Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Maternal Health Nursing
Fertilization and Fetal Development
FERTILIZATION AND
FETAL
DEVELOPMENT
Definition: It is the process during
which a haploid male gamete (sperm) unites with a haploid female gamete
(oocyte) to form a single cell (ZYGOTE). Is called fertilization.
The development of fetus
divided in to 3 periods.
1. Pre-embryonic period (0
to 2 weeks)
2. Embryonic period (3-8
weeks )
3. Fetal period (9th week
to birth of the baby)
1. Pre- embryonic period (0-2 Weeks)
•
During coitus, sperm is released by male partner into the vagina
of the female partner is called as insemination.
·
The motile sperms swim and pass the cervix to enter into the
uterus and finally to reach the ovum released by the ovary in the ampullary
isthmic junction.
·
Fertilization takes place in the ampulla-isthmic junction.
Chemical signals from oocyte attract the sperms.
·
The sperm after reaches the ovary in the ampullary isthmic
junction comes in contact with the zona-pellucida layer of the ovum and block
the entry of the additional sperms thus only one sperm fertilizes the ovum.
·
The secretions of acrosome help the sperm to enter into the ovum
through zonapellucida and the plasma membrane and thus secondary oocyte
completes meiosis II and results in the formation of a second polar body and
haploid ovum.
·
The haploid nucleus of the sperm and ovum fuse together to form a
zygote which develops into new individual.
Proces of Fusion of Gametes
Definition: The process of union of
sperm and ovum is called as fertilisation.
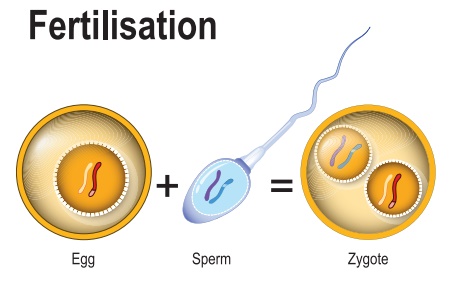
Process of Fertilization to Implantation
•
Zygote is genetically unique, a diploid cell (46 chromosomes)
resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum.
•
Male has two sex chromosomes X and Y hence male produces 50% of
sperms carrying X and 50% carrying Y, while female has two X chromosomes.
•
After fusion of the male and female gametes the zygote would carry
either XX or XY depending on whether the sperm carrying X or Y fertilized the
ovum.
•
