Maternal Health Nursing - Post Natal Care | 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Maternal Health Nursing
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Maternal Health Nursing
Post Natal Care
POST
NATAL CARE
Introduction
More than 60% of
maternal deaths take place during postpartum period. The first 48 hours are
most crucial because Most maternal and neonatal complications are occur during
this period. The puerperium is the period beginning after delivery and ending
when the woman’s body has returned as closely as possible to its prepregnant
state.
The period lasts
approximately 6 weeks. The postnatal care starts after the childbirth to 6 weeks
Aims of Postnatal Care
Prevention of sepsis at
placental site
Newborn care
Initiation of breast
feeding
Nursing Assessment
Immediate Postpartum
Assessment. The first 1 hour after delivery of the placenta (fourth stage of
labor) is the critical period; post partum hemorrhage is most likely to occur
at this time.
Components of
Postnatal Care
Postnatal check up includes Pulse, BP, RR. Temp and Pallor.
Monitor vital signs every 4 hours during the first 24 hours, then every 8 to 12
hours
BUBBLE-HE is a acronym used to denote the components of the
postpartum maternal nursing assessment.
• B: Breast
• U: Uterus
• B: Bladder
• B: Bowels
• L: Lochia
• E: Episiotomy and perineum
• H: Homan’s
• E: Emotional status
B- Breast: Assess for breast
engorgement and condition of nipples if breast-feeding.
·
Size, Shape, Firmness, Redness, Symmetry
·
Check the Breasts for - nodules, lumps
·
Check the Nipples - assess for eversion, flat, inverted, cracking,
bleeding, pain, blisters
·
Individualize teaching for breasts for breastfeeding
·
Check the breasts for signs of engorgement (swollen, tender,
tense, shiny breast tissue). If breasts are engorged and the woman is
breast-feeding:
• Allow warm to hot wet towel to cover the breasts and massage
to improve comfort.
• Express some milk manually or by breast pump to improve
comport and make nipple more available for infant feeding.
• Feeding the infant.
• A mild analgesic may be used to enhance comfort
U: Uterine Assessment
Abdomen : Monitoring of
involution process
Check firmness of the
fundus at regular intervals.
Palpating the uterine
fundus Firm or “Boggy” – not palpable by 10 days.
Ask for “afterpains”
(the pain occurs due to uterine contraction towards involution after delivery).
B: Bladder
Observe for the woman’s
first void within 6 to 8 hours after delivery.
Palpate the abdomen for
bladder distention if the woman is unable to void or complains of fullness after
voiding. a. Uterine displacement from the midline suggests bladder distention
Instruct the woman to void every several hours and after meals to
keep her bladder empty.
B: Bowels
Bowels in shock just
moved into some strange positions. So plenty of fiber , fluids and Take a stool
softener- to avoid harm to the episiotomy or trauma to the C-section incision
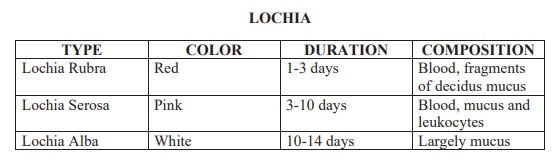
L: Lochia
Inspect the perineum
regularly for frank bleeding.
•
Note color, amount, and odor of the lochia.
•
Count the number of perineal pads that are saturated in each 8 hour
period.
•
Calculate the amount of bleeding
•
Check for lochia (vaginal discharge after delivery)
The Characteristics of Lochia
E: Episiotomy and Perineum
Assess perineal
incisions (episiotomy wound) for signs of infection and healing by REEDA
Assessment
• R: Redness
• E: Edema
• E: Ecchymosis
• D: Discharge
• A: Approximation
Assess for
lacerations/edema/hemorrhoids
Assess for
complications/hematoma
Nursing Intervention Sitz Bath: A rotating
fluid that moves the water, may fit over the commode or one can be
performed with no special equipment using the bathtub other than a bathing
ring. Turn tub on and allow drain to open and use a ring for circulating water.
It’s very shallow and only bathes the perineal area.
