Maternal Health Nursing - Antenatal Care | 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Maternal Health Nursing
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Maternal Health Nursing
Antenatal Care
ANTENATAL CARE
Every pregnancy needs
special care. All pregnant women should be registered and encouraged for
institutional delivery. Causes of maternal mortality are preventable by the
good antenatal care
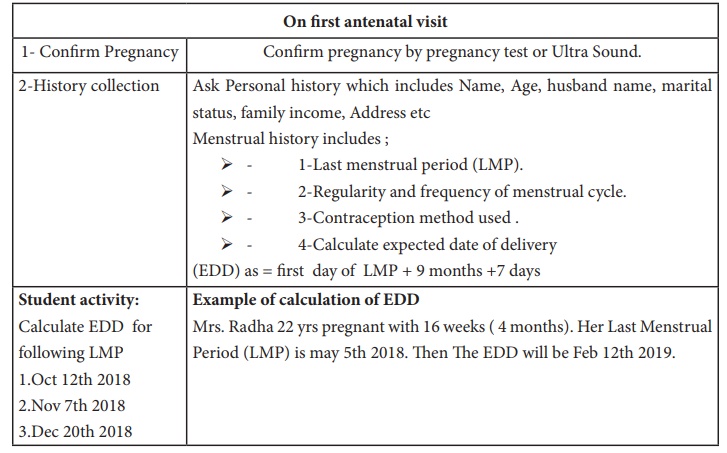

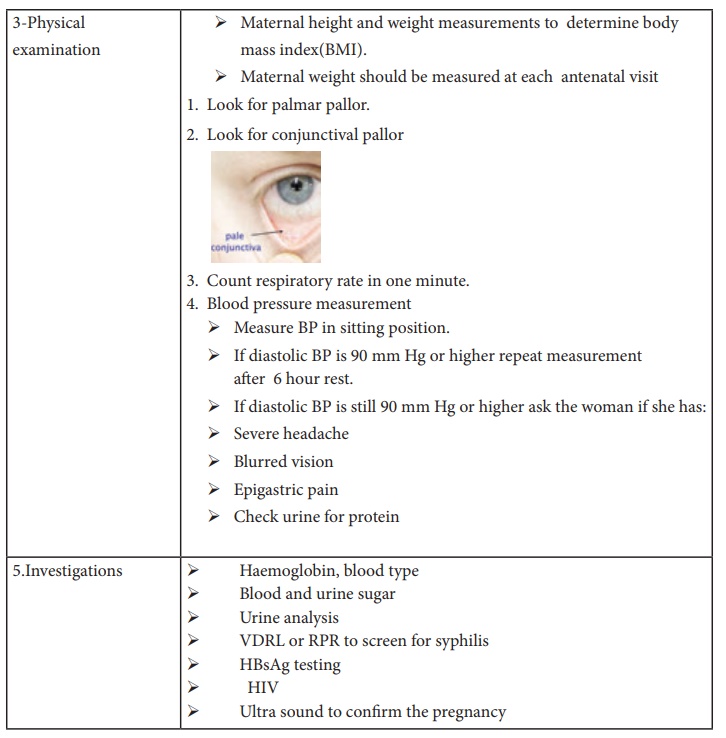
Definition of Antenatal Care
Antenatal care refers to
the care that is given to an expected mother from time of conception is confirmed
until the beginning of labor
Antenatal care is
systemic supervision of a woman during pregnancy at regular intervals to monitor:
– Maternal
wellbeing
– Fetal wellbeing
– Progress of
fetal growth
Goals of Antenatal Care
·
Ensure mother health
·
Ensure delivery of a healthy infant
·
Anticipate problem
·
Diagnose problem early
Objectives of Antenatal Care
·
Early detection and if possible, prevention of complications of
pregnancy.
·
Educate women on danger and emergency signs & symptoms.
·
Prepare the woman and her family for childbirth.
·
Give education & counseling on family planning.
Schedule of Antenatal Care
·
Medical checkup every four weeks up to 28 weeks gestation
·
Every 2 weeks until 36 weeks of gestation.
