Maternal Health Nursing - Family Planning Methods | 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Maternal Health Nursing
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Maternal Health Nursing
Family Planning Methods
FAMILY
PLANNING METHODS
“DELAY THE FIRST,
POSTPONE THE SECOND AND PREVENT THE THIRD”
Definition
An Expert committee
(1971) of the WHO defined family planning as: “A way of thinking and living
that is adopted voluntarily upon the basic of knowledge, attitudes and responsible
decision by individuals and couples, in-order to promote the health and welfare
of the family and thus contributes effectively to the social development of the
country”.
Natural Methods
·
Abstinence
·
Coitus interruptus or withdrawal method
·
Lactational amenorrhea
Biological Methods
•
Calender (rhythm) method
•
Basal body temperature method
•
Cervical mucus method (billings method)
Chemical Method
•
Foams
•
Creams, jellies and pastes
•
Soluble films
I. Mechanical Family Planning Method
·
Male condoms
·
Female condoms
·
Diaphragms
·
Cervical cap
·
Intrauterine devices (IUD)
·
Sponge
Hormonal Contraceptive Method
Contraceptive skin patch
·
Vaginal ring
·
Pills (Combined and Minipill)
·
Injection
·
Implant
·
Emergency Pill
·
Intrauterine device
COPPER T:
Copper T is a small
T-shaped, barium-sulphate incorporated, polythene device that is placed inside
uterus to obtain birth control. The placement is done with a plastic syringe
called the IUD inserter.
A fine copper wire
weighing 120 mg, with a surface area of 208 mm2, is wound round the
upright limb of T. Two fine filaments are attached to the lower tip of the
vertical limb. Copper T along with its inserter is supplied in a pre-sterilized
packet. Copper T is inserted on the 6th day following the menstrual period. The
ideal time for postpartum insertion of Copper T is immediately after delivery
.Copper T is introduced 12 weeks after abortion, a doctor or a trained
paramedical person carries out the insertion.
Types of IUDS
There are two types of
IUDs:
• Nonmedicated Intrauterine Devices • Medicated intrauterine devices
Nonmedicated
intrauterine devices or first generation IUDs
These are made out of
polyethylene or other polymers they actually entered market in different shapes
and sizes they are Loops, Spirals, Coils, Rings, Bows. The lippes loop is the
popularly known and commonly used device in the developing countries.
Medicated IUDs
The copper IUDs are
named as second generation IUDs there are several forms of copper devices
available now
Newer Devices
·
Variants of the T device
·
Cu-T-220C
·
Cu-T-380 A or Ag
·
Nova T
·
Multiload devices ML-Cu-250, ML- Cu -375
Advantages of Intra
Uterine Devices (IUDs)
·
This is the most cost-effective method
·
Easy to use
·
There is no interruption of intercourse
·
It can be removed immediately incase of any problems or not
required
·
Fertility returns with the first ovulation cycle following IUD
removal
Disadvantages
•
IUDs do not protect against STDs
•
Needs clinician for insertion and removal
•
It may lead to side effect in some women
II. Permanent Methods of Family Planning
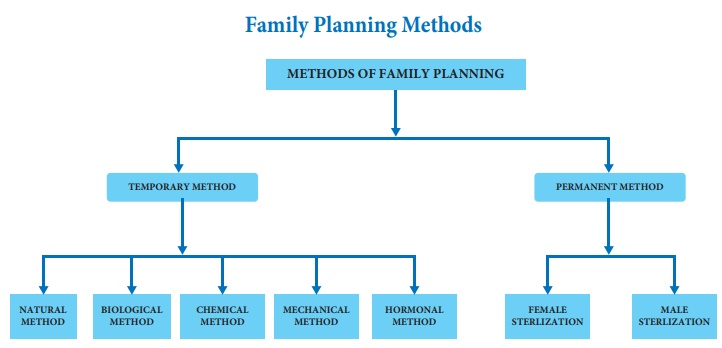
a. Female Sterilization
Laparoscopic
Sterilization
Female sterilization is
performed through abdomen using a laparoscope, the laparoscopic tubal ligation
is a surgical sterilization method in which female's fallopian tubes are
clamped or cut.
