Chapter: Mobile Networks : Pervasive Computing
Device Connectivity
DEVICE CONNECTIVITY:
PROTOCOLS
1. Wireless Protocols:
Wireless protocols are enhanced mainly for PDAs and
Mobile phones. The protocols such as WAP, Bluetooth, IrDA, Object Exchange Protocol
(OBEX) and other mobile phone technologies are concentrated.
WAP/WML:
WAP is a
technology which mainly pronounces on rapid access to internet.
WAP works
for Ericsson, Nokia, Motorola.
Integrates
telephony services with browser technology.
WAP
application includes e-commerce, online banking and messaging.
WAP is
similar to HTTP and then optimized for narrow band channel.
WML is
used for textual format and WBXML is used for compressed binary format.
OBEX:
OBEX was
originally designed for IrDA later due to creation of Bluetooth it was emerged
as high level protocol.
OBEX
simplifies communication enabled
application by using push and
pull
commands.
Two models- The Session Model and The Object Model.
Session
Model: Constructs the dialog between two devices by packet based client/server
request/response model.
Object
Model: It contains information about the object being sent with header and
the
header has name, length, descriptive text and the object body.
Security
is provided using challenge response scheme.
Bluetooth:
It is a
short range communication and data exchange.
The
various characteristics are
Frequency
Band: operates at 2.45 GHz.
Security:
Authentication based on private key and encryption.
Transmitting
Capability: It is omnidirectional and range upto 10m.
Bandwidth:
Data Transfer Rate of 1 Mbps.
Speech:
Support digital speech channel.
Cost:
Reasonable Price.
IrDA:
Pervasive
Computing device are IrDA-Data and Infrared Mobile Communication
(IrMC).
Frequency
Band: It is a physical transport medium.
Security:
Higher level protocol service.
Transmitting Capabilities: Point-point connection with narrow angle between
sender
and receiver. Range of communication is about 0-30 cm.
Bandwidth:
Data rate-4 Mbps
Speech:
one digital speech channel.
Cost:
very cheap.
2. Mobile Phone Technologies:
Cellular system for mobile
communication:
Mobile environment is in need of electromagnetic
waves at frequency 1Ghz. Small antennas emit only limited power and thus mobile
and cellular environment is designed as such the transmitters are placed in
small grid like space where the frequency in one grid is reused in another grid
which is placed far away and thus reusability is enhanced.
The grid
is called as cell. Base station within the cell and the mobile station should
be connected with stronger signal.
3. Mobile Internet Protocol:
Once the
mobile connection is available, the next step is to access internet and thus in
mobile environment we are moving to IPv6 working on Mobile IP.
Standard internet protocol and mobile devices:
The
standard protocol used to access internet is IPv4 which provides with unique
address to nodes. Similar to postal addresses IP addressing is provided to each
node. The data will be in the form of packets and the packet contains source
address, source port, and destination address and destination port. Then in
order to reach the destination, it is traversed through intermediate nodes and
this is achieved by routing.
Steps to
have connection to a mobile node:
Discover
a care-of-address
Register
the care-of address
Tunnel
the care-of address
Changes
to Internet Protocol Version 6:
IPv6
includes the features of IPv4 but the significance is address configuration and
neighbour discovery. Ipv6 expects all nodes to implement strong encryption and
authentication features. Supports mobility at greater extent.
4. Synchronization and
replication Protocols:
Synchronization
also called as replication in concern with database. For instance, if the
calendar application is stored in the PC and PDAs. The updation in one device
related to the application should be reflected in the other device also.
Software updation also comes under the same category.
Steps in
Synchronization Protocol:
Presynchronization:
Before the actual synchronization authentication (authenticates client and
server), authorization (allowed to perform action) and determination of device
capabilities (maximum buffer size) should be done.
Synchronization: Data exchanged here, al; local Ids
are mapped with global Ids. Only updated entries are allowed to exchange. if
both the partners are updating the same entry then the conflict is resolved by
deleting the duplicate one.
SyncML
Scope of SyncML
XML based
framework for data synchronization Message oriented data exchange protocol
Transport agnostic Universal deployment
Extension
for device management
5. Distributed Services:
Jini:
A Jini system consists of the
following parts:
A set of components that provides an
infrastructure for federating services in a distributed system.
A programming model that supports and
encourages the production of reliable distributed services.
Services that can be made part of a
federated Jini system and that offer functionality to any other member of the
federation.
Discovery: finds other members in the
jinni community and joins to enable networking capability.
Look-up: Search based on object type.
Leasing: Stable and self healing.
Resources are only leased since each have some timestamp.
Remote Events: Sending notification to the
participants. Transactions: similar
to database transaction.
Jini
scenario for accessing a remote service- first step
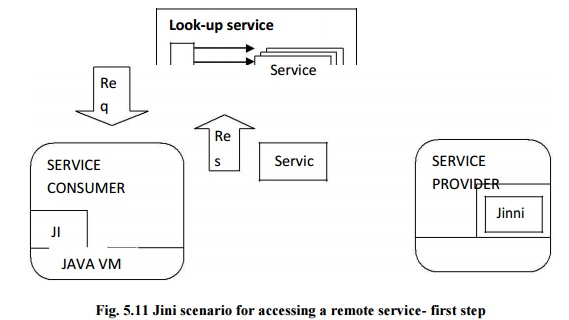
Jini
scenario for accessing a remote service- second step
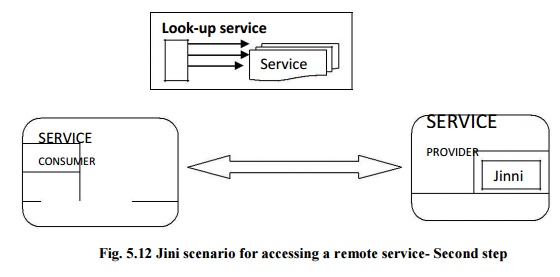
6. Message and Transaction Based
Protocol:
Messaging
and Transaction Technology:
Assured Message
delivery and atomic
operation are the
two different echnologies.
Standards are needed in order to implement these technologies.
SOAP
provides message exchanging structure and sends information between peers.
Message
queuing is another concept which emphasis on storing of messages and as soon as
the connection established, the message will be delivered. This is suitable for
asynchronous network.
Topology
can be build with multiple queues. One to one, one to many, many to one.
Related Topics