H: Homan’s Sign
•
Assess for Signs of DVT by the Homan’s Sign (Deep Vein
Thrombosis)
•
Inspect legs for signs of thromboembolism, and assess Homan’s sign
A
•
Positive Homan’s sign is indicative of DVT, although it’s not the
most reliable indicator
Performing the Homan’s Test
•
Most commonly performed with the supine position while laying in
bed
•
The calf is flexed at a 90° angle
•
The nurse manipulates the foot in a dorsiflexion movement
•
If pain is felt in the calf, the Homan’s Sign is said to be positive
E: Emotional Status
•
Fluctuations in estrogen levels are blamed for the emotional
roller-coaster that many moms experience after birth
•
High levels of stress, increased responsibility, and sleep deprivation
exacerbate the emotion
•
Bonding refers to the interactions between the mother and baby
Caregiving of self and baby is an indicator of emotional status.![]()
Preventing Infection
•
Observe for elevated temperature above 38°C.
•
Evaluate episiotomy/perineum for redness, ecchymosis, edema,
discharge (colour, amount, odour) and approximation of the skin.
•
Assess for pain, burning sensation, and frequency of urination.
•
Administer antibiotics as ordered.
Reducing Fatigue
·
Provide a quiet and minimally disturbed environment.
·
Organize nursing care to keep interruptions to a minimum.
·
Encourage the woman to minimize visitors and phone calls.
·
Encourage the woman sleep while the baby is sleeping. (8-10 hours
sleep).
·
Early ambulation.
·
Avoid strenuous activities for 6 weeks.
Minimizing Pain
•
Instruct the woman to apply ice packs to the perineal area for
the first 24 hours for perineal trauma or edema.
•
Initiate the Sitz bath for perineal discomfort after the first 24 hours.
Educate to do three times a day for 15 to 20 minutes.
•
Instruct the woman to contract her buttocks before sitting
to reduce perineal discomfort.
•
Assist the woman in the use of positioning cushions and pillows
while sitting or lying.
•
Administer pain medication as indicated.
Minor Ailments in Postnatal Period
•
After pains
•
Retention of urine
•
Pain at site of perineum
•
Engorgement of breast
•
Treatment of Anaemia
Postnatal Exercise
•
Pelvic floor exercise
•
Abdominal tightening
•
Pelvic tilting or rocking
•
Hip hitching
•
Foot and Leg Exercise
Immediate postpartum
exercises can be performed in bed.
•
Toe Stretch (tightens calf muscles)- While lying on your back, keep
your legs straight and point your toes away from you, then pull your legs
toward you and point your toes toward your chest. Repeat 10 times.
•
Pelvic floor exercise
(tightens perineal
muscles)-Contract your buttocks for the count of 5 and relax. Contract your
buttocks and press thighs together for the count of 7 and relax. Contract
buttocks, press thighs together, and draw in anus for the count of 10 and
relax.
Care of New Born
•
Keeping baby warm
•
Maintain Hygiene
•
Cord care
•
Breast feeding
•
Immunization
Health Education
Postpartum Care and
Hygiene
Advise the mother to
wash perineum daily and after passing urine and stools. Change perineal pads
every 4 - 6 hours. Wash hands frequently and take bath daily.
Nutritional Advice
Increase intake of fluid
and food especially iron and protein rich foods like green leafy vegetables,
jaggery, lentils, eggs and meat. Increase intake of milk and milk products like
curd, cheese etc. Calorie need per day 2200+700 =2900 Kcal Advise adequate
rest.
IFA Supplementation
Women with normal Hb are
advised to take 1 IFA tablet daily for 3 months. If Hb below 11 gm/dl, advise
her to take 2 IFA tabs daily and repeat Hb after 1 month.
Family planning advise
Counsel couple regarding
contraception.
Breastfeeding
Advise the mother for
exclusive breast feeding on demand, atleast 6 to 8 times during day & 2-3
times during night. Educate that breast feeding is best and Pre-Lacteal feeds
must be avoided.
Breast feeding
Problems
•
Cracked /sore nipples -Advise the mother to apply hind milk for
soothing effect, ensure correct positioning and attachment of baby.
•
Engorged breasts - Advise the mother to continue breast feeding
and to put warm compresses.
Registration of Birth
Emphasize the importance
of registration of birth with local panchayat.
It is a legal document
and it is required for many purposes.
Warning Signs of
Puerperium
Advise the mother to
report if following symptoms occur
• Fever, Convulsions
• Excessive bleeding
• Severe abdominal pain
• Difficulty in breathing
• Foul smelling lochia
Educate about the
Immunization for the child
Advise about the
importance of postnatal exercises
At 6 weeks following
delivery - Ask the mother for the following
Has vaginal bleeding
stopped?
Has menstrual cycle
returned?
Is there any foul
smelling vaginal discharge?
Any problems regarding
breast feeding?
Any other complaints?
Give relevant advice
& refer to doctor if needed.
Related Topics