Chapter: Civil : Construction Materials: Lime, Cement, Aggregates, Mortar
Cement: Air Permeability Method
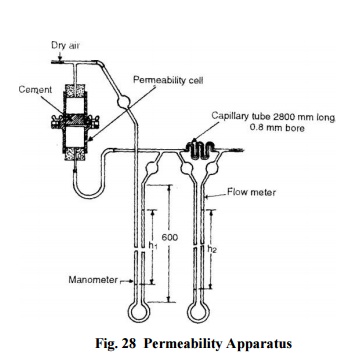
Air Permeability Method:
The fineness of cement is
represented by specific surface, i.e. total surface area in cm2
per gram or m2 per kilogram of cement and is measured by Lea and
Nurse apparatus or by wagner turbidimeter..
The Lea
and Nurse apparatus shown in Fig. 28 essentially consists of a permeability
test cell-where cement is placed and air pressure is
applied, flowmeter-to determine the quantity of air passing
per second through its capillary tube per unit difference of pressure, and
manometer-to measure the air pressure.
To
determine the fineness, a cement sample of 20 mm height is placed on a
perforated plate (40 micron perforations) and air pressure is applied. The
manometer is connected to the top of the permeability cell and the air is
turned on. The lower end of the permeability cell is then slowly connected to
the other end of the manometer. The rate of flow is so adjusted that the
flowmeter shows a pressure difference (h2) of 30-50 cm. The reading
(h 1) in the manometer is recorded. The process is repeated till the
ratio h1/h2 is constant. The specific surface is given by
the expression
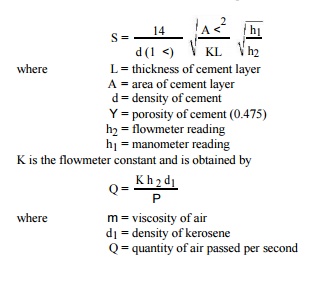
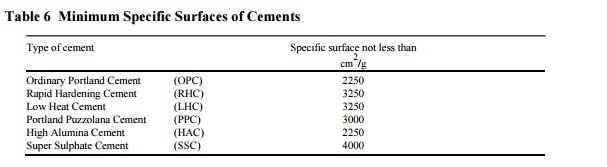
The minimum specific surface for various cements should be as
specified in Table 6.
Table 6 Minimum Specific Surfaces of Cements
Related Topics