The zygote carrying XX would develop into a female baby and XY
would form a male.
•
So, it is the father whose gamete decides the sex.
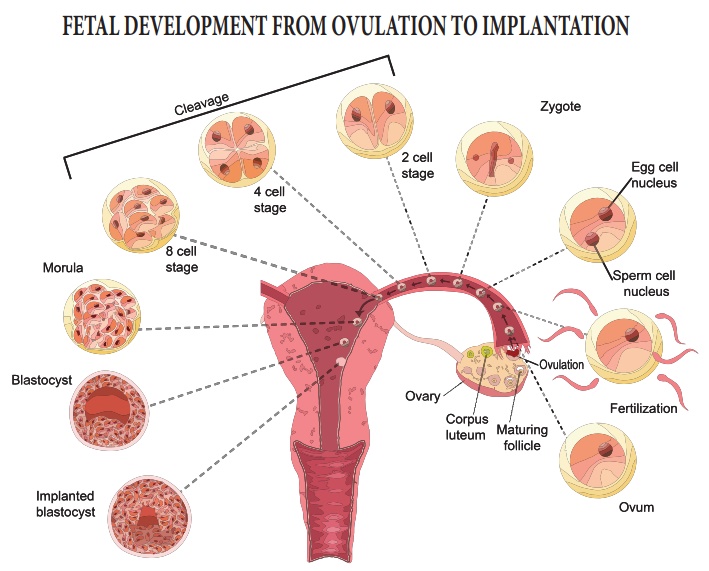
Sex determination
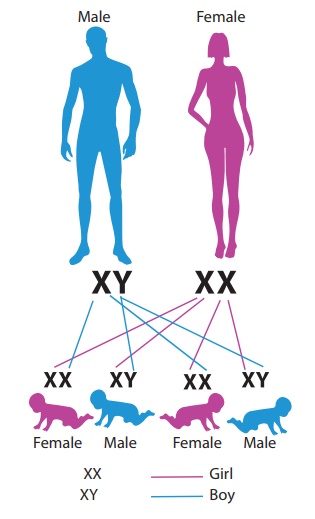
Stages of Clevation
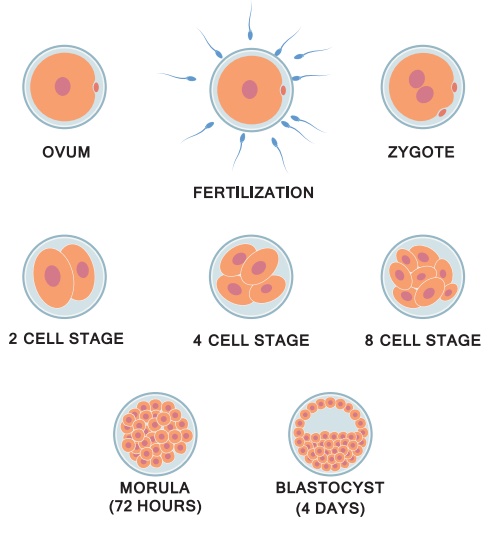
Structure of Blastocyst
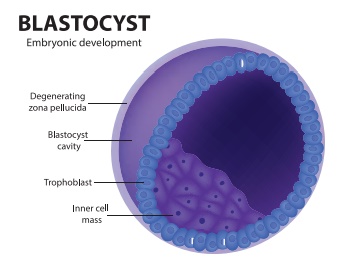
•
After fertilization cleavage of zygote takes place. It consists of
repeated mitotic divisions of the zygot which results in rapid increase in the
number of the cells. These smaller embryonic cells are called blastomeres. This
normally occurs in the uterine tube.
•
The embryo with 8 to 16 blastomeres is called a morula. The
Morula reaches the uterine cavity at this stage. Spherical Morula is formed
about 3 days after fertilization.
•
The morula divides further as it moves further into the uterus
and transforms into blastocyst.
•
The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into an outer
layer called trophoblast and inner mass of cells attached to trophoblast is
called as inner cell mass.
•
By 7th day, Trophoblast differentiated into 2 layers:
Cytotrophoblast, inner layer, mononucleated mitotically active cells.
Syncytiotrophoblast (outer multinucleated mass, with indistinct cell boundary).
•
By 8th day the blastocyst is superficially embedded in the compact
layer of the endometrium.
•
By the 10th day the blastocyst is completely buried in the uterine
lining, known as “Implantation” or “embedding" “some
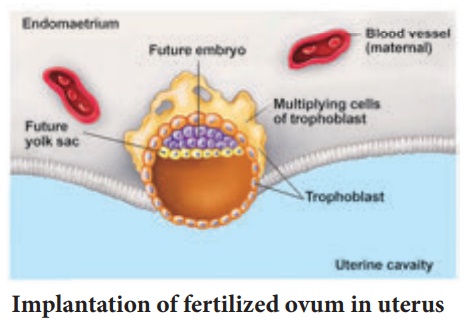
Implantation of fertilized ovum in uterus
•
The implantation of the fertilized ovum of embedding is known as
“Nidation or Nesting".
•
Uteroplacental circulation is established by 11th or 12th day.
implantation is completed by the 11th or 12th day. Implantation it can be
detected by:
•
Ultrasonography.
•
HCG (human chorionic gonadotrophin which is secreted by the syncytiotrophoblast) at
about the end of 2nd week
•
By the 13th day Proliferation of Cytotrophoblast cells produce extension inside
the Syncytiotrophoblast to form primary chorionic villi.
