Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Human Nervous system
Nervous Co-ordination
The coordinating system of the body contains suitable structures for detecting stimuli, transmitting information and responding to stimuli. There are feedback mechanisms that ensure that degree of responses is related to the intensity and direction of the stimuli.
Mammals have two main coordinating systems, namely the nervous system and the endocrine system.
Nervous system
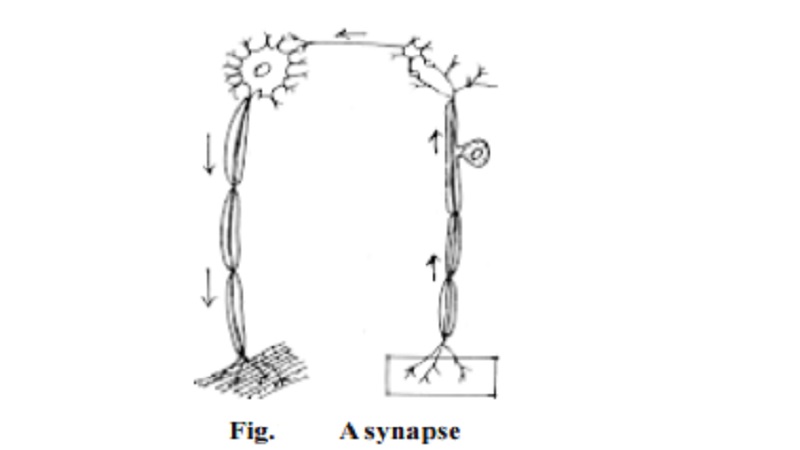
The junctions of neurons in nerve pathway are called the synapses. A synapse is formed between the bulb-like end structure of the axon called boutons and the cyton or dendrite of the adjacent neuron. At the junction there is a gap called the synaptic cleft, which is usually about 10 to 20 nm. At this point, transmission of stimulus happens through transmitter substances such asacetylcholine.
In the nervous system the bundles of parallel axons of the nervous tissue having myelin sheath constitute the white matter. Collection of neurons having unmyelinated axons form the grey matter.
The axons make up the white matter of the CNS for nerve tracts. They propogate action potentials. The grey matter performs integrative functions. The outer surface of the brain (cortex) and the central area of the spinal cord consist of grey matter. Within the brain, collections of grey matter form centers called nuclei.
The brain
There are more than a thousand million neurons in the adult human brain. An estimate shows that the cerebral cortex alone has about 102783000 synapses. Thus the brain is a complex organ.
On structural and functional basis the brain can be divided into 3 regions. They are (1). Fore brain, (2). Midbrain, (3). Hind brain.
Fore Brain (Prosencephalon) :- This region of the brain comprises Diencephalon and the cerebrum.
Related Topics