Types, Rules, Advantages, Disadvantages, Example - Notation | Problem Solving and Python Programming : Algorithmic Problem Solving
Chapter: Problem Solving and Python Programming : Algorithmic Problem Solving
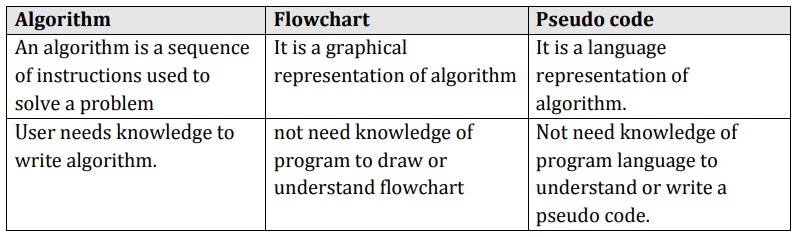
Notation
NOTATIONS
FLOW CHART
Flow chart is
defined as graphical representation of the logic for problem solving.
The purpose of
flowchart is making the logic of the program clear in a visual representation.
Rules for drawing a flowchart
1.
The flowchart
should be clear, neat and easy to follow.
2.
The flowchart
must have a logical start and finish.
3.
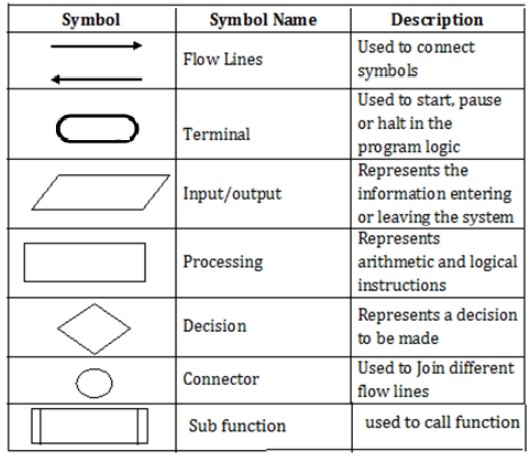
Only one flow
line should come out from a process symbol.
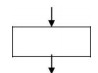
4. Only one flow
line should enter a decision symbol. However, two or three flow lines may leave
the decision symbol.
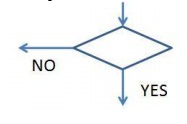
5. Only one flow
line is used with a terminal symbol.
6. Within
standard symbols, write briefly and precisely.
7. Intersection
of flow lines should be avoided.
Advantages of flowchart:
1.
Communication: - Flowcharts are better way of communicating the
logic of a system to all concerned.
2.
Effective analysis: - With the help of flowchart, problem can be
analyzed in more effective way.
3.
Proper documentation: - Program flowcharts serve as a good program documentation, which is needed for
various purposes.
4.
Efficient Coding: - The flowcharts act as a guide or blueprint
during the systems analysis and
program development phase.
5.
Proper Debugging: - The flowchart helps in debugging process.
6.
Efficient Program Maintenance: - The maintenance of operating program becomes
easy with the help of flowchart. It helps the programmer to put efforts more
efficiently on that part.
Disadvantages of flow chart:
1.
Complex logic: - Sometimes, the program logic is quite
complicated. In that case, flowchart
becomes complex and clumsy.
2.
Alterations and Modifications: - If alterations are required the flowchart may require re-drawing completely.
3.
Reproduction: - As the flowchart symbols cannot be typed,
reproduction of flowchart becomes a
problem.
4.
Cost: For
large application the time and cost of flowchart drawing becomes costly.
PSEUDO CODE:
v Pseudo code consists of short, readable and
formally styled English languages used for explain an algorithm.
v It does not include details like variable
declaration, subroutines.
v It is easier to understand for the programmer
or non programmer to understand the general working of the program, because it
is not based on any programming language.
v It gives us the sketch of the program before
actual coding.
v It is not a machine readable
v Pseudo code can’t be compiled and executed.
v There is no standard syntax for pseudo code.
Guidelines for writing
pseudo code:
v Write one statement per line
v Capitalize initial keyword
v Indent to hierarchy
v End multiline structure
v Keep statements language independent
Common keywords used in pseudocode
The following
gives common keywords used in pseudocodes.
1. //: This keyword used to represent a
comment.
2. BEGIN,END: Begin is the first statement
and end is the last statement.
3. INPUT, GET, READ: The keyword is used
to inputting data.
4. COMPUTE, CALCULATE: used for calculation
of the result of the given expression. 5.
ADD, SUBTRACT, INITIALIZE used for addition, subtraction and initialization.
6. OUTPUT, PRINT, DISPLAY: It is used to
display the output of the program.
7. IF, ELSE, ENDIF: used to make decision.
8. WHILE, ENDWHILE: used for iterative
statements.
9. FOR, ENDFOR: Another iterative
incremented/decremented tested automatically.
Syntax for if else:
IF
(condition)THEN
statement
...
ELSE
statement
...
ENDIF
Example: Greates of two numbers
BEGIN
READ a,b
IF (a>b) THEN
DISPLAY a is
greater
ELSE
DISPLAY b is
greater
END IF
END
Syntax for For:
FOR( start-value
to end-value) DO
statement
...
ENDFOR
Example: Print n natural numbers
BEGIN
GET n
INITIALIZE i=1
FOR (i<=n) DO
PRINT i
i=i+1
ENDFOR
END
Syntax for While:
WHILE
(condition) DO
statement
...
