Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Monotremata, Marsupialia and Placentalia -Classification of Class : Mammalia - Reptilia - sub phylum - Tetrapoda
Monotremata, Marsupialia and Placentalia -Classification of Class : Mammalia - Reptilia - sub phylum - Tetrapoda
Tetrapoda
The vertebrates with two pairs of limbs adapted for locomotion on land are known as tetrapods. The limbs are of pentadactyl type. The tetra-pods are identified by a cornified outer layer of skin and nasal passages communicating with mouth cavity and lungs. The super class Tetrapoda is divided into four classes namely. Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves and Mammalia.
Amniota
The tetrapods like reptiles, birds and mammals are referred to as amniotes. The amniotes have certain membranes associated with embryos inside the egg. It is an adaptation in terrestrial forms during development. These membranes are the amnion, chorion and allantois.
Class : Mammalia
The term 'mammalia' was given by Linnaeus (1758) to that group of animals which are nourished by milk from the breasts of the mother. They are a successful group, for they adapt themselves readily to new situations and to new food habits.
The body is generally covered with epidermal hairs. The integument is provided with sweat, sebaceous and scent glands. The mammary glandsare modified integumentary glands. The external ear or the pinna is present in most of the mammals. A muscular diaphragm is present in between thoracic and abdominal cavities. It helps in respiration. The red blood corpuscles are non-nucleated, biconcave and usually circular in form. The heart is four cham-bered. Only the left aortic arch is present. In brain cerebral hemispheres are very large and highly convoluted.
Corpus callosum, a transverse band of nerve fibres connecting the two ce-rebral hemispheres, is present. Dentition is thecodont, heterodont and di-phyodont. Cloaca is absent. Testes lie outside the body cavity, enclosed in scrotal sacs. Eggs are small with little or no yolk. Fertilization is always inter-nal. Mammals are Viviparous ie., they give birth to alive young ones. Pla-centa is usually present.
The class Mammalia is subdivided into three subclasses namely
Monotremata, Marsupialia and Placentalia.
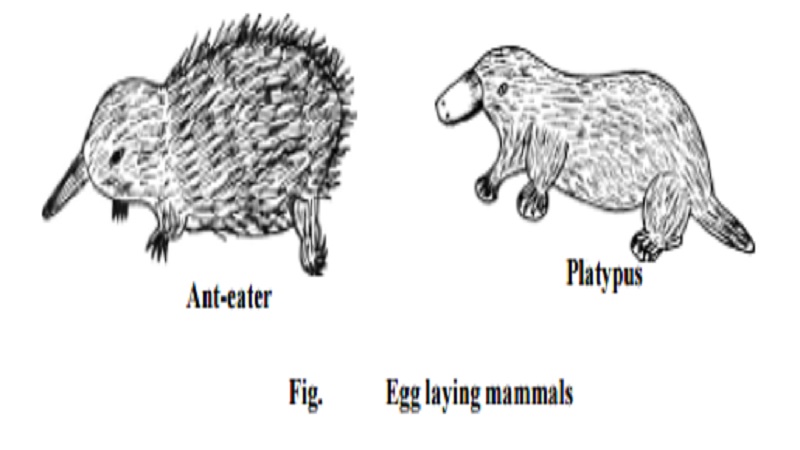
1. Sub class : Monotremata or Prototheria
These are primitive egg laying mammals Example : Spiny ant-eater, duck billed platypus.
2. Sub class : Marsupialia or Metatheria
These are popularly called as marsupials or pouched mammals. The young ones are born in an immature stage and migrate into the pouch on the mother's body. Further development is completed in the pouch or marsu-pium.
Example : Kangaroo
3. Sub class : Placentalia or Eutheria
In this group eggs develop within the uterus. The developing embryo receives nutrition through maternal blood circulation via the placenta.
Example : Elephant, tiger, lion, man, monkey, dog, cat , rat, bat.
Order Primates :
It is an order coming under the subclass Eutheria. This order is of interest because it includes man, besides lemurs, tarsiers, monkeys and apes. They inhabit chiefly the warmer parts of the world. This group stands first in the animal kingdom in brain development. However, most of them are unspecialized and tree dwelling (arboreal). Primates are omnivorous in habit. The body is covered with hairs except palm, sole and parts of face. The neck is mobile. The forelimbs are shorter than the hindlimb. The limbs have five digits and all the digits end in flat nail. The pollex or thumb or first toe are smaller than other digits and are opposable (except the hallux of man). The brain is highly developed. The cerebral hemispheres are much convoluted and cover the cerebellum. The eyes are directed forward and the vision is binocular and stereoscopic. Mammae are two and thoracic in position.
Related Topics