Atomic Structure | Term 1 Unit 4 | 7th Science - Questions Answers | 7th Science : Term 1 Unit 4 : Atomic Structure
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 1 Unit 4 : Atomic Structure
Questions Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer.
1. The basic unit of matter is
________
a.
Element
b.
Atom
c.
Molecule
d.
Electron
Answer: b. Atom
2. The subatomic particle
revolve around the nucleus is _______
a. Atom.
b. Neutron
c. Electron.
d.
Proton
Answer: c. Electron
3.
_______ is positively charged.
a. Protonb.
b. Electron
c. Moleculed.
d. Neutron
Answer: a. Proton
4.
The atomic number of an atom is ________
a. Number of neutrons
b. Number of protons
c. Total number of protons and
neutrons
d. Number of atoms
Answer: b. Number of protons
5.
_______________ Nucleons comprises of
a. Protons and electrons
b. Neutrons and electrons
c. Protons and neutrons
d. Neutrons and Positron
Answer: c. Protons and neutrons
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. The smaller particles found in
the atom is called sub-atomic particles.
2. The nucleus has Neutrons and protons.
3. The electrons revolve
around the nucleus.
4. If the valency of carbon is 4 and
that of hydrogen is 1 , then the molecular formula of methane
is CH4.
5. There are two electrons in the outermost orbit of the magnesium atom. Hence, the valency of magnesium is 2.
III. Match the following:
1.Valency - Fe
2. Neutral Particle - Proton
3. Iron - Electrons in the outermost Orbit
4. Hydrogen -
Neutron
5. Positively charged Particle - Monovalent
Answer:
1. Valency - Electrons in the outermost Orbit
2. Neutral Particle - Neutron
3. Iron - Fe
4. Hydrogen - Monovalent
5. Positively charged Particle - Proton
IV. True or False. If False, give the correct statement
(T/F).
1. The basic unit of an element is
molecule.
The basic unit of an
element is atom.
2. The electrons are positively
charged.
The electrons are
negatively charged.
3. An atom is electrically neutral.
4. The nucleus is surrounded by
protons.
The nucleus is
surrounded by electrons.
V. Complete the analogy.
1. Sun: Nucleus, planets: electrons.
2. Atomic number: number of protons,
Mass number: number of protons and neutrons.
3. K: Potassium, C: Carbon.
VI. Assertion and reason.
1.
Assertion: An atom
is electrically neutral.
Reason: Atoms have equal number of protons
and electrons.
2.
Assertion: The
mass of an atom is the mass of nucleus.
Reason: The nucleus is at the centre.
3.
Assertion: The
number of protons and neutrons is atomic number.
Reason: The mass number is sum of protons
and neutrons.
Answer:
1) A and R True
2) A and R are true
but R is not the correct explanation of A
3) A False and R
True
VII. Give very short answer.
1.
Define an atom.
Matter consists of very small particles which he named atoms. An
atom is smallest indivisible particle, it is spherical in shape of a chemical
element that retains its chemical properties.
2.
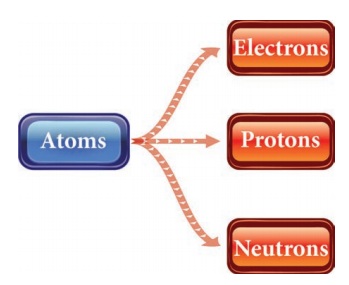
Name the sub-atomic particles.
Atoms
|→ Electrons
|→ Protons
|→ Neutrons
3.
What is atomic number?
The number of electrons or protons in an atom is called the
atomic number of that atom. It is represented by the letter Z.
4.
What is the characteristics of proton?
The proton is the positively charged particle and its located in
the nucleus. Its positive charge is of the same magnitude as that of the
electron's negative charge.
5.
Why neutrons called neutral particles?
The neutron does not have any charge.
VIII. Give short answer.
1.
Distinguish Isotopes from Isobar.