·
Every week until delivery
·
An average 7-12 antenatal visits/pregnancy
·
More frequent visits may be required if complications arise
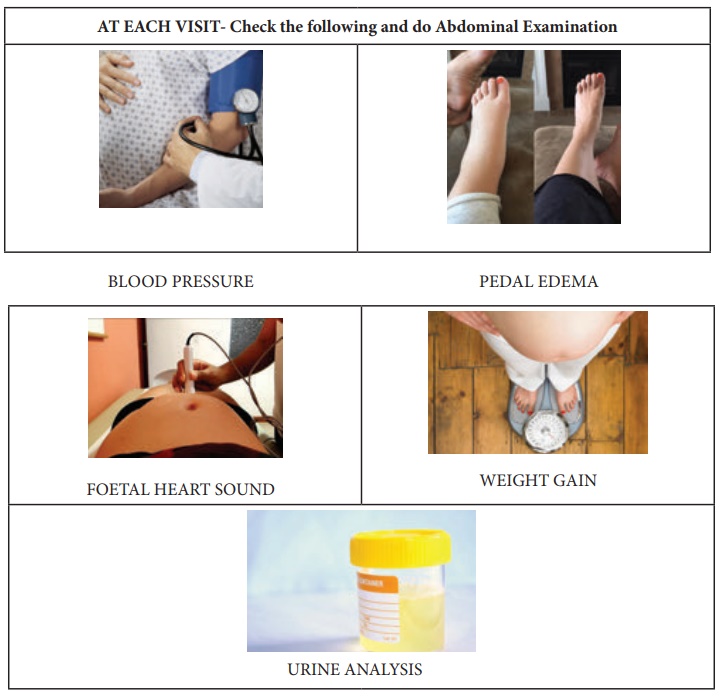
Importance of Abdominal Examination
•
Monitor progress of pregnancy and fetal growth
•
Check for fetal lie and presentation
•
Auscultate fetal heart sounds
What does it include?
•
Measurement of fundal height
•
Assessment of fetal lie and presentation
•
Assessment of fetal movement
•
Auscultation of fetal heart sounds
•
Inspection for scars
Methods of Abdominal Examination
•
Inspection
•
Palpation
•
Auscultation
Preparation for Abdominal Examination
•
Ensure privacy
•
Examination room should be well lighted and airy
•
Woman is asked to empty her bladder
•
Explain the women about the procedure/ process
•
To make her comfortable, keep talking to her
•
She lies supine with legs partially flexed
•
Stand on her right side
First start with Inspection
•
Shape - Check whether the uterine shape is ovoid or longitudinal or transverse or
oblique
•
Size - Appropriate to the weeks of pregnancy or not?
•
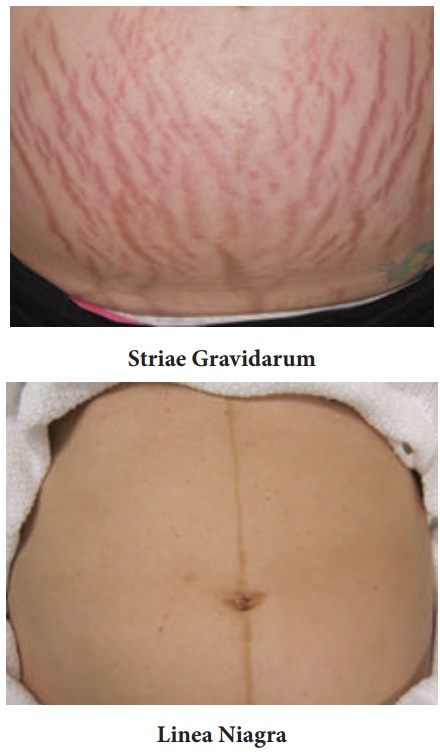
Skin Changes - look for
Striae Gravidarum - (The brown and silvery
lines all over the abdomen and)
Linea Niagra - (the pigmented line
from the symphysis pubis to umblicus)
•
Cullen's Sign - Bruishing discoloration around the umblicus
•
Scars - Any incision scars present or not
•
Contour of the abdomen- The general contour of the entire abdominal wall is observed. The contour
should be checked carefully for distention and note must be made as to whether
any distention is generalized or localized to a portion of the abdomen.
