Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Disease causing organisms - Vectors : Housefly - Musca domestica, Sand flies - Phlebotomus papatasi, Rat fleas - Xenopsylla cheopis, The human louse - Pediculus humanus, Mosquitoes : Anopheles, Culex, Aedes sp
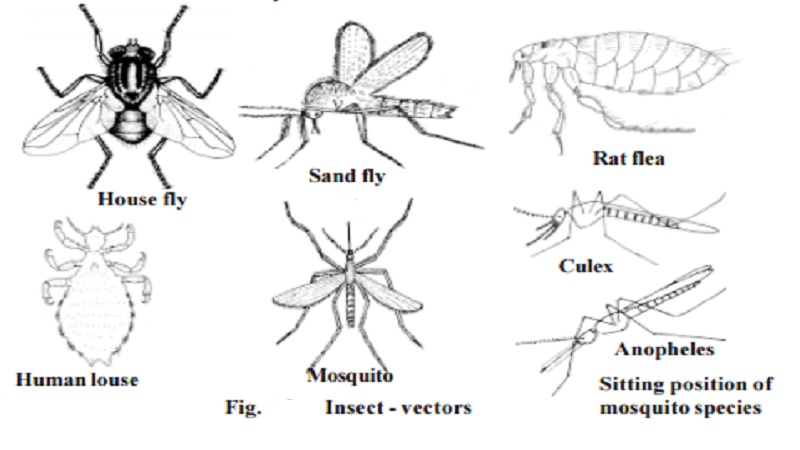
Disease causing organisms - Vectors : Housefly - Musca
domestica, Sand flies - Phlebotomus papatasi, Rat
fleas - Xenopsylla cheopis, The human louse - Pediculus
humanus, Mosquitoes : Anopheles, Culex, Aedes sp.
Disease causing organisms - Vectors :
Some
insects are injurious to man as vectors of human diseases. Through the ages
millions of people have died of dieases transmitted by insects. There are a
number of insect-borne diseases, and they may be transmitted in different ways.
1. Housefly - Musca domestica
House
flies are cosmopolitan in distribution. They are closely associ-ated with
humans and thrive best where people are careless in the disposal of wastes.
Adult flies are non-parastic.
They feed on all kinds of decaying and decomposing matter. It is an important mechanical vector in the transmission of diseases like typhoid (Salmonellatyphosa - a bactericum), dysentery (Entamoeba histolytica) and cholera (Vibrio sps.) The housefly cause diseases through food contaminations.
Control : Housefly control is normlly done in 3 different ways, namely sanitary, mechanical and chemical methods. Populations of houseflies can be controlled by proper disposal of manure, garbage, sewage, food waste, human excreta and other organic materials. Mechanical practices such as screening, using of traps or sticky paper or baits can be valuable in excluding houseflies. Insecticides may be used against larvae. Spraying with 2% malathion 1% chlordane or lindane, 0.5% tremephos are effective.
2. Sand flies - Phlebotomus papatasi
These
flies are 4 mm long. Only the female possess piercing-sucking mouth parts and
are haematophagous. The males are non parasitic, feeding on moisture. They are
small slender insects with hairy bodies. Through biting this fly transmits the
disease called kala-azar. The causative oraganisms isLeish-mania, a parasitic
protozoan. During the day time the flies remain hiding. At night
they come out to feed. The sand fly attacks during night times. The insect
sucks the parasite from an infected person, along with blood. In side the body
of the fly, the parasite undergoes changes. When an infected fly bites man, the
parasites pass into the blood and fresh infection is effected. The parasites
mostly concentrate in the capillaries of spleen, liver and bone mar-row. The
disease is characterized by the symptoms like anaemia and emacia-tion.
Control :
Spraying of 5 % DDT / BHC easily kills the flies. The pyrethrum
ointment used on exposed part of the body works as a repellent.
3. Rat fleas - Xenopsylla cheopis
The insect parasite, Xenopsylla cheopis is commonly known as the Asiatic rat flea. Both male and female fleas take in the bacillus pasteurella pestis from infected rats during feeding. This rat - flea is responsible for the transmission of plague from man to man, or from rat to man. When this bacterium is introduced into the skin, the lymph glands become inflammed. This is known as bubonic plague. Frequently, the bacilli become established in the victims blood. The condition is then referred to as septicemic plague. If the victim's lungs become involved, it is referred to as pneumonic Plague
When the rat flea sucks the blood of man or a rat infected with
plague, the bacilli enter into its stomach and grow there into large numbers.
The flea thus heavily laden with the bacilli, may bite a healthy man and
introduce the bacilli into the wound and cause infection. The bacilli are
deposited by the flea on the skin along with the faeces. The bite of the flea
causes scratchings and the bacilli are introduced into the blood when the skin
is scratched.
Control :
Destruction of rats and other rodents is an effective method.
Dusting of 1 to 2 % chloradane, or 2 % Y - BHC is very much effective in the
elimination of fleas on the body of pet animals. Application of 5% DDT is
recommended for spraying at the time of the spread of plague in all the areas.
4. The human louse - Pediculus humanus:
Louse is a blood sucking ectoparasite of man. It is cosmopolitan
in distribution .
The human louse is a major vector for three important human
dis-eases, relapsing fever, typhus and trench fever.
Disease
- Parasite
Relapsing
fever
- Borrelia sp
Typhus
- Rickettsia sp
Trench fever -
Rickettsia sp
Control : Wearing clean clothes, and having regular bath avoids infestation.
5. Mosquitoes : Anopheles, Culex, Aedes sp.
Mosquitoes are cosmopolitan in distribution. They are nocturnal
in habit and are found in abundance in damp, marshy lands near stagnant water.
Only female mosquitoes are adapted to suck the blood of human beings and
func-tion as carrier of viral, protozoan and nematode diseases.
Culex mosquitoes serve as the vectors for filariasis or elephantia-sis.
This disease is caused by the nematode parasite, Wuchereria
bancrofti. It is commonly known as filarial worm. It is
found in the lymphatic vessels and lymph glands of man. The female worms give
birth to living embryos known asmicrofilariae. The microfilariae
normally circulate at night(10 to 2 am) in the peripheral blood. At that time
they are ingested by the mosquito along with blood, the mosquito is not just a
mechanical carrier of the parasite. Developmental changes take place in the
body of the parasite. When the infected mosquito next bites another person, the
larvae penetrate the superficial skin to find their way into the lymphatic
vessels, and attain sexual maturity. In severe infection the adults cause
blocking of lymphatic system which results in the enlargement of legs, arms,
scrotum, and mammary glands. It is known aselephantiasis.
The
Anopheles mosquito transmits plasmodium, a causative protozoan for malaria
(Refer : Plasmodium)
Another type of
mosquito, Aedes transmits yellow fever through a
Harmful Animals
The
harmful animals are those that cause injury to plants and domes-tic animals.
Human beings are affected directly or through bites or stings or by
transmission of various kinds of pathogens. The nature of harmful insects
ranges from simple nuisance value of cockroaches to spreading of epidemic
diseases, such as malaria, filariasis by mosquitos. For the convenience of our
study the harmful animals are grouped under the following categories namely
disease causing organisms, poisonous animals, fouling organisms and pests.
ECONOMIC ZOOLOGY
Since
time immemorial, human beings have used animals for food and other purposes.
While some animals are very useful to mankind certain others cause loss to the
economy of man. Though every organisms has its own im-portance in nature, some
of them such as a few mammals, birds, fishes, prawns and insects have become
valuable. Some pests are competitors of human be-ings for natural resources and
food. Thus a study of economically important animals will always be useful.
Related Topics