Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Maternal Health Nursing
Placenta and Membranes
PLACENTA
AND MEMBRANES
This is a feto maternal
organ. It has two components:
•
Fetal part – develops from the chorionic sac
•
Maternal part – derived from the endometrium
The placenta and the
umbilical cord are a transport system for substances between the mother and the
fetus.
Structure of placenta: It is a flat, round
mass, about 15 to 20 cm in diameter, 2.5-3 cm thickness, 15-20 lobes,
weighs 1/6th of baby’s weight or 500 – 600gms at birth. It has two surfaces
maternal surface and fetal Surface
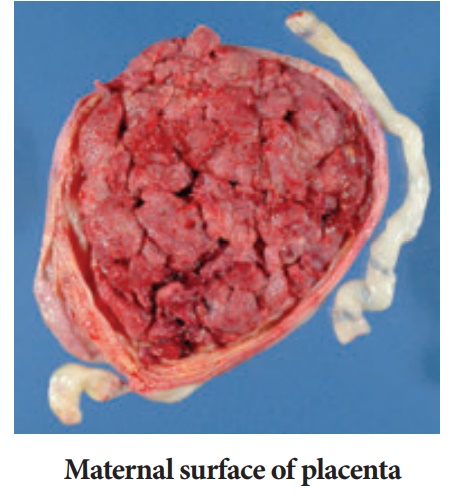
Maternal surface
It is irregular, and
divided into convex areas (cotyledons)
• Cotyledons –about 15 to 20 slightly bulging villous areas.
Their surface is covered by shreds of decidua basalis from the uterine wall.
• After birth, the placenta is always carefully inspected for
missing cotyledons. Cotyledons remaining attached to the uterine wall after
birth may cause severe bleeding.
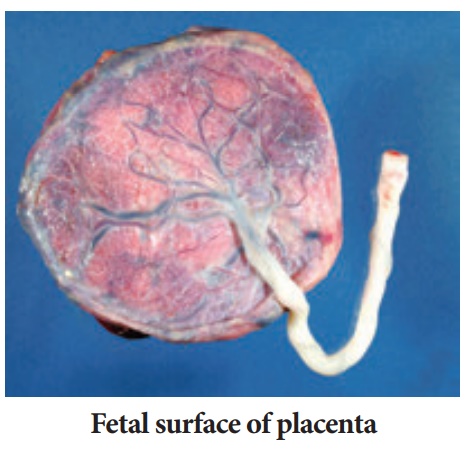
Fetal surface:
•
This side is smooth and shiny. It is covered by amnion.
•
The umbilical cord is attached close to the center of the placenta.
•
The umbilical vessels radiate from the umbilical cord.
•
They branch on the fetal surface to form chorionic vessels.
•
They enter the chorionic villi to form arteriocapillary-venous
system.
Placental Membranes
The placental membrane
separates maternal blood from fetal blood. The fetal part of the placenta is known as
the chorion. The maternal component of the placenta is known as the decidua
basalis.
Fetal membranes: It consists of two
layers.
• Chorion: It is the outer layer of fetal membranes. it is thick
friable and shaggy.
• Amnion: It is the inner layer of fetal membrane. It is smooth, shiny ,
and transparent
Placental Circulation Fetal – from Umbilical Arteries to chorionic
plate to branches to stem villi to capillaries in terminal villi and return via
umbilical vein.
Placental circulation Maternal – Free-flowing with Spiral arteries
open into intervillous space and bath the villi with 150 ml of maternal blood
Exchanged - 3-4 times/minute Reduced blood pressure in intervillous space helps
the Oxygenated blood to the chorionic plate, return back to the villi.
Functions of Placenta
· Respiratory: Placenta act as lungs to the fetus taking in oxygen from
the mother’s haemoglobin and giving of CO2 into the maternal blood.
· Nutritive: The fetus selects from the mother blood protein for tissue
building, glucose for energy and growth. Calcium and phosphorus for bones and
teeth, vitamins, iron and other minerals for blood formation.
· Storage: The liver is not sufficiently developed. Placenta stores
glucose is the form of glycogen and reconverts it into glucose as required by
the fetus.
· Excretory: The waste products are given off and taken away by the
ovarian and uterine veins.
· Protective: To protect the fetus, the placenta prevents a number of
organisms from passing through into the fetal blood.
· Endocrine: The placenta also has an endocrine action producing
hormones like follicular stimulating and leutinizing hormones of the
gonadotrophic hormone and oestrogen and progestetone.
Related Topics