Water | Chapter 13 | 8th Science - Electrolysis of Water | 8th Science : Chapter 13 : Water
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 13 : Water
Electrolysis of Water
Electrolysis of Water
Electrolysis of water can be easily
demonstrated with the help of an experiment. In this experimental set up, a
glass beaker fixed with two carbon electrodes is filled with water upto one
third of its volume. The positive carbon electrode acts as anode and the
negative carbon electrode acts as cathode. Two test tubes are placed on the
electrodes as shown in Figure 13. 1.
The electrodes are connected to a battery
and current is passed until the test tubes are filled with a particular gas.
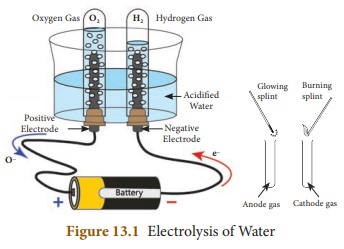
If the gas collected is tested using
a burning splint we can notice that the gas in cathode side burns with a
popping sound when the extinguish splint is brought near the mouth of the test
tube. This property is usually shown by hydrogen gas and so it is confirmed
that the gas inside the test tube is hydrogen. The burning splint placed near
the anode side burns more brightly confirming that it is oxygen gas. This
experiment shows that water is made up of hydrogen and oxygen. The ratio of
hydrogen and oxygen is 2:1. Hence, for every two volumes of hydrogen collected
at the cathode, there is one volume of oxygen collected at the anode.
2H2O ---Electrolysis
→ 2H2↑ + O2↑
Activity 1
Take some anhydrous
copper (II) sulphate powder and place it in a watch glass. Add water drop by
drop to the anhydrous copper sulphate. Do you notice any colour change in the
powder? You can notice the powder turning blue. It is a test for water.

Answer:
(i) The reaction between anhydrous copper (II) sulphate and
water is used as a test for water.
(ii) The white solid turns blue in the presence of water.
Related Topics