Water | Chapter 13 | 8th Science - Questions Answers | 8th Science : Chapter 13 : Water
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 13 : Water
Questions Answers
TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
I. Choose the correct
answer.
1.
Water changes to ice at
a) 0ºC
b) 100ºC
c) 102ºC
d) 98ºC
[Answer: (a) 0°C]
2.
Solubility of carbon dioxide in water is high when the
a) pressure is low
b) pressure is high
c) temperature is high
d) None of the above
[Answer: (b) pressure is high]
3.
The gas collected at the cathode on electrolysis of water is
a) oxygen
b) hydrogen
c) nitrogen
d) carbon dioxide
[Answer: (b) hydrogen]
4.
Which of the following is a water pollutant?
a) Lead
b) Alum
c) Oxygen
d) Chlorine
[Answer: (a) Lead]
5.
Permanent hardness of water is due to the presence of __________
a) sulphates and chlorides
b) dust particles
c) carbonates and bicarbonates
d) other soluble particles
[Answer: (a) Sulphates and Chlorides]
II. Fill in the
blanks.
1. Water is colourless, odourless and tasteless.
2. The boiling point of water is
3. Temporary hardness of water can
be removed by boiling of water.
4. The density of water is maximum at
5. Loading speeds up the process of
III. State true or
false. If false, correct the statement
1. Sewage should be treated well
before being discharged it into water bodies.
2. Sea water is suitable for
irrigation as it contains dissolved salts.
Correct statement: Sea water is not suitable
for irrigation as it has high salinity.
3. Excessive use of chemical
fertilizers depletes the soil and causes water pollution.
4. The density of water will not
change at all temperature?
Correct statement: The density of water is different
at different temperatures.
5. Soap lathers well in hard water.
Correct statement: Soap lathers well in soft water.
IV. Match the
following.
1. Universal solvent - Water
pollutant
2. Hard water - Kills germs
3. Boiling - Ozonisation
4. Sterilization - Water
5. Sewage - Stomach ailments
Answer:
1. Universal solvent - Water
2. Hard water - Stomach ailments
3. Boiling - Kills germs
4. Sterilization - Ozonisation
5. Sewage - Water Pollutant
V. Give reasons for
the following.
1.
Alum is added to water in sedimentation tanks.
Reason :
(i) Chemical substance potash alum is added to water to speed up
the process of sedimentation.
(ii) This process is called loading.
(iii) The particles of potash alum combine with the suspended
impurities and make them settle down at a faster rate.
2.
Water is a universal solvent.
Reason :
(i) Water has a unique property to dissolve more substances than
any other liquids.
(ii) It can dissolve solids such as salt and sugar, liquids such
as honey and milk and gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide in it.
(iii) Water can dissolve more number of substances than any
other solvent.
(iv) Therefore, it is called as universal solvent.
3.
Ice floats on water.
Reason:
(i) This is because ice is lighter than water.
(ii) It means that the density of ice is lower than that of
water.
(iii) Since ice is a bad conductor of heat it does not allow
heat to pass through it.
(iv) So, the water below the ice remains in liquid form, where
most of the aquatic life lives.
4.
Aquatic animals can breathe in water.
Reason :
(i) Air dissolved in water is important for the aquatic animals
to survive.
(ii) Aquatic animals extracts the oxygen form the water and
expels water.
(iii) They can breathe in water only through the dissolved
oxygen present in water.
5.
Sea water is unfit for drinking.
Reason :
(i) Every litre of sea water contains 35 grams of dissolved
salts most commonly known as sodium chloride (NaCl).
(ii) Such water is called saline water.
(iii) It is not suitable for drinking and is said to be
non-potable water.
6.
Hard water is not good for washing utensils.
Reason :
Hard water damages the utensils and containers in which it is
stored and forms a hard layer.
VI. Define the
following.
1.
Freezing point
Answer: The temperature at which a liquid turns into solid when cooled
is known as freezing point. The freezing point of water is 0°C.
