Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Earthworm : External features , External apertures
Earthworm
Phylum - Annelida
Class - Chaetopoda
Order - Oligochaeta
Type - Lampito mauritii
Earthworms are nocturnal animals. They lie in the burrows during the day and come out at night for food. Earthworms leave the burrow only during the rainy season when their burrows are flooded with water.
External features
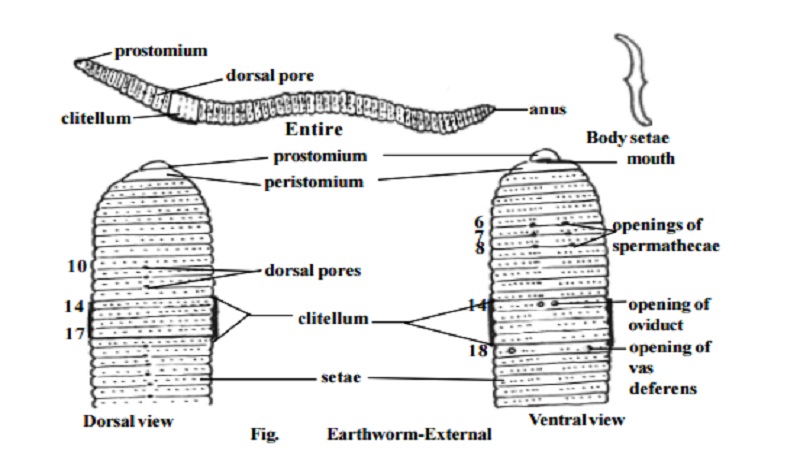
Lampito (Megascolex) mauritii is a common earthworm found in South India. The body is long, slender, cylindical and bliaterally symmetrical. It is about 8 to 21 cm long and 3 to 4 mm in thickness. The dorsal surface is dark purplish brown, and the ventral surface is paler in colour. It is marked by a series of segments. The segments are separated from one another by inter-segmental grooves. The division is both external and internal. Inside the body, each cavity of the segment is separated from the next, by a thin partition called the septum. All the segments look alike. This kind of repetitive ar-rangement of the segments is called metamerism.
The mouth is found in the centre of the first segment of the body, called the peristomium. Overhanging the mouth is a small flap called theupperlip or prostomium. The last segment has the anus. It is called the pygidium. In mature worms, segments 14 to 17 may be found swollen with aglandular thickening of the skin called clitellum.
Body setae
Tiny curved bristles called setae are found embedded in small pits of the body wall. These pits are called the setigerous pits. The setae are arranged around the body. They are made of chitin and have a swollen middle part and pointed curved ends. The setae resemble the mathematical symbol ' ![]() '. They can be moved in any direction and extended or withdrawn by the action of muscles. They are used for locomotion.
'. They can be moved in any direction and extended or withdrawn by the action of muscles. They are used for locomotion.
External apertures :
(i). Dorsal pores : These are minute openings situated in the mid dorsal line in the intersegmental grooves commencing from the 10th segment. The co-elom communicates to the exterior through these pores and keep the body surface moist and free from harmful micro organisms.
(ii). Spermathecal openings : Three pairs of openings are situated ventrolat-erally in the intersegmental grooves between segments six and seven, seven and eight and eight and nine. These opening can be easily seen in mature worms.
(iii). Openings of oviduct : These are a pair of apertures lying close together on the ventral surface of the 14th segment.
(iv). Openings of Spermiduct : A pair of apertures are situated on the lowerside of the 18th segment.
(v). Nephridiopores : Numerous minute openings scattered on the body wall from 14th segment onwards.
Related Topics