Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Classification of Phylum Chordata
Classification
of Phylum Chordata
In chordates, the food laden blood from the digestive tract
passes through the capillary net work in the liver, before reaching the heart.
Thus the veins originating from the digestive tract as capillaries and ending
in the liver again as capillaries constitute the hepatic portal system.
Classification.
The Phylum Chordata is
classified into four sub phyla:
Sub phylum 1. Hemichordata,
Sub phylum 2. Cephalochordata
Sub phylum 3. Urochordata
Sub phylum 4. Vertebrata.
First three sub phyla are collectively known as Protochordates.
Since the members of these sub phyla do not have a cranium or skull they are
also referred to as Acrania.
Protochordata (Acrania)
The protochoradates are considered as the fore runners of
vertebrata The classification of the protochordates is based on the nature of
the noto-chord.
Sub phylum : Hemichordata.
These are exclusively marine organisms. They are solitary or
colonial forms. They mostly remain as tubiculous forms. The body is soft,
vermiform, unsegmented,bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic. The body is
divisible into three distinct regions namely proboscis, collar and trunk. The
body wall is composed of single layer of epidermal cells. The dermis is absent.
They have no endoskeleton. A projection from pharynx, projecting inside the
proboscis may be considered as notochord. They have a spacious
coelom lined by coelomic epithelium. The alimentary canal is a straight tube
running between mouth and anus. They are ciliary feeders. Sexes are separate.
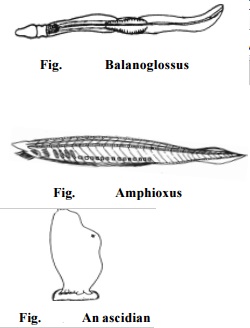
Examples : Balanoglossus, Saccoglossus.
Sub phylum : Cephalochordata.
Cephalochordates are small fish like marine chordates. The
persistent notochord extends forward beyond the brain. Hence these
are called cephalochordates. The epidermis is single layered.
Paired fins are absent. Muscles, nephridia and gonads are segmentally arranged.
The pharynx is large with numerous gills. It is a filter feeder.
Example : Amphioxus.
Sub phylum : Urochordata
This taxon constitutes a unique group of animals exhibiting
diversity in form and habit. In Urochordata the notochord is confined
to the tail re-gion of the larva. The adults are mostly degenerate,
sessile forms. The body is enveloped by a tunic or test. The free
end of the body bears two openings, the mouth and the atriopore. The proximal
part of the alimentary canal is greatly enlarged to form a spacious pharynx.
They are hermaphroditic ani-mals. The development occurs through free swimming
tadpole like larva.
Example : Ascidia, Doliolum, Salpa.
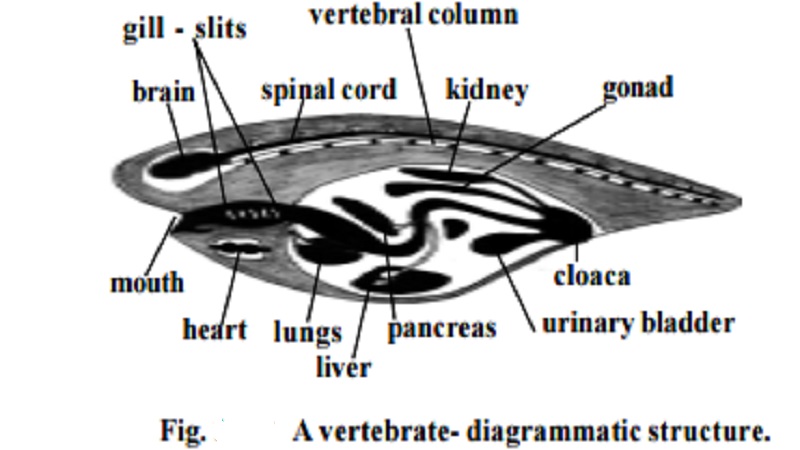
Sub phylum : Vertebrata (Craniata)
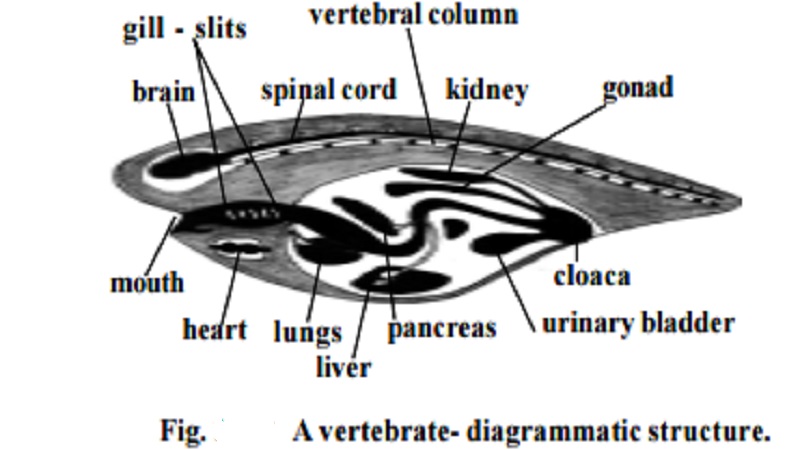
This group is characterized by the presence of brain
case or cranium and a vertebral column which
forms the chief skeletal axis of the body.
The notochord is an embryonic structure. It is replaced in the
adult stage by a cartilaginous or bony vertebral
column. The body is covered with an integument having an
outer epidermis and an inner dermis. The skin has
many modifications such as glands, scales, feathers, claws horns and hairs.
The digestive system is ventral to the vertebral column. It is
provided with a large liver and pancreas. The circulatory system consists of
the ven-tral, chamberd heart. The circulatory system is of a closed type with
arteries, veins and capillaries. The blood plasma contains red and white blood
cor-puscles. Gill slits are limited in number (usually 5 pairs). There are two
pairs of appendages. The anterior part of the nerve cord becomes differentiated
into brain and spinal cord. The special organs of sense like the nose, eyes and
ears are closely connected with the brain. Urinary and genital systems are
closely connected to form an urinogenital system.
Related Topics