Chapter: Civil : Construction Materials: Lime, Cement, Aggregates, Mortar
Rate Of Hydration
Rate Of Hydration
The reaction of compound C3A
with water is very fast and is responsible for flash setting of cement
(stiffening without strength development) and thus it will prevent the
hydration of C3S and C2S. However, calcium sulphate (CaSO4)
present in the clinker dissolves immediately in water and forms insoluble
calcium sulphoaluminate. It deposits on the surface of C3A forming a
colloidal membrane and consequently retards the hydration of C3A.
The amount of CaSO4 is adjusted to leave a little excess of C3A
to hydrate directly. This membrane in the process breaks because of the pressure
of the compounds formed during hydration and then again C3A becomes
active in the reaction.
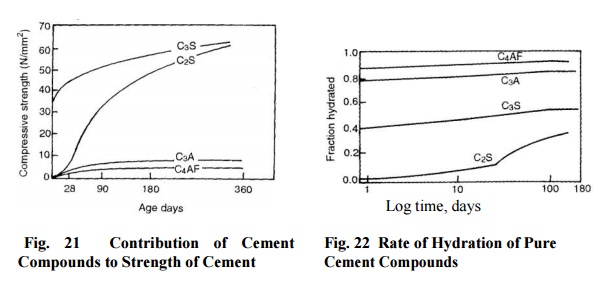
The
hardening of C3S can be said to be catalyzed by C3A and C3S
becomes solely responsible for gain of strength up to 28 days by growth and
interlocking of C-S-H gel. The increase in strength at later age is due to
hydration of C2S.
Notes: 1. The development of strength of the four
principal compounds of cement with age is shown in Fig. 21
2.The rate of heat evolution of the compounds if
equal amount of each is considered will be in the following descending order:
C3A,C3S,
C4AF, C2S
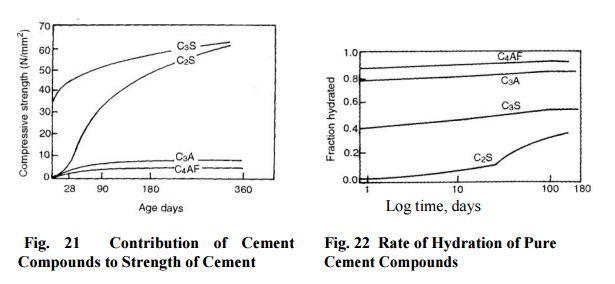
3.The rate of hydration is increased by an
increase in fineness of cement. However, total heat evolved is the same. The
rate of hydration of the principal compounds is shown in Fig. 5.2 and will be
in the following descending order:
C4AF,
C3A, C3S, C2S
Related Topics