2.
Boiling point
Answer: The temperature at which water boils and changes to steam is called as
boiling point. The boiling point of water is 100°C at atmospheric pressure.
3.
Specific heat capacity
Answer: Amount of heat that is needed to raise the temperature of a unit mass of
a substance by 1 °C is called specific heat capacity.
4.
Latent heat of fusion
Answer: The amount of heat energy required by ice to change into water is
called latent heat of fusion.
5. Potable water
Answer: The water suitable for drinking is called potable water.
VII. Answer in brief.
1.
Name the gas evolved at cathode and anode when water is electrolysed. State
their ratio by volume.
Answer:
(i) The gas which is evolved at cathode : Hydrogen (H2).
(ii) The gas which is evolved at anode : Oxygen (O2)
(iii) The ratio of H2 and O2 = 2 : 1.
2.
State the importance of dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide in water.
Answer:
(i) Fish extracts the oxygen from the water and expels water
through the gills. Fish can survive in water only through the dissolved oxygen
present in water.
(ii) Aquatic plants make use of dissolved carbon dioxide for
photosynthesis.
(Hi) Carbon dioxide dissolved in water reacts with limestone to
form calcium bicarbonate.
(iv) Marine organisms such as snails, oysters, etc., extract
calcium carbonate from calcium bicarbonate to build their shells.
3.
What are the causes of temporary hardness and permanent hardness of water?
Answer:
(i) Temporary hardness
is due to the presence of carbonate and bicarbonate salts of calcium and
magnesium.
(ii) Permanent hardness
is due to the presence of chloride and sulphate salts of calcium and magnesium.
4.
Explain specific latent heat of vaporization of water.
Answer:
(i) When water attains the temperature of 100°C, it starts
changing its state from liquid to gaseous state, however, the temperature of
water does not rise above 100°C.
(ii) It is because the heat energy supplied only changes the
state of the boiling water.
(iii) This heat energy is stored in steam and is
commonly called latent heat of vaporization of steam.
5.
What are the methods of removing hardness of water?
Answer:
(i)
Boiling : Temporary hardness is easily removed
from water by boiling.
(ii) Adding
washing soda : Washing soda is used to
remove permanent hardness of water.
(iii) Ion-exchange : This converts hard water into soft water.
(iv) Distillation : Temporary and permanent hardness both can be removed by the
method of distillation.
VIII. Answer in
detail.
1.
How is water purified at a water purification plant?
Answer: In conventional water treatment plant, water is subjected to
different process. They are :
Sedimentation
:
i) Water from lakes or rivers is collected in large sedimentation
tanks.
(ii) There, it is allowed to stand undisturbed so that suspended
impurities settle down at the bottom of the tank.
(iii) Sometimes, a chemical substance such as potash alum is
added to water to speed up the process of sedimentation, this is called
loading.
(iv) The particles of potash alum combine with the suspended
impurities and make them settle down at a faster rate.
Filtration
:
(i) Water from the sedimentation tanks is then pumped to the
filtration tanks.
(ii) Filtration tanks contain filter beds made up of gravel,
sand, pebbles, activated charcoal and concrete.
(iii) Water passes through these layers and becomes free from
any remaining dissolved or suspended impurities completely.
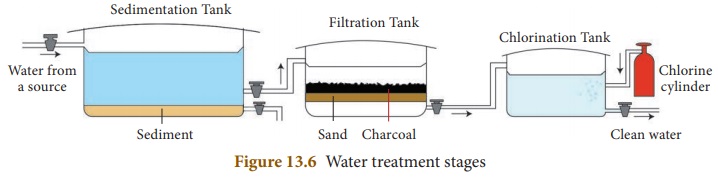
Sterilisation
:
(i) The filtered water is treated chemically to remove the
remaining germs or bacteria, this process is called sterilisation.
(ii) The chemicals that are used in this process are chlorine
and ozone.