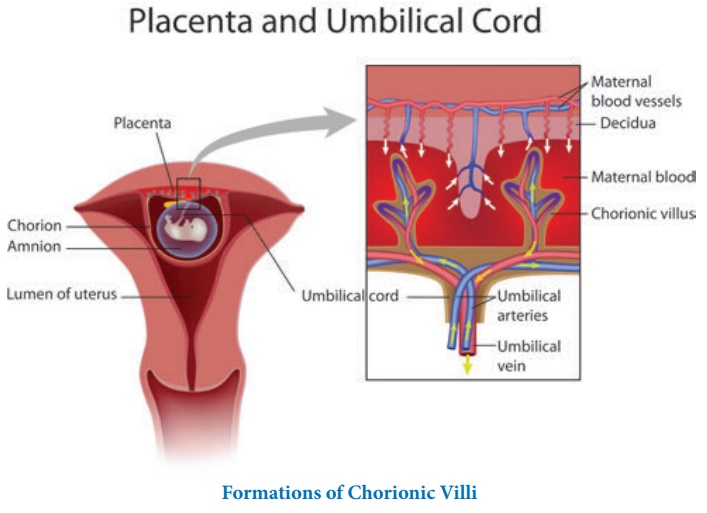
•
The chorionic villi and uterine tissue together form a structural and functional
organic structure between developing embryo and tissues of the mother called as
placenta.
•
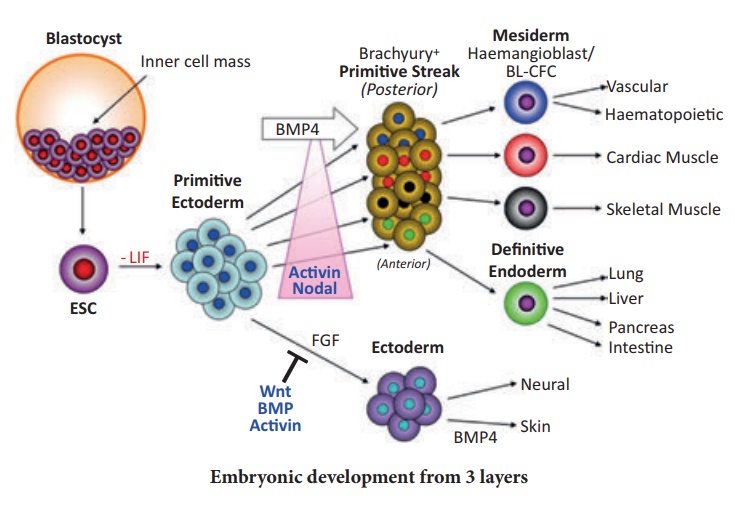
After implantation, the inner
cell mass is differentiated into
outer layer called
ectoderm and an inner
layer called endoderm with a
middlelayer is mesoderm Three layers give rise
to all organs in adults. As shown in the picture above the cells are res ponsible for those
organs.
•
If the implantation occur outside it is called as Ectopic pregnancy. 95
to 97% of ectopic pregnancies occurs in the uterine tube. Most are in the
ampulla & isthmus. ( see the figure for types of ectopic pregnancy)
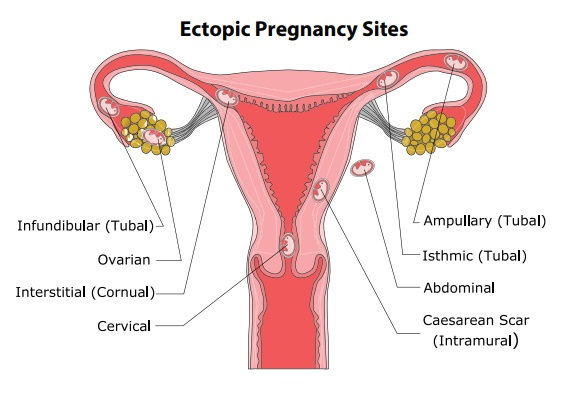
•
Placenta previa: placenta attach to the lower uterine segment.
2 .Embryonic period (3-8 weeks )
3rd week
Heart Tube fuses
Cardiac muscle
contraction begins
Eye & ear cells are
present
Neural tube starts
closing
4th week
Optic vesicle appears,
two pharyngeal arches appear.
A primitive S-shaped
tubal heart is beating and peristalsis.
The rhythmic flow
propelling fluids throughout the body begins at this stage,
The neural tube
determines the form of the embryo.
5th Week
Valve & septa appear
in the heart.
The digestive epithelium
layer begins to differentiate into the future locations of the liver, lung,
stomach and pancreas.
Liver cells form in the
digestive system.
Forebrain, midbrain and
hindbrain forms.
