Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Poisonous Organisms : Physalia, Scorpion, Centipede, Honey bees and Wasps, Poisonous fishes, Poisonous snakes
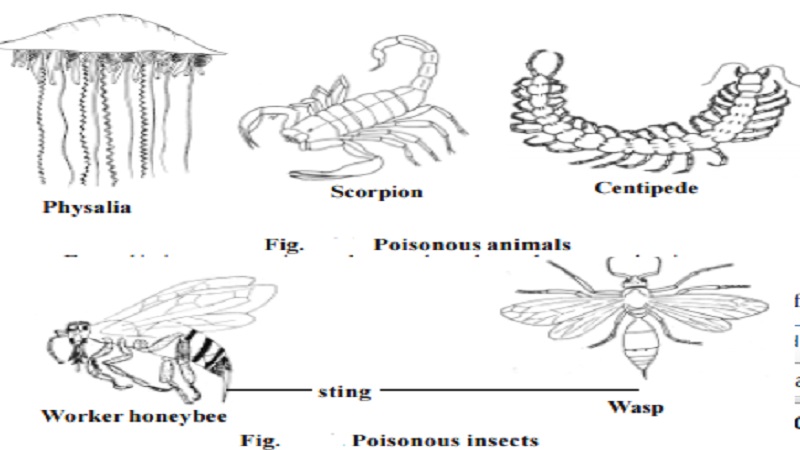
Poisonous Organisms : Physalia, Scorpion,
Centipede, Honey bees and Wasps, Poisonous fishes, Poisonous snakes
Poisonous Organisms
Free living organisms have developed some device to protect
themselves against predators. These protective devices ranges from the simple
stinging cells of Physalia to the massive poison glands of the snakes. The list
of poisonous organisms is exhaustive. A few of the important poisonous
organisms are mentioned here.
Physalia
These are marine
coelenterates. They are notorious for the painful sting they can inflict on
unsuspecting swimmers who accidently brush against them. They attack using
stinging cells on their trailing tentacles. Their powerful stings cause painful
local inflammation and can even be fatal.
Scorpion.
In scorpion the sting
is attached to the posterior part of the last segment. It consists of bulbous
base and a sharp curved barb that injects the venom. The venom is produced by a
pair of oval glands. The scorpion raises the posterior abdomen over the body
making it curved forward. A stabbing motion is used in stinging.
The venom of most
scorpions is sufficiently toxic to kill a vertibrate. The venom of the
scorpion Androctonus is equivalent in toxicity to cobra
venom.
The neurotoxic venom
of scorpions is very painful and may cause paralysis of the respiratory muscles
or cardiac failure in fatal cases. Anti venoms are available for these species.
Centipede :
Centipedes are
distributed throughout the world. They live in soil and humus and beneath stones.
The largest centipede is the tropical AmericanScolopendra
gigantea which may reach 26 cm in length. They have a large pair
of poison claws sometimes called maxillipeds. Each claw bears a terminal
pointed fang. The venom although painful is not sufficiently toxic to be lethal
to man even to small children. However S. gigantea has
been known to cause human death.
Honey bees and Wasps :
In worker
honey bee (undeveloped females) the poisonous sting is situated at the
hind end of the body. It is a pointed structure provided with minute hooks or
barbs at its free end. On stinging the tip of sting gets detached. Hence a bee
can sting only once.
Unlike the bee the wasp is
able to withdraw its sting from the wound. Hence it can sting again. In wasp
the sting is a modified ovipositor and once it has penetrated the skin of the
victim poison is injected as in a hypodermic syringe. The wasp's poison is
a histamine.
The
sting by honey bees and wasps lead to pain and inflammation.
Poisonous fishes
More than 700 species of fishes have poison glands. Venom in fishes is of two kinds. One kind of venom is produced by specialized glands which may occur in various parts of the body. In the second, the flesh itself may secrete some toxic substance and the fish becomes poisonous and inedible.
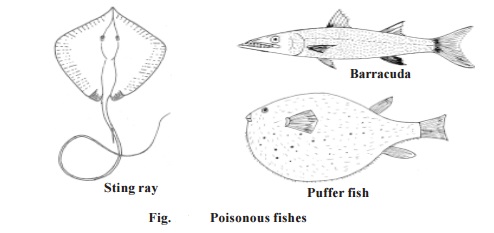
There are several
poisonous cartilaginous fishes. The poison glands are usually
associated with a spine or sting as in the case of sting ray. In
the sting ray(Trygon), the poison glands lie along a lateral groove on
each side of the spine on its tail. The spine causes pain and numbness in the
flesh of victim.
The large Barracuda of
Cuba and other tropical islands have poisonous flesh, which when eaten cause
pain in joints and extremities, nausea, vomiting and general trembling.
