Features, Functional block diagram, Pin diagram, circuit description, Applications - Power Audio Amplifier IC LM 380 | Linear Integrated Circuits : Waveform Generators and Special Function ICs
Chapter: Linear Integrated Circuits : Waveform Generators and Special Function ICs
Power Audio Amplifier IC LM 380
Power
Audio Amplifier IC LM 380:
Introduction:
Small
signal amplifiers are essentially voltage amplifier that supplies their loads
with larger amplifier signal voltage.
On
the other hand, large signal or power amplifier supply a large signal current
to current operated loads such as speakers & motors.
In
audio applications, however, the amplifier called upon to deliver much higher
current than that supplied by general purpose op-amps. This means that loads
such as speakers & motors requiring substantial currents cannot be driven
directly by the output of general purpose op-amps. To handle it following is
done
·
To
use discrete or monolithic power transistors called power boosters at the
output of the op-amp
·
To
use specialized ICs designed as power amplifiers like LM 380.
Features of LM380:
1.
Internally
fixed gain of 50 (34dB)
2.
Output
is automatically self centering to one half of the supply voltage.
3.
Output
is short circuit proof with internal thermal limiting.
4. Input stage allows the input to be ground
referenced or ac
5.
Wide
supply voltage range (5 to 22V).
6.
High
peak current capability.
7.
High
impedance.
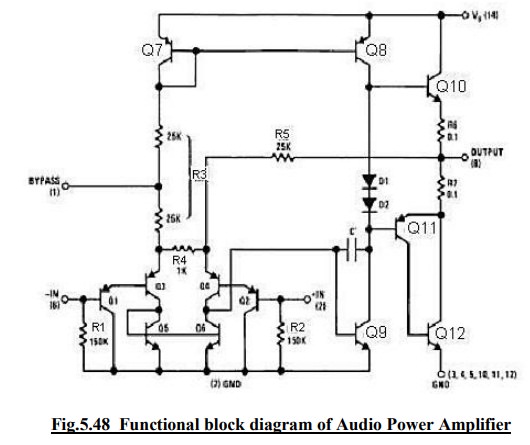
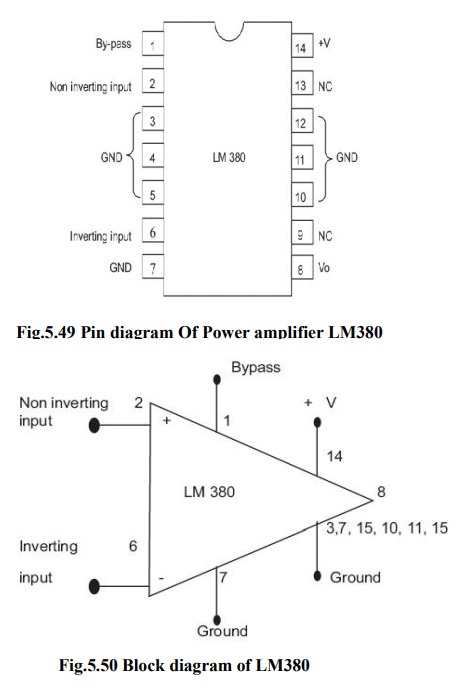
LM380 circuit description:
It
is connected of 4 stages,
(i)
PNP
emitter follower
(ii)
Different
amplifier
(iii) Common emitter
(iv) Emitter follower
(i)
PNP Emitter follower:
·
The
input stage is emitter follower composed of PNP transistors Q1 & Q2 which
drives the PNP Q3-Q4 differential pair.
·
The
choice of PNP input transistors Q1 & Q2 allows the input to be referenced
to ground i.e., the input can be direct coupled to either the inverting &
non-inverting terminals of the amplifier.
(ii) Differential
Amplifier:
·
The
current in the PNP differential pair Q3-Q4 is established by Q7, R3 & +V.
·
The
current mirror formed by transistor Q7, Q8 & associated resistors then
establishes the collector current of Q9.
·
Transistor
Q5 & Q6 constitute of collector loads for the PNP differential pair.
·
The
output of the differential amplifier is taken at the junction of Q4 & Q6
transistors & is applied as an input to the common emitter voltage gain.
(iii) Common
Emitter amplifier stage:
·
Common
Emitter amplifier stage is formed by transistor Q9 with D1, D2 & Q8 as a
current source load.
·
The
capacitor C between the base & collector of Q9 provides internal
compensation & helps to establish the upper cutoff frequency of 100 KHz.
·
Since
Q7 & Q8 form a current mirror, the current through D1 & D2 is
approximately the same as the current through R3.
·
D1
& D2 are temperature compensating diodes for transistors Q10 & Q11 in
that D1 & D2 have the same characteristics as the base-emitter junctions of
Q11. Therefore the current through Q10 & (Q11-Q12) is approximately equal
to the current through diodes D1 & D2.
(iv) (Output
stage) - Emitter follower:
·
Emitter
follower formed by NPN transistor Q10 & Q11. The combination of PNP
transistor Q11 & NPN transistor Q12 has the power capability of NPN
transistors but the characteristics of a PNP transistor.