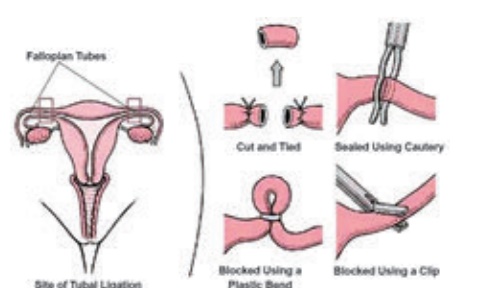
Mini-lap (Mini
Laparotomy) Operation
A small abdominal
incision measuring 2.5-3 cm is performed under local anaesthesia through the
small incision, by following the fundus of the uterus fallopian tubes are
reached and hooked up, knots are applied in two places this procedure is
repeated for both the tubes.
Advantages
·
It is a permanent method to prevent unintended pregnancies
·
It is effective immediately
·
Does not need any daily attention
·
Cost-effective in the long term
·
Does not affect sexual pleasure
Disadvantages
·
Need to face surgery and its consequences
·
More complicated than male sterilization
·
Does not protect against sexually-transmitted infections
·
Lifting heavy weights not permitted for at least 6 months to avoid
the occurrence of incisional hernia
b. Male Sterilization
Vasectomy is a surgical
procedure for permanent male sterilization. During the procedure the male vas
deference are cut and then tied or sealed in a way to prevent sperm from
entering into the seminal stream and thereby prevent fertilization.
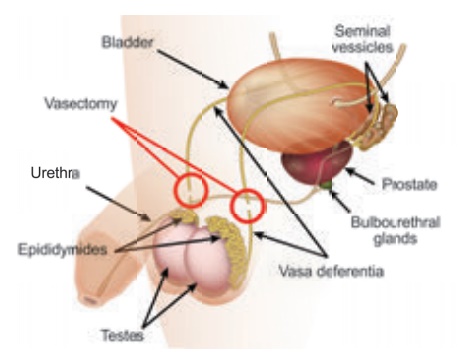
Advantages
·
Permanent method of contraceptive
·
Highly effective method
·
Very safe surgical procedure
Disadvantages
·
Usually irreversible
·
It does not provide protection against sexually transmitted
disease and infections including HIV
·
Need skilled medical personnel to perform the procedure
National Family
Welfare Services
The national family
welfare services includes primary, secondary, and tertiary care. The care is
provided at different levels including District, Taluk, PHC, and PHU level.
Family Welfare Schemes
·
National family welfare programme
·
National population policy
·
National Rural health mission
·
Urban family welfare schemes
·
sterilization schemes
·
Child survival and safe mother hood programmes
·
Reproductive and child health programmes
·
Implementation machinery
·
Social marketing of contraceptives
·
Medical termination of pregnancy
·
Prevention of prenatal sex determination
Benefits for the
Pregnant Women Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act 2017
The maternity benefit
amendment act has increased the duration paid maternity leave available for
women employees from the existing 12 weeks to 36 weeks.
Modi Government
Maternity Benefits
Pregnant women and
lactating mothers will receive `6000,
`5000 of which will be
given in three instalments, provided that certain conditions related to
completion of registration of pregnancy and birth, antenatal care and
immunisation are met. The scheme is also restricted to the first live birth.
Janani Suraksha Yojana
The aim of JSY Scheme is
to encourage poor pregnant women to give birth in registered health
institutions. Mothers receive `1600
when they arrive and register at the health institution to give birth. The ASHA
receives `600 when accompanying a
women to a health institution for delivery.
Dr. Muthulakshmi Reddy
Maternity Benefit
Dr. Muthulakshmi Reddy
Maternity benefit scheme fund is enhanced with `12000. the cash assistance will be given in
three instalment. `4000
who avails all required antenatal services during pregnancy in PHC, `4000 is given to the
mothers who deliver in the government institution, `4000 at the completion
of immunization for the child upto three doses.
Dikri Yojana
Financial assistance for
those families without male child and those adopted permanent family planning
measures with one or two female children.
Varumun Kappom Scheme
The aim of the scheme is
to reduce maternal mortality and morbidity of the pregnant and expected mothers
and utilising the vast resources of health care providers with the involvement
of federation of obstetrics and gynaecological society of India.
BPL Desi Ghee Scheme
Below poverty line
pregnant women in Rajasthan are entitled to receive five litres of desi ghee
after their first institutional delivery. Three litres to be given after the
first ANC test (between 4 to 6 month of pregnancy) and the other two litres at
the time of discharge after the delivery.
Kalewa Yojna (KY)
Kalewayojna is funded by
NHRM and implemented by DWCD where in free warm and nutritious food is provided
for two days to women who have delivered in health facility especially at
Community health centre level. This food is cooked by self-help groups.
Janani Express Yojana
Providing benefit of
transportation to expectant mothers for institutional deliveries to deal with
emergency circumstances during the pre and post delivery period.
Related Topics