Similarly, the flanks should be checked for any bulging
•
Check for visible foetal movements if not visible, confirm with
the mother about the foetal movement
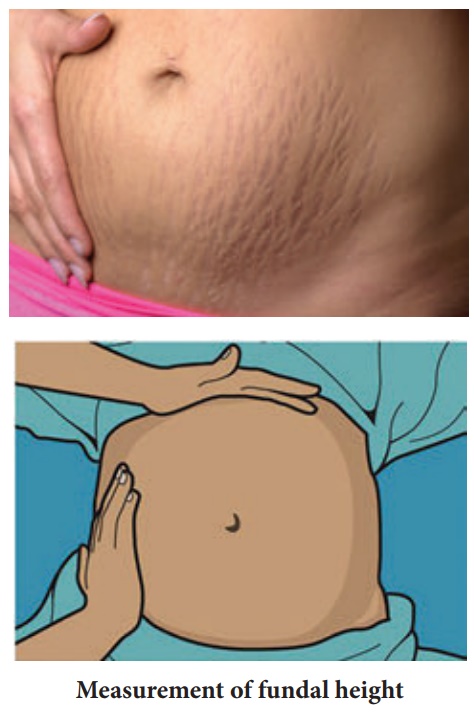
2. Palpation:
Palpate the Uterus with warm hands
Step 1: Measure the fundal
height keep the ulnar border of curved left hand on woman’s abdomen parallel to
symphysis pubis
Start from xiphisternum and gradually proceed towards symphysis pubis
lifting the hand between each step till a bulge / resistance of uterine fundus
is felt
Mark the level of fundus
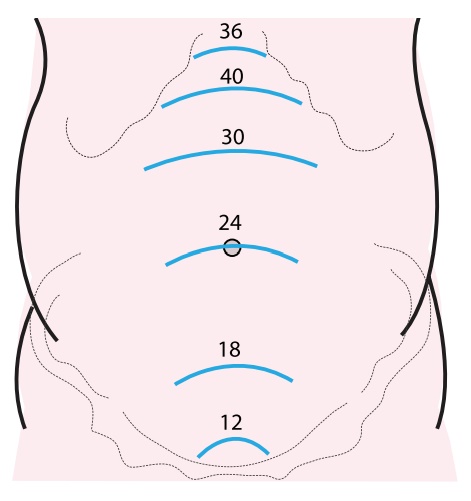
Measure the fundal
height by finger or inch tape it is measured by the inch tape each cm is week.
If it is 35 cms then it is considered as 35 weeks up to umbilicus it is 24
weeks. Then each finger is 1 cm measure from the umbilicus till the fundus of
the uterus.
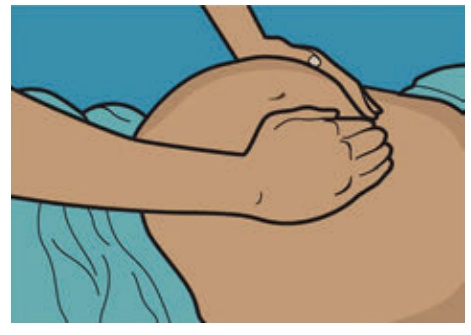
Step 2: Leopold’s maneuvers -It
includes four grips
•
Fundal grip
•
Lateral grip
•
Pelvic Grip I /Superficial pelvic grip and Pelvic Grip II / Deep Pelvic Grip
1. Fundal Palpation /
Fundal Grip - Helps to determine lie and presentation of fetus
2. Lateral Palpation /
Lateral Grip (both Right and left lateral) - Helps to locate fetal back
and limbs
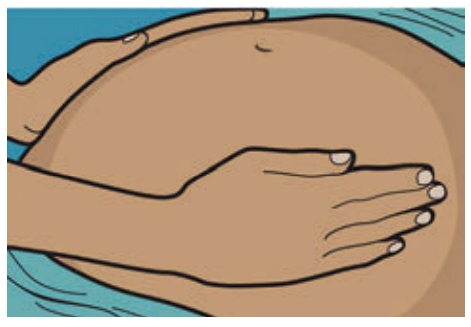
3. Pelvic Grip I /
Superficial Pelvic Grip -Helps to determine whether head or breech is presenting at
pelvic brim. Whether the presenting part is engaged / fixed / free.