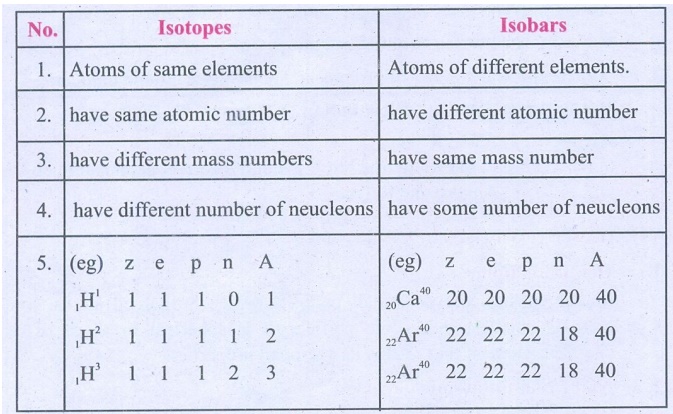
Isotopes
1. Atoms of same elements
2. have same atomic number
3. have different mass numbers
4. have different number of neucleons
5. (eg) z e p n A
1H1 1 1 1 0 1
1H2 1 1 1 1 2
1H3 1 1 1 2 3
Isobars
1. Atoms of different elements.
2. have different atomic number
3. have same mass number
4. have some number of neucleons
5. (eg) z e p
n A
20Ca40 20 20 20 20 40
22Ar40 22 22 22 18 40
22Ar40
22 22 22 18 40
2.
What are the isotones give one example.
Isotones have same number of neutrons, but different number of
protons or electrons.
(e.g) :
1) Boron 5B12
(5e, 5p, 7n)
Carbon 6C13 (6e, 6p, 7n)
Both are having 7 neutrons
(e.g) :
2) Sulphur 16S36 - 16e, 16p, 20n
Chlorine 17Cl37 -
17e, 17p, 20n
Argon 18A38 -
18e, 18p, 20n
Calcium 20Ca40 - 20e,
20p, 20n
All the four are having 20 neutrons.
3.
Differentiate mass number from atomic number.
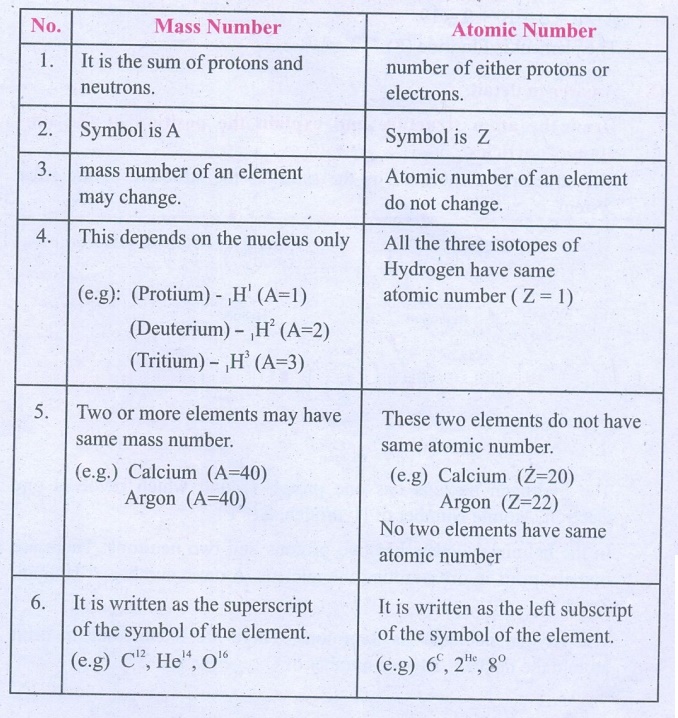
Mass Number
1. It is the sum of protons and neutrons.
2. Symbol is A
3. mass number of an element may change.
4. This depends on the nucleus only
(e.g): (Protium) - 1H1 (A=l)
(Deuterium) - 1H2 (A=2)
(Tritium) - 1H3 (A=3)
5. Two or more elements may have same mass number.
(e.g.) Calcium (A=40), Argon (A=40)
6. It is written as the superscript of the symbol of the
element.
(e.g) C12, He14, O16
Atomic Number
1. number of either protons or electrons.
2. Symbol is Z
3. Atomic number of an element do not change.
4. All the three isotopes of Hydrogen have same atomic number (Z
= 1)
5. These two elements do not have same atomic number.
(e.g) Calcium (Z=20), Argon (Z=22)
No two elements have same atomic number
6. It is written as the left subscript of the symbol of the
element.