The Puffer
fish, (Tetrodon) is considered to be world's most dangerous
fish. Its ovaries, intestine, kidneys, skin and eyes contain a neurotoxin
calledTetradoxin. This toxin has no antidote. It is several times
deadlier than cyanide. In a dilute form, tetradoxin is used as a pain killer
for victims of neuralgia, arthritis and rheumatism
Poisonous snakes
Indian poisonous
snakes are the cobras, the kraits, the vipers and
the sea snakes. These can be distinguisted from the non poisonous
by the tail, the arrangement and size of scales, plates and shields found over
the body.
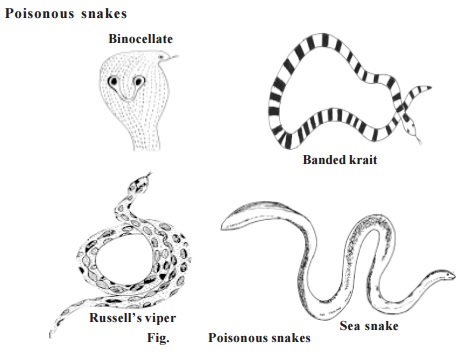
Cobra : It is well known all over India. When provoked it raises its head and expand the skin of the neck region in the form of a characteristic hood. The hood may bear a spectacle mark. Such cobras are called two ringed or spectacled forms. In others there is a oval spot surrounded by an ellipse. These are known as the one ringed or monocled variety. They are found in Bengal. In still others there is no mark on the hood. Only two species of cobra are found in India. They are Naja naja (Indian cobra) and Ophiophagus hannah (king cobra).
Krait : These are common
poisonous snakes of India. There are two com-mon Indian kraits. They are the
common krait (Bungarus coeruleus) and the banded krait (B.
fasciatus).
Vipers : There are two
classes of vipers. Some have a distinct pit on the sides of the
head between the nostril and the eye in the region called 'lore'. These are
called pit vipers. The other one is the pitless viper.Vipers
are vivipa-rous in nature.
The vipers have movable upper jaw, so that the fangs when not in
use can be folded backwards. It gets erected with the opening of the mouth
while inflict-ing injury. It produces a loud hissing sound by expelling air
through nostrils.
Pitless Viper - Vipera russellir (Russell's
viper) Echis carinata (The little Indian viper).
Pit viper - Trimeresurus sp
Sea Snakes : Sea
snakes can always be distinguished from other snakes by their
laterally compressed tails. This is an adaptation to their life in the sea. All
sea snakes are highly poisonous.
Eg. Hydrophis sp Enhydrina sp
Poison Apparatus of a Snake
The poisonous snake
possesses a poison apparatus comprising of a pair of poison glands, a pair of
poison ducts and a pair of fangs. The poison glands are situated on either side
of the upper jaw below and behind eyes. They are specialized salivary glands. A
duct carries the venom secreted from each gland to the fang. A fang is meant
for injecting the venom into the body of the prey. Fangs are specialized teeth
of the upper jaw which are tubular or grooved.
Biting mechanism in Cobra
Cobra is not an aggressive snake. When disturbed, it attempts to
escape. When the snake attacks, the mouth opens by lowering the lower jaw. This
makes the fangs to be erect to penetrate the muscles of the victim. When the
mouth is closed the poison glands are pressed. The venom thus reaches the fangs
and is injected into the body of the victim. This whole process takes place in
no time.
Snake Venom
There are two types of snake venoms. One type acts mainly on the
nervous system (neurotoxic). It affects the optic nerves (causing
blindness) or the phrenic nerve of the diaphragm (causing paralysis of
respiration). The other type is haemolytic. It breaks down
the red blood corpuscles and blood vessels and produces extensive extravasation
of blood into the tissue spaces.
Harmful Animals
The harmful animals are those that cause injury to plants and
domes-tic animals. Human beings are affected directly or through bites or
stings or by transmission of various kinds of pathogens. The nature of harmful
insects ranges from simple nuisance value of cockroaches to spreading of
epidemic diseases, such as malaria, filariasis by mosquitos. For the
convenience of our study the harmful animals are grouped under the following
categories namely disease causing organisms, poisonous animals, fouling organisms
and pests.
ECONOMIC ZOOLOGY
Since time immemorial, human beings have used animals for food
and other purposes. While some animals are very useful to mankind certain
others cause loss to the economy of man. Though every organisms has its own
im-portance in nature, some of them such as a few mammals, birds, fishes,
prawns and insects have become valuable. Some pests are competitors of human
be-ings for natural resources and food. Thus a study of economically important
animals will always be useful.
Related Topics