Problem Solving and Python Programming - Python Algorithmic Problem Solving: brief important questions and answers | Problem Solving and Python Programming : Algorithmic Problem Solving
Chapter: Problem Solving and Python Programming : Algorithmic Problem Solving
Python Algorithmic Problem Solving: brief important questions and answers
1. What are the building blocks of an algorithm? Explain in detail.
The
building blocks of algorithm are -Statements
-State
-Control
flow
-Functions
Statements:
There are
3 types of statements:
-Input/Output
Statement
-Assignment
Statement
-Control
Statement
State:
There are
3 types of state:
-Initial
state
-Current
state
-Final
state
Control flow:
-Sequence
The
sequence structure is the construct where one statement is executed after
another -Selection
The
selection structure is the construct where statements can executed or skipped
depending on whether a condition evaluates to TRUE or FALSE. There are three
selection structures in C:
1.
IF
2.
IF – ELSE
3.
SWITCH
Repetition
The
repetition structure is the construct where statements can be executed
repeatedly until a condition evaluates to TRUE or FALSE. There are two
repetition structures in C:
1.
WHILE
2.
FOR
Functions:
A
function is a block of organized reusable code that is used to perform a single
action.
2. Briefly describe iteration and recursion. Illustrate with an example.
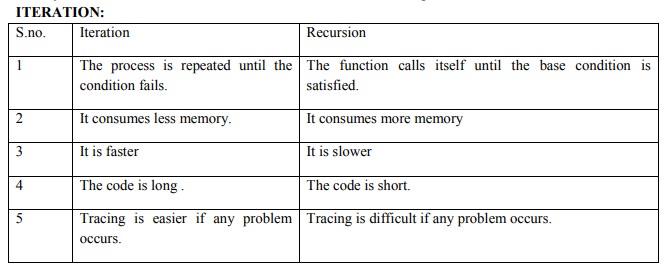
Example: Iterative algorithm for factorial of a number

Example: Recursive algorithm for factorial of
number

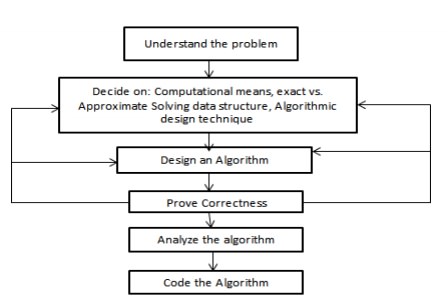
3. Explain in detail Algorithmic problem solving.
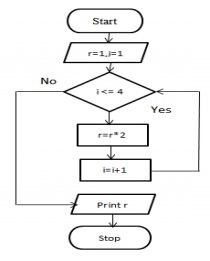
4. Write an algorithm and draw a flowchart to calculate 24.
Algorithm:
Step 1:
Start
Step 2:
Initialize the value of result, r=1.
Step 3:
Repeat step4 for 4 times
Step 4:
calculate r=r*2
Step 5:
Print the value of r
Step 6:
Stop
Flowchart:
5. a) Describe pseudo code with its guidelines.
Pseudo
code consists of short, readable and formally-styled English language used for
explaining an algorithm. Pseudo code does not include details like variable
declarations, subroutines etc.
Preparing a Pseudo Code
·
Pseudo code is written using structured English.
·
In a pseudo code, some terms are commonly used to
represent the various actions. For example,
for
inputting data the terms may be (INPUT, GET, READ),
for
outputting data (OUTPUT, PRINT, DISPLAY),
for
calculations (COMPUTE, CALCULATE),
for
incrementing (INCREMENT),
in
addition to words like ADD, SUBTRACT, INITIALIZE used for addition,
subtraction, and initialization, respectively.
·
The control structures—sequence, selection, and
iteration are also used while writing the pseudo code.
·
The sequence structure is simply a sequence of
steps to be executed in linear order.
·
The selection constructs—if statement and case
statement. In the if-statement, if the condition is true then the THEN part is
executed otherwise the ELSE part is executed. There can be variations of the
if-statement also, like there may not be any ELSE part or there may be nested
ifs. The case statement is used where there are a number of conditions to be
checked. In a case statement, depending on the value of the expression, one of
the conditions is true, for which the corresponding statements are executed. If
no match for the expression occurs, then the OTHERS option which is also the
default option, is executed.
·
WHILE and FOR are the two iterative statements.
b) Give an example for pseudo code.
Pseudocode for finding maximum in a list:
BEGIN
SET
numlist=[ ]
GET n
FOR i=1
to n
GET
numlist elements
ENDFOR
SET
maximum = numlist[0]
FOR i in
numlist
IF (n
> maximum)
maximum =
n
ENDIF
ENDFOR
PRINT
maximum
END
c) Write the pseudo code for Towers of Hanoi.
Pseudocode
START
Procedure
Hanoi(disk, source, dest, aux)
IF disk =
= 0, THEN
move disk
from source to dest
ELSE
Hanoi(disk
- 1, source, aux, dest)
move disk
from source to dest
Hanoi(disk
- 1, aux, dest, source)
END IF
END
Procedure
6. a) What is flowchart?