(e.g) 6C, 2He, 8°
4.
The atomic number of an element is 9, it has 10 neutrons. Find the element from
the periodic table. What will be its mass number?
Element is Atomic
number: 9
F Automic Mass :19
Fluorine Protons : 9
Neutrons
: 10
Electrons
: 9
A = p + u = 10 + 9= 19
The element is Fluorine (F)
IX. Answer in detail.
1.
Draw the atom structure and explain the position of the sub-atomic particles.
The structure of the atom is the same as the structure of the
solar system.
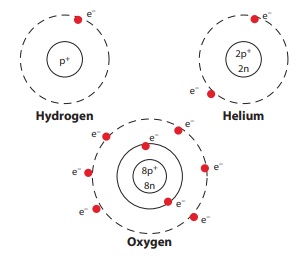
The hydrogen nucleus has one proton around which revolves one
electron. Atomic Number of Hydrogen, Z = 1
In the helium neucleus has two protons and two neutrons. There
are two electrons in orbit around the nucleus. Atomic number of Helium, Z = 2
The oxygen nucleus has 8 protons. There are 8 electrons in orbit
around the nucleus. Atomic number of Oxygen, Z = 8
2.
The atomic number and the mass number of an element is 26 and 56 respectively.
Calculate the number of electrons protons and neutrons in its atom. Draw the
structure.
Atomic number (z) = 26
Mass Number (A) = 26
Number of electrons (e) = 26
Number of protons (p) = 26
Number of neutrons (n) = 30
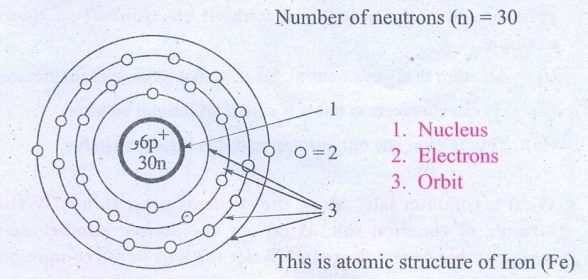
1. Nucleus
2. Electrons
3. Orbit
This is atomic structure of Iron (Fe)
3.
What are nucleons. Why are they so called? Write the properties of the
nucleons.
Protons and Neutrons are called nucleous. Since these two types
of particles are in the nucleus of an atom, they are called nucleons. Proton
has positive charge of the same magnitude as that of electrons negative charge.
It has one unit of atomic mass. Neutron does not have any charge. It also had
one unit of atomic mass.
4.
Define valency? What is the valency of the element with atomic number 8. What
is the compound by the element with hydrogen.
Valency is defined as the combining capacity of an element.
Atoms of different elements combine with each other to form molecules. Valency
determines the number of atoms of an element that combines with atom or atoms
of another type. Valency of an element depends on the number of electrons in
the outer mast orbit of its atom.
This combining property of an atom is called as Valency. It is a
measure of how many hydrogen atoms it can combine with For example: oxygen can
combine with two hydrogen atoms and create water molecule, the velency of
oxygen atom is two. In case of chlorine, it can combine with only one hydrogen
to create HC1 m(hydrochloric acid) here the valency of chlorine is one.
X. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking
Skills.
1. Anatom
of an element has no electron, will that atom have any mass or not? Can atom
exist without electron? If so then give example.
(i) An atom is always neutral. So it cannot exist without
electrons.
(ii) H+ has no electron but it is called an ion not an atom.
(iii) This H+ ion has only proton and it is highly unstable.
2.
Find what is common salt? Name the elements present in it? Write the formula of
common salt. What are the atomic number and the mass number of the elements?
Write the ions in the compound.
Common salt is sodium chloride with chemical formula NaCl
containing two elements Sodium and Chlorine
Sodium
Chlorine
Atomic number 11 17
Mass number 23 35
They exist as ions : Sodium ion Na+ and Chloride ion
Cl−
XI. Project.
To
have an idea of what atoms are, students will construct atoms using pipe
cleaners (thin metal wires-electron shells), pom-poms (balls) (different colors
for protons and neutrons) and beads (electrons). Students will love and enjoy
putting them together and they look great hanging from the ceiling in the
classroom.
Related Topics