellite
image capture. E.g. major earthquakes in China and
New Zealand, bushfire
in Victoria and floods in Kerala. Dynamic phenomena such as flood, movement of wild animals, shoreline changes, finding lost ships and planes.
Researchers use satellite imageries
for these.
4. Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
Have you ever booked a cab using a smart
phone app? Did you see the map showing the route of your travel and movement of your vehicle on mobile phones? How is it possible
to calculate the time duration of your travel?
In the 21st century, GNSS has become a part of
our lives to promote the safety and convenience of transport. Global Navigation
Satellite System (GNSS)
is a satellite system
connected with a small electronic
receiver or tracker to locate, monitor and track a
user's vehicle wherever in the world. It can also set up instant alerts when a driver of a
vehicle speeds or deviates from a particular
area. GNSS applications are used in tracking
or mapping vehicles, ships and aircraft.
A group of satellites (Space Segment)
working with a network of ground stations
(Control Segment)
provide location data. The receiver
(User Segment) converts satellite
signals into location, speed and time data.
Examples of GNSS
Europe’s Galileo
USA’s
NAVSTAR Global Positioning System (GPS)
Russia’s Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema
(GLONASS)
China’s BeiDou Navigation Satellite System
India’s
NAVIC satellite system
a. Global Positioning System (GPS)
Without the Global Positioning System (GPS) on our vehicles and mobile
phones, we would feel lost. GPS is the U.S.
implementation of the world's first and
currently the most used Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
created by the
U. S. Department Of
Defense (DOD). It became fully operational in 1995.

NAVSTAR (Navigation Satellite Timing and Ranging) is a network of 24 U.S. satellites in six different orbits in space flying 20,350 km above the surface
of the Earth; each one circles
the planet twice
a day to provide continuous, worldwide coverage. GPS receivers now come in all shapes
and sizes, Most are the size of a cellular
phone. Some are handheld, others are installed in ships, planes, trucks and cars.
Advantages of GPS
GPS technology has tremendous applications in everything from mobile
phones, watches, bulldozers, shipping containers
and ATMs.
The main purpose of GPS is to help in providing
accurate transport data (distance, route and direction). It helps in
military searches and rescue in wars. It can work as a reliable tourist guide.
GPS helps during accident
and rescue efforts, speeding the
delivery of emergency services and
disaster relief.
Weather forecasting, earthquake monitoring and environmental
protection can be done effectively by using GPS.
b. Geographic Information System (GIS)
Geographic Information System
is a computer-based tool for managing
a large amount of data collected
for a given geographic region through
remote sensing, GPS and other sources. The Geographic Information System is a combination of computer hardware, software,
geographic data and the personnel.
G - Geographic - A particular
area
I - Information - facts in order
S - System - arrangement
GIS was first
recognised in the late 1950s
by Waldo Tobler and Roger Tomlinson
(Canada). Prime examples of importing GIS for public welfare are Google Maps, Yahoo Maps and Google Earth.
The key ingredient is location. We must have a coordinate, an address or a distance from a known point that helps us to link the information to a location on a map.
Each type of data of an area
is stored as a separate 'layer' of the map.
In GIS, layers
may be used some times and removed according to need. Examples are hospitals, schools, water bodies, parks and ATMs. The computers can create
maps showing any combination of data.
Advantages of GIS
Maps produced by GIS
analysis can be used to pinpoint problem areas.
GIS finds
its strongest use in resources
management, telecommunications and urban and
regional planning.
GIS helps in planning
the land-use requirements. The local
government uses GIS for taxation and planning.
The hardware and software functions of a GIS include
Data input and verification
Compilation
Storage
Updating
and changing
Management
and exchange
Manipulation
Retrieval and presentation
Analysis and combination
Cyber cartography is a term that is used to define all the aspects of current
state of Web and virtual mapping.
Related Topics