Flowchart
is a diagrammatic representation of the logic for solving a task. A flowchart
is drawn using boxes of different shapes with lines connecting them to show the
flow of control. The purpose of drawing a flowchart is to make the logic of the
program clearer in a visual form.
b) List down symbols and rules for writing flowchart.
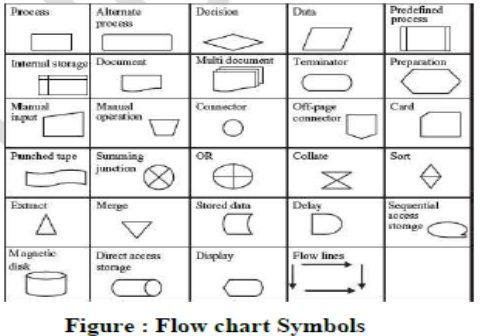
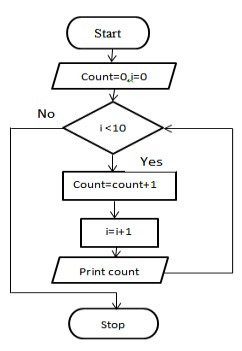
c) Draw a flowchart to count and print from1 to 10.
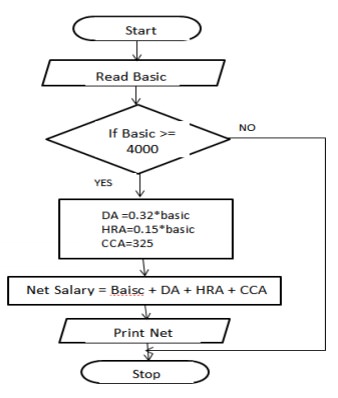
7. a) Write an algorithm and give the flowchart to find the net salary of an employee.
Algorithm:
Step 1:
Start
Step 2 :
Read the basic salary
Step 3 :
IF the basic is greater than or equal to 4000 ELSE Goto Step 4
Step 3.1
: DA= 0.32 * basic (Dearness Allowance)
Step 3,2
: HRA = 0.15 * basic (House Rent Allowance)
Step 3.3
: CCA = 325 (City Compensatory Allowance)
Step 3.4
: Net Salary basic + DA HRA + CCA
Step 4 :
Print the Net Salary
Step 5 :
Stop
b) Write an algorithm and give the pseudo code to guess an integer number in a range.
Algorithm:
step 1:
Start the program
step 2:
Read an 'n' number
step 3:
Read an Guess number
step 4:
if Guess> n; print "Your Guess too high" Step 5: elif Guess <n
; print "Your Guess
too
low" step 6: elif Guess = = n; print "Good job"
Step 7:
else print"Nope "
Step :8
Stop the program
Pseudocode:
BEGIN
READ n
READ
Guess = 20
IF
Guess> n
print"Your
Guess too High" elif Guess< n
print
"Your Guess too low" elif Guess = = 20
print
"Good Job"
ELSE
print"Nope"
8. a) Write an algorithm to insert a card in a list of sorted cards.
ALGORITHM:
Step 1:
Start
Step 2:
Declare the variables N, List[],I and X
Step 3:
READ Number of element in sorted list as N
Step 4:
SET i=0
Step 5:
IF i<N THEN go to step 6 ELSE go to step 9
Step 6:
READ Sorted list element as List[i]
Step 7:
i=i+1
Step 8:
go to step 5
Step 9:
READ Element to be insert as X
Step 10:
SET i=N-1
Step 11:
IF i>0 AND X<List[i] THEN go to step 12 ELSE go to step 15
Step 13:
i=i-1
Step 14:
go to step 11
Step 15:
List[i+1]=X
Step 16:
Stop
b) Write an algorithm to find the minimum number in a list.
Algorithm:
Step 1 :
Start
Step 2 :
Initialize the value of minimum = 0
Step 3 :
Enter the input number (n) of items in a list.
Step 4 :
Get all the elements using for loop and store it in a list.
Step 5:
Assign the first element in a list as minimum.
Step 6:
Compare maximum with the first element in a list,n.
Step 7:
Repeat step 8,9 until list becomes empty.
Step 8 :
If n is less than the minimum
Step 9 :
Assign minimum = n
Step 10 :
Display mi nimum
Pseudocode:
BEGIN
SET
numlist=[ ]
GET n
FOR i=1
to n
GET
numlist elements
ENDFOR
SET
minimum = numlist[0]
FOR i in
numlist
IF (n
< minimum)
minimum =
n
ENDIF
ENDFOR
PRINT
minimum
END
BART B:
1.
Explain in
detail about problem solving techniques?
2.
Explain in
detail about building blocks of algorithm?
3.
Discuss the
symbols and rules for drawing flowchart with the example?
4.
Explain in
detail about programming language?
5.
Discuss briefly
about algorithmic problem solving?
6.
Write algorithm,
pseudo code and flow chart for any example?
7.
Explain in
detail about simple strategies for developing algorithms?
Related Topics