Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Maternal Health Nursing
Fetal Circulation
FETAL CIRCULATION
Definition: The circulation Of oxygenated blood, de-oxygenated blood, nutritive material
etc, in the foetus is termed as foetal circulation. The blood vessels responsible for foetal circulation are
1. One Umblical Vein: It carries the oxygenated blood from the
placenta to the growing fetus.
2. Two Umblical Arteries: Both arteries carries all the de-oxygenated
blood out of the fetus and carries de-oxygenated blood from the fetus to the
placenta.
The shunts involved in foetal circulation
There are three shunts present in a fetus, they are:
1.Ductus Venosus: The Ductus Venosus shunts
the portion of left umblical vein blood flow directly to the inferior vena cava
2.Ductus Arteriosus: It
allows most of the blood from the right-ventricle to bypass the
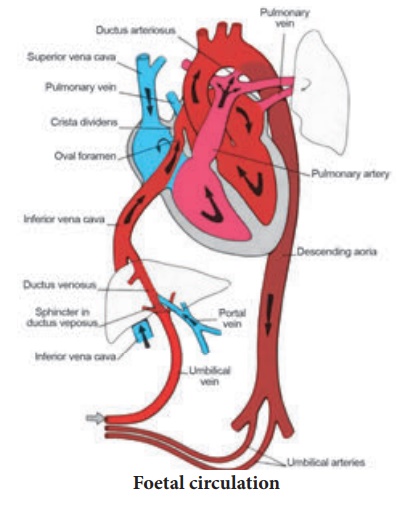
3. Foramen Ovale:
It allows the blood to enter
the left atrium from the
right atrium It is an opening in the intra-atrial septum.
Step 1: The placenta accepts
the blood without oxygen from the fetus through blood vessels that leave the
fetus through the Umbilical Cord (Umblical Arteries).
Step 2: When blood
goes through the placenta it picks up oxygen
Step 3: The oxygenated
blood then returns to the fetus via the umbilical cord (umbilical vein). Step 4: The oxygenated blood that enters
the fetus passes through the fetal liver and enters the right atrium of the
heart.
Step 5: Foramen Ovale
allows the oxygenated blood to go from the right atrium to left atrium and then
to the left ventricle and out the aorta. As a result the blood with the more
oxygen gets in to the brain.
Step 6: Blood coming
back from the fetus’s body also enters the right atrium, but the fetus is able
to send this deoxygenated blood from the right atrium to the right ventricle
(the chamber that normally pumps blood to the lungs). Most of the blood that
leaves the right ventricle in the fetus bypasses the lungs through the ductus
arteriosus.
Step 7: The ductus
arteriosus sends the deoxygenated blood to the organs in the lower half of the
fetal body. This also allows for the deoxygenated blood to leave the fetus
through the umbilical arteries and get back to the placenta to pick up oxygen.
The Circulatory Changes After Birth:
The Placenta is replaced
by the Lungs as the organ of respiratory exchange.
The lungs and pulmonary
vessels expand thereby significantly lowering the resistance to blood flow.
Subsequently the pressure in the pulmonary artery and the right side of the
heart is decreased.
The pressure of the left
side of the heart increases.
The increasing pressure
of blood in the left side of the heart decreases the vascular resistance of the
lungs, therefore, the blood now enters the lungs for a respiratory exchange.
Closure of the Ductus Venosus – functional closure occurs within
few minutes of birth and becomes as ligamentum venosum.
Closure of ductus
arteriosus – is by smooth muscle contraction and it is further replaced by
fibrous tissue, called ligamentum arteriosum.
Closure of the Foramen
Ovale – closes at birth due to decreased
flow from placenta and Inferior Vena Cava to hold open foramen. It become as
fossa ovalis
Related Topics