Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Pteridophytes : Salient features and Salient features
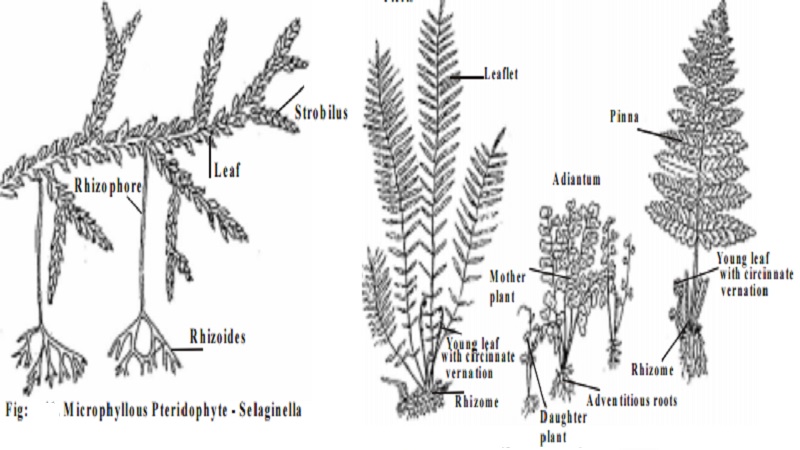
Pteridophytes
This division includes club mosses, horsetails and ferns. The oldest known pteridophytes are fossils from the end of the silurian period, 380 million years ago. Pteridophyta constitutes the earliest known vascular plants. Vascular plants are those plants that contain the vascular tissue that is the conducting tissues of xylem and phloem. Sometimes all vascular plants are included in one division theTracheophyta . This is to emphasise the advance nature of vascular tissue over the simple conducting cells of some Bryophytes and Algae. Tracheophyta includes pteridophytes and the more advanced spermatophytes (seed bearing plants) as two subdivisions.
Presence of vascular tissue is a feature of the sporophyte generation, which in the bryophytes is small and dependent on the gametophyte. The occurrence of vascular tissue in the the sporophyte is one reason why sporophyte generation has become the dominant one in all vascular plants. The vascular tissue of pteridophytes shows certain primitive features compared with flowering plants. The xylem of pteridophytes contains only tracheids rather than vessels and the phloem contains sieve cells rather than sieve tubes.
Vascular tissue has two important roles to perform. Firstly it forms a transport system, conducting water and food around the multi- cellular body, thus leading to the development of large, complex bodies. Secondly, xylem, one of the vascular tissues, supports these large bodies since xylem contains lignified cells of great strength and rigidity.
Salient features of Pteridophytes
Pteridophytes are the vascular Cryptogams. They are seedless and they are the simplest plants among the Tracheophytes (Plants having vascular tissues). Pteridophytes were world wide in distribution and abundant in the geological past. Today, they are best represented by the ferns. The non-fern pteridophytes are comparatively less in number. These plants are mostly small and herbaceous. They grow well in moist, cool and shady places where water is available.
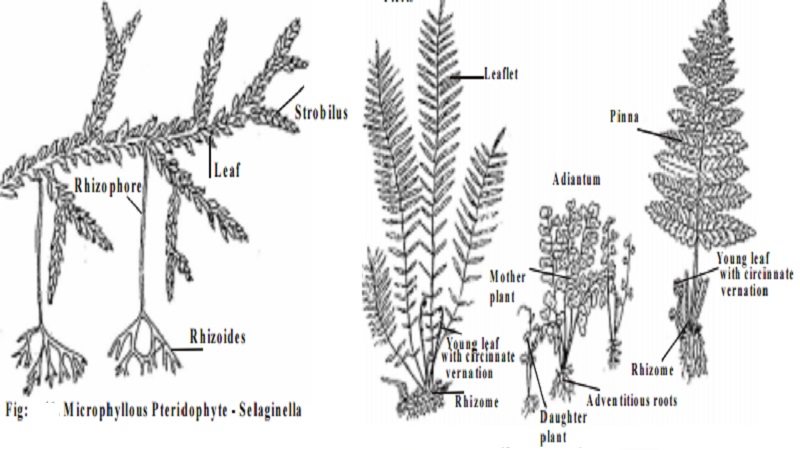
Distinguishing characters of Pteridophytes
2. Plant body of Sporophyte is dominant phase.
4. Vascular tissue i.e xylem and phloem are present. Xylem lacks vessels but tracheids are present. In phloem sieve tubes and companion cells are absent.
5. Asexual reproduction takes place by spores.
7. Spores are produced from spore mother cells after meiosis in multi-cellular sporangia.
8. Sporangia bearing leaves are called sporophylls.
9. Spores on germination develop into gametophyte which is haploid, multi-cellular, green and an independent structure.
10. develops multi-cellular sex organs. The male sex organ is called antheridium and the female sex organ is calledarchegonium.
11. Sex organs have a sterile jacket.
12. Antherozoids are spirally coiled and multiflagellate
Some common examples of microphyllous pteridophytes are Psilotum, Lycopodium, Selaginella, Isoetes, Equisetum etc.
Ferns represent a more specialized group of higher pteridophytes with larger leaves (megaphyllous). They are world wide in distribution and grow luxuriantly in forests, mountains, valleys etc. Some common examples of ferns are Nephrolepis, Ophioglossum, Osmunda, Pteris, Adiantum, Marsilea, Azolla, Salvinia etc.
Related Topics