Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Human Circulatory System : Functioning of Human heart
Human Circulatory System
All cells of our body require constant nutrition and waste removal since they are metabolically active. Most of the body cells are located at some distance from the nutrient sources such as the digestive tract and sites of waste disposal such as kidneys. The cardiovascular system which consists of the heart, blood vessels and blood, connects the various tissues of the body. While the heart pumps the blood through the blood vessels, the blood delivers nutrients and collect waste products.
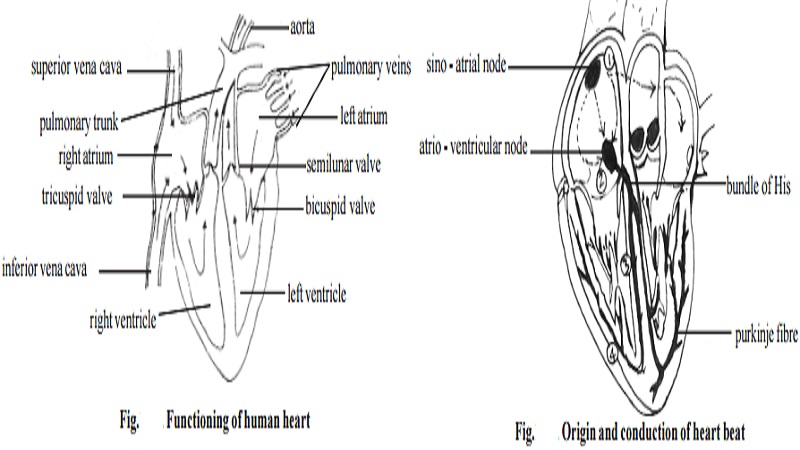
Functioning of Human heart
Heart is a pumping organ. It receives blood from different parts of the body through the veins that open through inferior andsuperior vena cavae and pulmonary veins. While the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood, the left atrium receives the oxygenated blood from the lungs. When the wall of the atria contract the right and left atria pump the blood into the right and left ventricles respectively. A pulmonary trunk arising from the right ventricle takes away the blood to the lungs for oxygenation. The left ventricle gives rise to an aorta, from which oxygneated blood is supplied to the coronary arteries and the systemic circulation of the body.
The blood flow between the right atrium and the right ventricle is regulated by the tricuspid valve. The bicuspid or mitral valve regulates the flow on the left chambers of the heart. In the pulmonary trunk and the aorta, back flow of blood is prevented by a set of semilunar valves.
Origin and conduction of heart beat
During pumping action of heart, the heart muscles cause rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart chambers in a specific sequence. The rhythmic, sequential functioning of the cardiac chamber is maintained by sino-atrial node (SA node), atrio-ventricular node (AV node), bundle of His and Purkinje fibres.
The SA node situated in the upper, lateral wall of the right atrium is a small, flattened strip of muscle fibre that is 1.5cm x 3mm in size. The fibres of the SA node are closely associated with the muscles of auricles. SA node is capable of generating action potential that can travel throughout the auricles. The velocity of conduction is 0.3m/sec. The excitation from the SA node stimulates the AV node. The AV node in turn conducts the stimulus to bundle of His and Purkinje fibres. These myocardial fibres are found all over the wall of the ventricles. In the conduction of stimulus through the AV node and the fibrous system there is a delay in transmission.
Cardiac cycle
The sequential events occuring from the initiation of one heartbeat to the commencement of the next is called as one cardiac cycle. In this cycle, the contraction phase is called systole. The relaxation phase is the diastole.
A single heart beat comprises a systole and diastole in both atria and ventricles.
Atrial systole : There is a continuous flow of blood into the right atrium through superior and inferior vena cava and coronary sinus. Simultaneously the left atrium receives blood from 4 plulmonary veins. There is a passive movement of nearly 70% of the blood. The remaining 30% is pumped into the ventricles by atrial contraction.
Ventricular filling : When the valves in between atria and ventricles open nearly two-third of the ventricle is filled. Remaining space gets filled up by atrial contraction.
Ventricular systole : As the atrial systole ends, the action potential generated by the SA node reaches the AV node and rest of the fibrous system. It causes contraction of the ventricular wall. Thus ventricular pressure results. The very strong ventricular pressure pumps the blood into respective arteries by causing the semilunar valves to open.
Ventricular diastole : Soon after the blood leaves the ventricles there is a fall in the ventricular pressure. The semilunar valves close and the atrial valves open to begin the next cycle.
Heart sound : The heart sound felt by a stethescope is caused due to the closure and opening of the valves. The generation of sound is rhythmic. The first sound is louder (lubb) and of longer duration (0.16-0.90sec). It is due to closure of the atrioventricular valves at the beginning of the ventricular systole. The second sound is of shorter duration (dubb) (0.10sec). It is caused at the end of the ventricular systole by the closure of semilunar valve. The heart beats at the rate of about 72-80 times per minute in adults. The ventricular systole causes a wave of distension due to blood flow. It is called as arterial pulse. It can be felt on the wrist. The pulse rate corresponds to rate of heartbeat.
Coronary blood vessel and its significance
There are two main coronary arteries the left and the right. The left one branches into the left circum flex artery and the left anterior descending artery. Right main coronary artery and the left coronary arteries branch off from the aorta, surround and penetrate the heart muscle. Arterioles and capillaries
branch off from the coronary arteries to supply heart muscle with oxygen rich blood. Deoxygenated blood drains into the coronary veins, which carry it back into the heart's right atrium.
Damage to the coronary blood vessel or narrowing of the coronary vessel leads to coronary artery disease (CAD). Blood flow through the arteries is restricted, leading to damages of the heart muscle. Heart disor-ders like heart attack, myocardial infarction, the chest pain or Angina are usually caused by CAD. In many parts of the world mortality from coronary artery disease is rising due to changing life style factors.
Related Topics