Problem Solving and Python Programming - Python Algorithmic Problem Solving: short important questions and answers | Problem Solving and Python Programming : Algorithmic Problem Solving
Chapter: Problem Solving and Python Programming : Algorithmic Problem Solving
Python Algorithmic Problem Solving: short important questions and answers
ALGORITHMIC PROBLEM SOLVING
1. What is an algorithm?
Algorithm is an ordered sequence of finite, well defined, unambiguous instructions for completing a task. It is an English-like representation of the logic which is used to solve the problem. It is a step- by-step procedure for solving a task or a problem. The steps must be ordered, unambiguous and finite in number.
2. Write an algorithm to find minimum of 3 numbers in a list. ALGORITHM : Find Minimum of 3 numbers in a list
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Read the three numbers A, B, C
Step 3: Compare A and B.
If A is minimum, go to step 4 else go to step 5. Step 4: Compare A and C.
If A is minimum, output “A is minimum” else output “C is minimum”. Go to step 6.
Step 5: Compare B and C.
If B is minimum, output “B is minimum” else output “C is minimum”.
Step 6: Stop
3. List the building blocks of an algorithm.
The building blocks of an algorithm are
· Statements
· Sequence
· Selection or Conditional
· Repetition or Control flow
· Functions
4. Define statement. List its types.
Statements are instructions in Python designed as components for algorithmic problem solving, rather than as one-to-one translations of the underlying machine language instruction set of the computer.
There are three types of high-level programming language statements Input/output statements make up one type of statement. An input statement collects a specific value from the user for a variable within the program. An output statement writes a message or the value of a program variable to the user’s screen.
5. Write the pseudo code to calculate the sum and product of two numbers and display it.
INITIALIZE variables sum, product, number1, number2 of type real
PRINT “Input two numbers”
READ number1, number2
sum = number1 + number2
PRINT “The sum is “, sum
COMPUTE product = number1 * number2
PRINT “The Product is “, product
END program
6. How does flow of control work?
Control flow (or flow of control) is the order in which individual statements, instructions or function calls of an imperative program are executed or evaluated. A control flow statement is a statement in which execution results in a choice being made as to which of two or more paths to follow.
7. What is a function?
Functions are "self-contained" modules of code that accomplish a specific task. Functions usually "take in" data, process it, and "return" a result. Once a function is written, it can be used over and over and over again. Functions can be "called" from the inside of other functions.
8. Write the pseudo code to calculate the sum and product displaying the answer on the monitor screen.
INITIALIZE variables sum, product, number1, number2 of type real
PRINT “Input two numbers”
READ number1, number2 sum = number1 + number2
PRINT “The sum is “, sum
COMPUTE product = number1 * number2
PRINT “The Product is “, product
END program
9. Give the rules for writing Pseudo codes.
· Write one statement per line.
· Capitalize initial keywords.
· Indent to show hierarchy.
· End multiline structure.
· Keep statements to be language independent.
10. Give the difference between flowchart and pseudo code.
Flowchart and Pseudo code are used to document and represent the algorithm. In other words, an algorithm can be represented using a flowchart or a pseudo code. Flowchart is a graphical representation of the algorithm. Pseudo code is a readable, formally styled English like language representation of the algorithm.
11. Define a flowchart.
A flowchart is a diagrammatic representation of the logic for solving a task. A flowchart is drawn using boxes of different shapes with lines connecting them to show the flow of control. The purpose of drawing a flowchart is to make the logic of the program clearer in a visual form.
12. Give an example of iteration.
a = 0
for i from 1 to 3 // loop three times
{
a = a + I // add the current value of i to a
}
print a // the number 6 is printed (0 + 1; 1 + 2; 3 + 3)
13. Write down the rules for preparing a flowchart.
While drawing a flowchart, some rules need to be followed—
(1) A flowchart should have a start and end,
(2) The direction of flow in a flowchart must be from top to bottom and left to right, and
(3) The relevant symbols must be used while drawing a flowchart.