ENDWHILE
Example: Print n natural numbers
BEGIN
GET n
INITIALIZE i=1
WHILE(i<=n)
DO
PRINT i
i=i+1
ENDWHILE
END
Advantages:
v Pseudo is independent of any language; it can
be used by most programmers.
v It is easy to translate pseudo code into a
programming language.
v It can be easily modified as compared to
flowchart.
v Converting a pseudo code to programming
language is very easy as compared with converting a flowchart to programming
language.
Disadvantages:
v It does not provide visual representation of
the program’s logic.
v There are no accepted standards for writing
pseudo codes.
v It cannot be compiled nor executed.
v For a beginner, It is more difficult to follow
the logic or write pseudo code as compared to flowchart.
Example:
Addition of two numbers:
BEGIN
GET a,b
ADD c=a+b
PRINT c
END
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE
A programming
language is a set of symbols and rules for instructing a computer to perform
specific tasks. The programmers have to follow all the specified rules before
writing program using programming language. The user has to communicate with
the computer using language which it can understand.
Types of programming language
1.
Machine language
2.
Assembly
language
3.
High level
language
Machine language:
The computer can
understand only machine language which uses 0’s and 1’s. In machine language
the different instructions are formed by taking different combinations of 0’s
and 1’s.
Advantages:
Translation free:
Machine language
is the only language which the computer understands. For executing any program
written in any programming language, the conversion to machine language is
necessary. The program written in machine language can be executed directly on
computer. In this case any conversion process is not required.
High speed
The machine
language program is translation free. Since the conversion time is saved, the
execution of machine language program is extremely fast.
Disadvantage:
Ø It is hard to find errors in a program written
in the machine language.
Ø Writhing program in machine language is a time
consuming process.
Machine dependent: According to architecture used, the computer
differs from each other. So machine
language differs from computer to computer. So a program developed for a
particular type of computer may not run on other type of computer.
Assembly language:
To overcome the
issues in programming language and make the programming process easier, an
assembly language is developed which is logically equivalent to machine
language but it is easier for people to read, write and understand.
Ø Assembly language is symbolic representation
of machine language. Assembly languages are symbolic programming language that
uses symbolic notation to represent machine language instructions. They are
called low level language because they are so closely related to the machines.
Assembler
Assembler is the
program which translates assembly language instruction in to a machine
language.
Ø Easy to understand and use.
Ø It is easy to locate and correct errors.
Disadvantage
Machine dependent
The assembly
language program which can be executed on the machine depends on the
architecture of that computer.
Hard to learn
It is machine
dependent, so the programmer should have the hardware knowledge to create
applications using assembly language.
Less efficient
Ø Execution time of assembly language program is
more than machine language program.
Ø Because assembler is needed to convert from
assembly language to machine language.
High level language
High level
language contains English words and symbols. The specified rules are to be
followed while writing program in high level language. The interpreter or
compilers are used for converting these programs in to machine readable form.
Translating high level language to machine language
The programs
that translate high level language in to machine language are called
interpreter or compiler.
Compiler:
A compiler is a
program which translates the source code written in a high level language in to
object code which is in machine language program. Compiler reads the whole
program written in high level language and translates it to machine language.
If any error is found it display error message on the screen.
Interpreter
Interpreter
translates the high level language program in line by line manner. The
interpreter translates a high level language statement in a source program to a
machine code and executes it immediately before translating the next statement.
When an error is found the execution of the program is halted and error message
is displayed on the screen.
Advantages
Readability
High level
language is closer to natural language so they are easier to learn and
understand
Machine independent
High level
language program have the advantage of being portable between machines.
Easy debugging
Easy to find and
correct error in high level language
Disadvantages
Less efficient
The translation
process increases the execution time of the program. Programs in high level
language require more memory and take more execution time to execute.
They are divided into following categories:
1.
Interpreted
programming languages
2.
Functional
programming languages
3.
Compiled
programming languages
4.
Procedural
programming languages
5.
Scripting
programming language
6.
Markup
programming language
7.
Concurrent
programming language
8.
Object oriented
programming language
Interpreted programming languages:
An interpreted
language is a programming language for which most of its implementation
executes instructions directly, without previously compiling a program into
machine language instructions. The interpreter executes the program directly
translating each statement into a sequence of one or more subroutines already compiled
into machine code.
Examples:
Pascal
Python
Functional programming language:
Functional
programming language defines every computation as a mathematical evaluation.
They focus on the programming languages are bound to mathematical calculations
Examples:
Clean
Haskell
Compiled Programming language:
A compiled
programming is a programming language whose implementation are typically
compilers and not interpreters.
It will produce
a machine code from source code.
Examples:
C
C++
C#
JAVA
Procedural programming language:
Procedural
(imperative) programming implies specifying the steps that the programs should
take to reach to an intended state.
A procedure is a
group of statements that can be referred through a procedure call. Procedures
help in the reuse of code. Procedural programming makes the programs structured
and easily traceable for program flow.
Examples:
Hyper talk
MATLAB
Scripting language:
Scripting
language are programming languages that control an application. Scripts can
execute independent of any other application. They are mostly embedded in the
application that they control and are used to automate frequently executed
tasks like communicating with external program.
Examples:
Apple script
VB script
Markup languages:
A markup language
is an artificial language that uses annotations to text that define hoe the
text is to be displayed.
Examples:
HTML
XML
Concurrent programming language:
Concurrent
programming is a computer programming technique that provides for the execution
of operation concurrently, either with in a single computer or across a number
of systems.
Examples:
Joule
Limbo
Object oriented programming language:
Object oriented
programming is a programming paradigm based on the concept of objects which may
contain data in the form of procedures often known as methods.
Examples:
Lava
Moto
Related Topics