Chapter: Mobile Networks : Pervasive Computing
Pervasive Computing Infrastructure
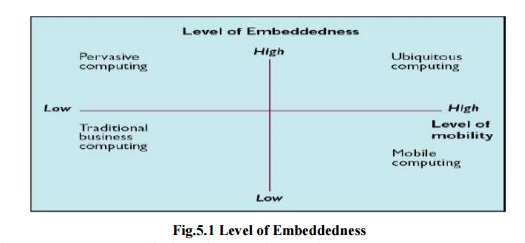
PERVASIVE COMPUTING
Introduction:
Our life
in the future should be very carefree with little to no hassle.
Less
searching, faster and accurate access to information, when needed.
Time and location boundaries will eventually be
eliminated, resulting in a true information age style of civilization.
Future devices will become more and more
intelligent; they will start to talk among themselves to serve us better.
PERVASIVE COMPUTING
INFRASTRUCTURE
The aim of ubiquitous computing is to design computing infrastructures in such a manner that they integrate seamlessly with the environment and become almost invisible. The essence of that vision was the creation of environments saturated with computing and communication capability, yet gracefully integrated with human users.
Pervasive – all around us
Should be there where we need them
Not go and get them
Human
Centred
Computers
should adapt to the humans
Computations
enter our world
Must be
unobtrusive and minimize user distraction
Computers as we know it will disappear
Better
ways of Computer-Human interaction
The computers need to be aware of humans – Context
Pervasive computing integrates computation into the
environment, rather than having computers which are distinct objects.
Other
terms for pervasive computing:
Ubiquitous
computing
Calm technology
Things that
think
Pervasive
internet
Ambient
intelligence
Proactive computing
Augmented reality
Sentient Computing
Urban Computing
Ubiquitous
Computing
3 Artificial
intelligence.
Ubiquitous
computing (ubicomp) integrates computation into the environment, rather than
having computers which are distinct objects.
Promoters of
this idea hope that embedding computation into the environment
Everyday
objects would enable people to interact with information-processing devices
more naturally and casually than they currently do, and in ways that suit
whatever location or context they find themselves in.
Ubiquitous
computing encompasses wide range of research topics, including distributed
computing,
Mobile
computing
Sensor
networks
Human-computer
interaction
Pervasive
– diffused among us
It will make information available everywhere
Ubiquitous
– State of being everywhere
The most important
characteristics of pervasive environments are:
Heterogeneity:
Computing
will be carried out on a wide spectrum of client devices, each with different configurations and functionalities.
Prevalence
of "Small" Devices: Many devices will be small, not
only in size but also in computing
power, memory size, etc.
Limited
Network Capabilities: Most of the devices would have some form of connection. However, even with the new
networking standards such as GPRS, Bluetooth, 802.11x, etc., the bandwidth is
still relatively limited compared to
wired network technologies. Besides, the connections
are usually unstable. High
Mobility: Users can carry devices from one place to another without
stopping
the services.
Related Topics