Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Characteristics of Pteridophytes and Economic importance
Characteristics of Pteridophytes
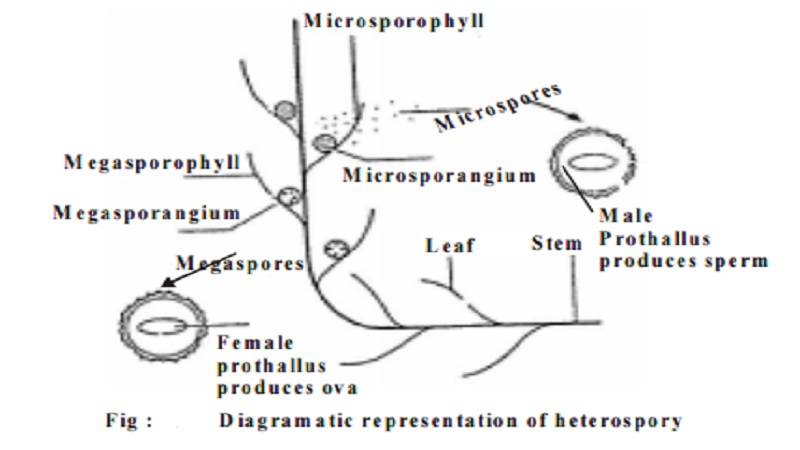
Heterospory
In some pteridophytes the gametophyte is protected by remaining in the spores of the previous sporophyte generation. In such cases there are two types of spore and the plants are therefore described as heterosporous. Plants producing only one type of spore, like the Bryophytes, are described as homosporous.
In heterosporous plants two types of spores are produced. 1. large spores called megaspores and 2. small spores calledmircrospores. Megaspores give rise to female gametophytes (prothalli). Female gametophyte bears the female sex organs namely archegonia. The microspores give rise to male gametophytes (Prothalli). This bears the male sex organs namely antheridia. Sperms (antherozoids) produced by the antheridia travel to the female sex organ namely archegonium found in female gametophyte. Both male and female gametophytes remain protected inside their respective spores. The microspore is small and they are produced in large numbers and they are dispersed by wind from the parent sporophyte, the male gametophyte that the microspore contains within is therefore dispersed with it. The evolution of heterospory is an important step towards the evolution of seed bearing plants.
Economic importance of pteridophytes
Ferns are grown as ornamental plants for their beautiful fronds.
The rhizomes and petioles of the fern Dryopteris yield a vermifuge drug.
The sporocarps of Marsilea ( a water fern) are used as food by certain tribal people.
Related Topics