·
The
negative dc feedback applied through R5 balances the differential amplifier so
that the dc output voltage is stabilized at +V/2;
·
To
decouple the input stage from the supply voltage +V, by pass capacitor in order
of micro farad should be connected between the bypass terminal (pin 1) &
ground (pin 7).
·
The
overall internal gain of the amplifier is fixed at 50. However gain can be
increased by using positive feedback.
Applications:
(i) Audio Power Amplifier:
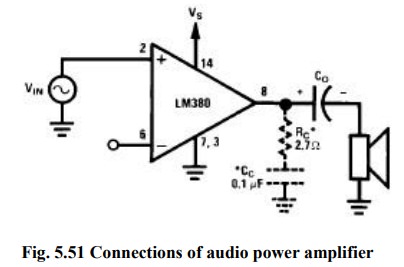
·
Amplifier
requires very few external components because of the internal biasing,
compensation & fixed gain.
·
When
the power amplifier is used in the non inverting configuration, the inverting
terminal may be either shorted to ground, connected to ground through resistors
& capacitors.
·
Similarly
when the power amplifier is used in the inverting mode, the non inverting
terminal may be either shorted to ground or returned to ground through resistor
or capacitor.
·
Usually
a capacitor is connected between the inverting terminal & ground if the
input has a high internal impedance.
·
As
a precautionary measure, an RC combination should be used at the output
terminal (pin 8) to eliminate 5-to-10 MHz oscillation.
·
C1
is coupling capacitor which couples the output of the amplifier to the 8 ohms
loud speaker which acts as a load. The amplifier will amplify the Vin applied
at the non-inverting terminal.
(ii) LM 380 as a High gain amplifier:
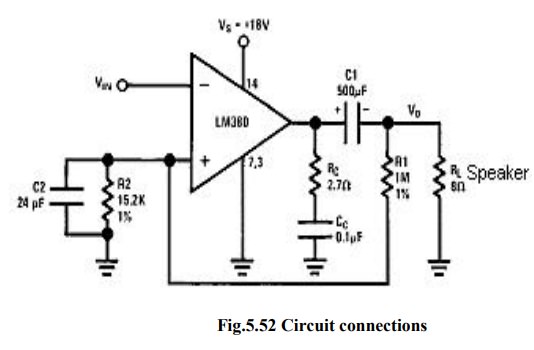
·
The
gain of LM380 is internally fixed at 50. But it can be increased by using the
external components.
·
The
increase in gain is possible due to the use of positive feedback, this setup to
obtain a gain 200.
(iii) LM 380 as a variable Gain:
·
Instead
of getting a fixed gain of 50, it is possible to obtain a variable gain up to
50 by connecting a potentiometer between the input terminals.
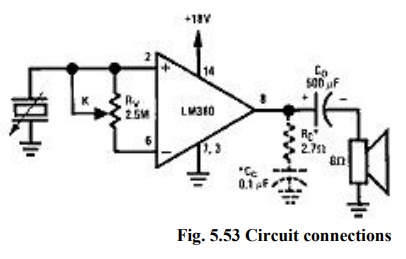
(iv) LM 380 as a Bridge Audio Power Amplifier:
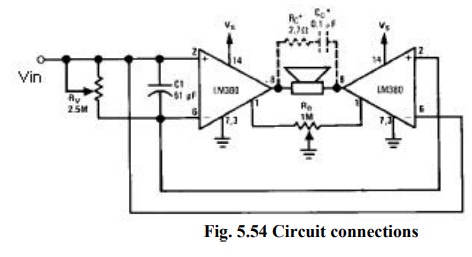
·
If
a certain application requires more power than what is provided by a single
LM380 amplifier, then 2 LM380 chips can be used in the bridge configuration.
·
With
this arrangement we get an output voltage swing which is twice that of a single
LM380 amplifier.
·
As
the voltage is doubled, power output will increase by four times that of a
single LM380 amplifier. The pot R4 is used to balance the output offset
voltages of the two chips.
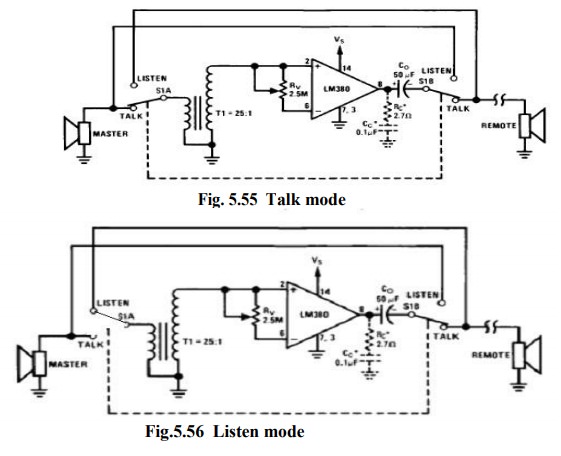
(v) Intercom system using LM 380:
·
When
the switch is in Talk mode position, the master speaker acts as a microphone.
·
When
the switch is in Listen position, the remote speaker acts as a microphone.
·
In
either phone the overall gain of the circuit is the same depends on the turns
of transformer T.
Related Topics