Lymphatic & thyroid
start to develop.
Limb buds.
First thin layer of
skin.
The baby yawns.
6th Week
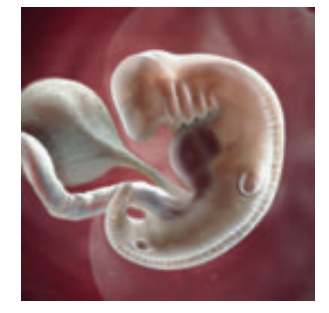
Further development of
nervous system, heart.
Innervation, the
distribution of nerves, begins in the lower limb buds.
7th Week
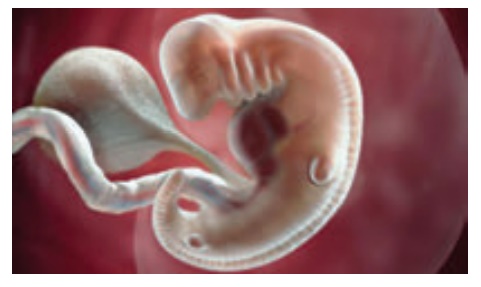
A four chambered heart
and a sense of smell.
Primitive germ cells
arrive at the genital area and will respond to genetic instructions to develop into either
female or male genitals.
8th Week
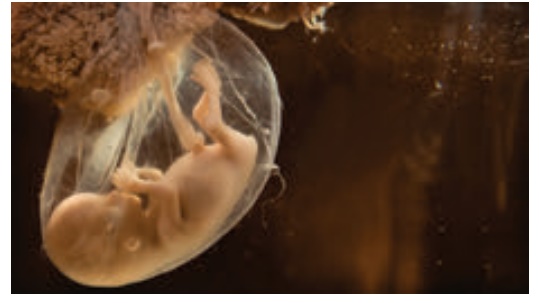
Spontaneous Involuntary
Movement.
Brain is connected to
tiny muscles and nerves and enables the embryo to make spontaneous movements.
Testes or ovaries are
distinguishable.
3. Fetal Period (9th week to birth of the baby) 9-12 Weeks
9-12 Weeks
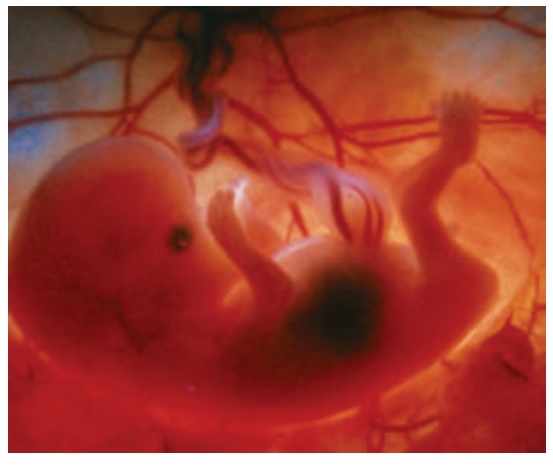
•
Brain continues to develop, liver enlarges, blood cell formation
begins.
•
Sex can be determined by genitals.
•
10th week.
•
The fetus passes urine.
•
The Fetal Heart Rate can be heared by Doppler.
13-16 Weeks (Month 4)
•
Sucking starts
•
Hard palate is fused
•
Kidney structure developed
•
Bones are distinct joint cavities are apparent
•
Meconium is present in gut
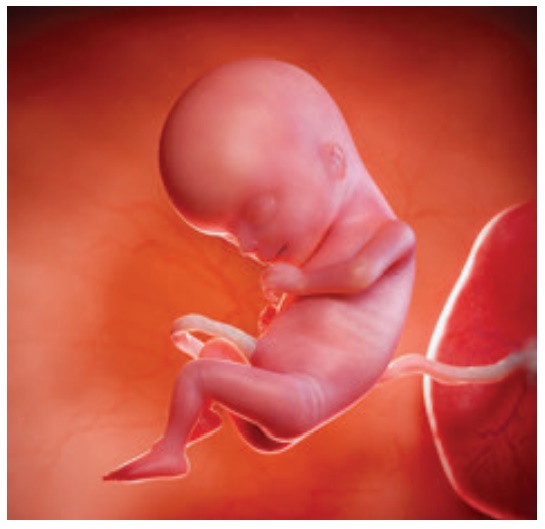
17-20 weeks (Month 5)
•
Eyeballs and eyebrows present.