(iii) The process of adding chlorine in adequate amounts to
water is called chlorination.
(iv) The water from filtration tanks is pumped into chlorination
tanks, where chlorine is added to remove harmful bacteria and other germs.
(v) Ozonisation is a process in which water is treated with
ozone gas to kill the germs present in it.
(vi) The sterilisation of water can also be done by exposing it
to air and sunlight.
(vii) Oxygen from the air and sunlight destroy the germs present
in water.
(viii) Aeration is the process in which air under pressure is
blown into filtered water, this also helps to kill the germs.
2.
What is permanent hardness of water? How can it be removed?
Answer: The hardness due to the presence of chloride and sulphate salts
of calcium and magnesium is known as permanent hardness of water.
Removal
of hardness :
Adding
washing soda :
(i) Washing soda is used to remove permanent hardness of water.
(ii) It converts chlorides and sulphates into insoluble
carbonates.
(iii) These insoluble carbonates are removed by filtration.
Distillation
:
(i) Temporary and permanent hardness both can be removed by the
method of distillation.
(ii) The water obtained after distillation is called distilled
water.
(iii) It is the purest form of water.
3.
What is Electrolysis? Explain the electrolysis of water.
Answer: The process of breaking down of water molecules by the passage
of electric current is known as electrolysis of water.
Electrolysis
of Water:
(i) A glass beaker is fixed with two carbon electrodes and it is
filled with water up to one third of its volume.
(ii) The positive carbon electrode acts as anode and the
negative carbon electrode acts as
cathode.
(iii) Two test tubes are placed on the electrodes.
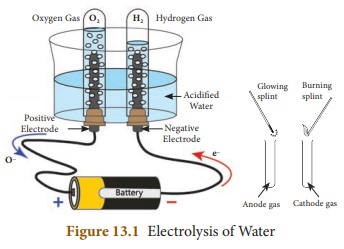
(iv) The electrodes are connected to a battery and current is
passed until the test tubes are filled with a particular gas.
(v) If the gas collected is tested using a burning splint we can
notice that the gas in cathode side burns with a popping sound when the burning
splint is brought near the mouth of the test tube.
(vi) This property is usually shown by hydrogen gas and so it is
confirmed that the gas inside the test tube is hydrogen.
(vii) The burning splint placed near the anode side burns more
brightly confirming that it is oxygen gas. This experiment shows that water is
made up of hydrogen and oxygen.
(viii) The ratio of hydrogen and oxygen is 2:1. Hence, for every
two volumes of hydrogen collected at the cathode, there is one volume of oxygen
collected at the anode.
2H2O Electrolysis→ 2H2 + O
4. Explain the different ways by which water gets polluted.
Answer:
Domestic
Sewage :
Untreated sewage contains impurities such as organic matter from
food waste, toxic chemicals from household products and it may also contain
disease-causing microbes.
Domestic
waste and plastics :
Plastics block drains spreading vector borne diseases such as
malaria and dengue. Waste in water bodies negatively impact aquatic life.
Agricultural
activities :
(i) Fertilizers, pesticides and insecticides used in agriculture
can dissolve in rainwater and flow into water bodies such as rivers and lakes.
(ii) This causes an excess of nutrients such as nitrates and
phosphates as well as toxic chemicals into the water bodies and they can be
harmful to aquatic life.
Industrial
waste :
(i) Many industries release toxic waste such as lead, mercury,
cyanides, cadmium, etc.
(ii) If this waste is unregulated and is released into water
bodies, it negatively impacts humans, plants, animals and aquatic life.
Oil
spills :
Oil spills cause water pollution which is harmful to aquatic
life.
Thermal
pollution :
Water used for cooling purposes is discharged back to a river or
to original water source at a raised temperature and sometimes with chemicals.
This rise in temperature decreases the amount of oxygen dissolved in water
which adversely affects the aquatic life.
Related Topics