14. List the categories of Programming languages.
Programming languages are divided into the following categories:
Interpreted, Functional, Compiled, Procedural, Scripting, Markup, Logic-Based, Concurrent and Object-Oriented Programming Languages
15. Mention the characteristics of an algorithm.
· Algorithm should be precise and unambiguous.
· Instruction in an algorithm should not be repeated infinitely.
· Ensure that the algorithm will ultimately terminate.
· Algorithm should be written in sequence.
· Algorithm should be written in normal English.
· Desired result should be obtained only after the algorithm terminates.
16. Compare machine language, assembly language and high-level language.
Machine language is a collection of binary digits or bits that the computer reads and interprets.
This language is not easily understandable by the human.
An assembly language directly controls the physical hardware. A program written in assembly language consists of a series of instructions mnemonics that correspond to a stream of executable instructions, when translated by an assembler can be loaded into memory and executed. The programs written in this language are not portable and the debugging process is also not very easy.
A high level language is much more abstract, that must be translated or compiled in to machine language. It is easily understandable and the programs are portable. Debugging the code is easy and the program written is not machine dependent.
17. What is the difference between algorithm and pseudo code?
An algorithm is a systematic logical approach used to solve problems in a computer while pseudo code is the statement in plain English that may be translated later to a programming language. Pseudo code is the intermediary between algorithm and program.
18. List out the simple steps to develop an algorithm. Algorithm development process consists of five major steps.
Step 1: Obtain a description of the problem.
Step 2: Analyze the problem.
Step 3: Develop a high-level algorithm.
Step 4: Refine the algorithm by adding more detail.
Step 5: Review the algorithm.
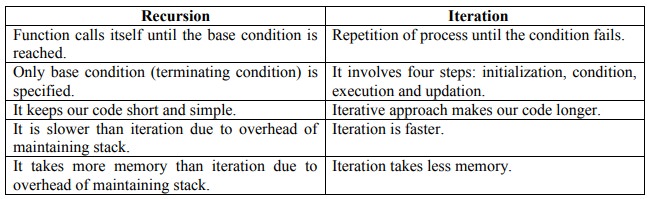
19. Give the differences between recursion and iteration.
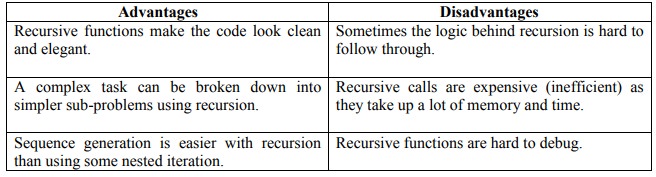
20. What are advantages and disadvantages of recursion?
1.
What is mean by
problem solving?
2.
List down the
problem solving techniques?
3.
Define
algorithm?
4.
What are the
properties of algorithm?
5.
List down the
equalities of good algorithm?
6.
Define
statements?
7.
Define state?
8.
What is called
control flow?
9.
What is called
sequence execution?
10.
Define
iteration?
11.
What is mean by
flow chart?
12.
List down the
basic symbols for drawing flowchart?
13.
List down the
rules for drawing the flowchart?
14.
What are the
advantages of flowchart?
15.
What are the
disadvantages of flowchart?
16.
Define pseudo
code?
17.
List down the
keywords used in writing pseudo code?
18.
Mention the
advantages of using pseudo code?
19.
Mention the
disadvantages of using pseudo code?
20.
What are the
ways available to represent algorithm?
21.
Differentiate
flowchart and pseudo code?
22.
Differentiate
algorithm and pseudo code?
23.
What is
programming language?
24.
Mention the
types of programming language?
25.
What is mean by
machine level language?
26.
What are the
advantages and disadvantages of machine level language?
27.
What is high
level programming language and mention its advantages?
28.
What are the
steps in algorithmic problem solving?
29.
Write the
algorithm for any example?
30.
Draw the flow
chart for any example?
31.
Write pseudo
code for any example?
Related Topics