Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Pigeon : Exoskeleton , Quill feather
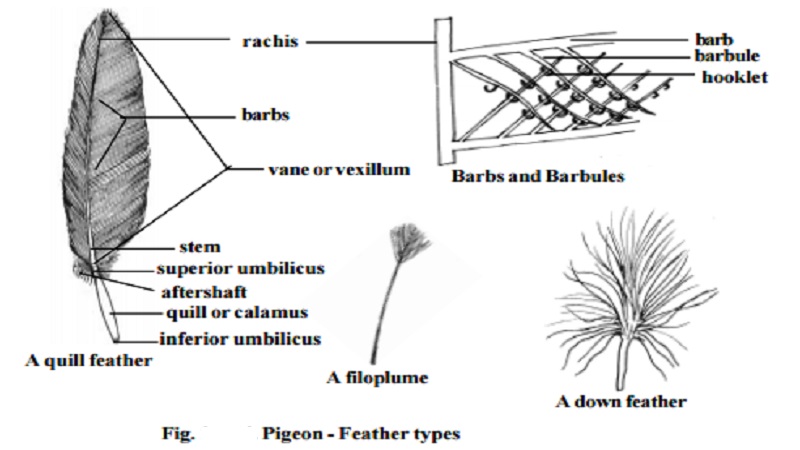
Pigeon - Exoskeleton : Quill feather
Pigeon
Sub phylum - Vertebrata
Class - Aves
Order - Columbiformes
Type - Columba livia
Birds are easily recongnised group of vertebrates. In birds every part of the body is modified to suit their aerial mode of life. Birds possess feathers, beak and feet modified in relation to their aerial life.
The Pigeons are flying birds(carinate). They are known both as wild and domesticated forms. The Pigeons are seen both in tropical and temperate zones. About 10 species of Pigeons are found in India. The pigeons fly in flocks and roost together. The domestic pigeons have many varieties, namely panter, fantail and tumblers. They differ in size, colouration and feather ar-rangement. All of them are, however, descendants of the rock pigeon-columba livia.
Exoskeleton :-
The feathers are integumentary structures. They are characteristic of birds. The feathers are derived from the epidermis. They are seasonally or periodically cast off and the new one being developed from the old papillae. They are arranged on the skin in definite tracts, called feather tracts or ptery-lae. The interspaces without feathers are known as apteria or featherless tracts.
There are three types of feathers in pigeon. They are the large quill feathers found on wings and tail for flight, the contour feathers, forming a covering for the body and the filoplumes, lying between the contour feath-ers.
Quill feather :
Each quill feather has a central stem or scapus. It is divided into lower hollow part called the quill or calamus and a solid upper part termed rachis. The quill has at its lower end an opening called inferior umbilicus, through which vascular processes or papilla of the dermis project into the growing feather. Another opening the Superior umbilicus occurs at the junc-tion of quill and the rachis on the inner face of feather. Close to this opening, there is a small tuft of soft feathers called aftershaft. Attached to the rachis are small filaments or barbs. The rachis with the barbs constitute the vane or vexillum. Each barb is provided with barbules and hooklets. The barbs remain attached with one another to form a continuous blade for striking the air in flight.
There are twenty three quill feathers or remiges in each wing. Eleven of these known as primaries. are attached to the hand. The remaining twelve fixed on the forearm are called secondaries. Attached to the thumb is a small tuft of feathers known as ala spuria or bastard wing. The tail bears twelvetail feathers or rectrices which are arranged in the form of a fan.
The contour feathers are soft and the barbs are plume like with no interlocking mechanisms. These help to keep the body warm and lock air pock-ets. The filoplumes have delictae hair like long axis and a few barbs devoid of barbules. Down feathers have small axis and a few barbs devoid of locking structures at the distal end. Nestlings are covered with down feathers.
Related Topics