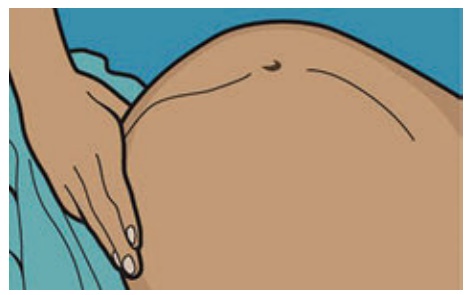
4. Pelvic Grip II /
Deep Pelvic Grip - Helps to know the degree of flexion of head.
Check or ask for Foetal Movements
Fetal movement are reliable
sign of foetal well - being.
These are felt around 18-22 wks of pregnancy (felt earlier
in multigravida than primigravida).
Normally 10-12 foetal
movements should be felt by the pregnant woman in a day.
Decreased foetal
movements may be an indication of foetal distress.
Pattern of foetal
movement may change prior to labour due to reduced space.
If Foetal Movements are
absent or not felt, consult ANM or doctor.
3. Auscultation
•
Use a fetoscope or stethoscope.
•
Best heard on the side of the back of the fetus.
•
In vertex presentation FHS is best heard midway between the line
joining the umbilicus and the anterior superior iliac spine on the side of the
back.
•
In breech presentation FHS is heard above the umbilicus (Fetal
Heart Sound).
•
Count the FHS for one full minute FHR (Fetal Heart Rate).

•
FHS is heard over the abdomen by stethoscope / fetoscope after 24 weeks of
pregnancy.
•
Normal FHR is 120 – 160 beats per min.
•
FHR < 120 beats per min or > 160 beats per minute, indicates fetal
distress.
•
Confirm that you are listening to the FHS and not maternal pulse.
DIET in Pregnancy
•
Total caloric intake should be increased to 300 kcal /day due to 15%
increase in BMR.
•
Diet should contain 20% Protein (better from animal source), 30%
fat, and 50% carbohydrates.
•
Sufficient fluids should be taken. (10 glasses for a day).
•
Absorption of iron is interfered if taken with tea, coffee or foods
rich in fluoride.
•
Enhanced if taken with lemon water or orange juice.
•
Encourage mother to take plenty of fruits and vegetables like
mango, guava, orange, amla etc containing vitamin C.
•
Emphasize the importance of high protein diet like black gram,
ground nuts, whole grains, milk, eggs etc.
Supplementation - Iron, folic acid and calcium as prescribed
WEIGHT gain in Pregnancy
•
Total weight gain approximately 12 Kgs.
•
Weight gain of 2 kgs in first trimester. 5 kgs in second and 5 kgs in
third trimester.
•
Monitoring of weight gain should be done in conjunction with
close monitoring of BP.
•
Overweight or sudden increase of weight is to be notified
immediately.
Oral Care
•
It is easy to have an increase in dental decay cavities due to
pregnancy. Heartburn,increased snacking, morning sickness can all
increase chances of developing tooth decay or gum disease. Good oral care is an
important during pregnancy as it is the most important time of life.
CARE OF BREAST
•
Breast engorgement may cause discomfort during late pregnancy. A
well-fitting brassiere can give relief.
•
Travelling during pregnancy is not prohibited but some
precautions must be taken.
•
Avoid long trips if possible. Always check with care provider
before travelling. Wear seatbelt, the shoulder belt shouldd go between the
breasts and the lap belt should go under the tummy. Plan for frequent stops.
Get out and walk as much as possible. This will prevent swelling of the foot.
•
When travelling by air, need to drink extra fluids. Walk around
whenever possible. Do isometric exercises of legs and foot to help prevent
swelling and blood clots. Do not plan to travel after 34 weeks of pregnancy.
Related Topics