•
Lanugo( Silk like hair)present.
•
Quickening occurs (first fetal movement).
•
Approximate crown rump length at the end of 20 weeks is 19 cm.
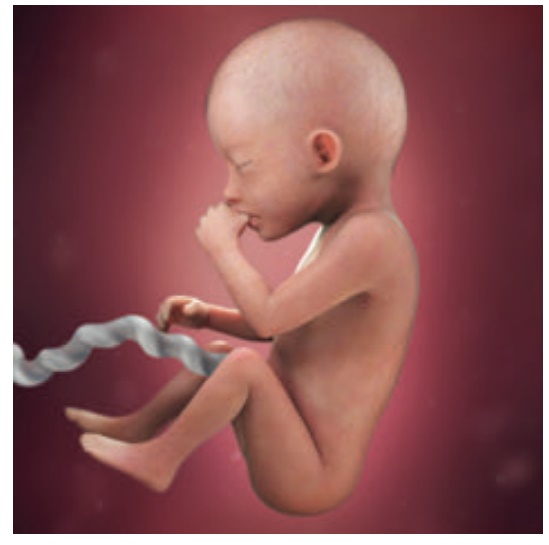
21-30 weeks
•
Eyes are opened.
•
Finger and toe nails are complete.
•
Skin is wrinkled and red. Fatty layer under the skin is formed.
•
lanugo prominent.
•
Testes descent in the scrotum for male babies.
•
Approximate crown rump length at the end of 30 weeks is 28 cm.
•
Vernix ( white creamy substance) present.
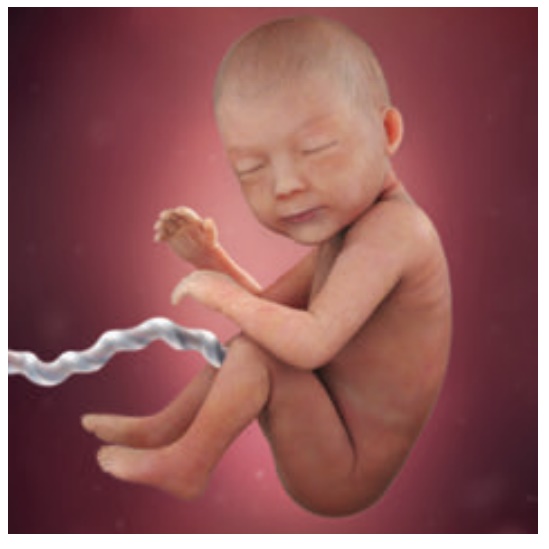
30-38 weeks
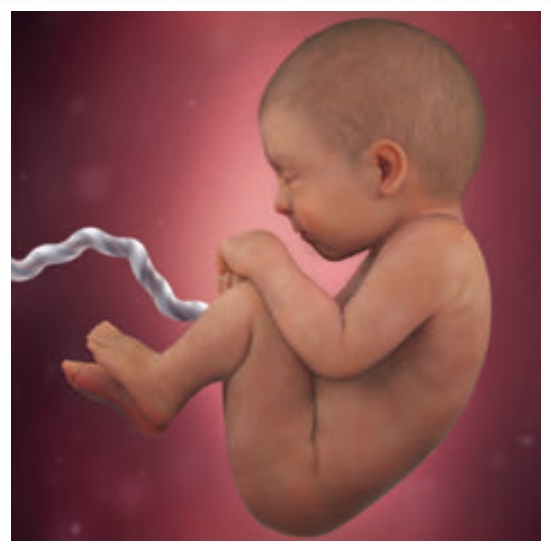
•
Constant weight gain.
•
Lanugo disappears from face.
•
Fat accumulates under
the skin
•
(hypodermis).
•
Plantar creases visible.
•
Ear cartilage soft.
•
Approximate crown rump length at the end of 38 weeks is 36 cm.
•
At birth, weight - 2.5-3.5 kg.
Related Topics