Chapter: Mobile Networks : Pervasive Computing
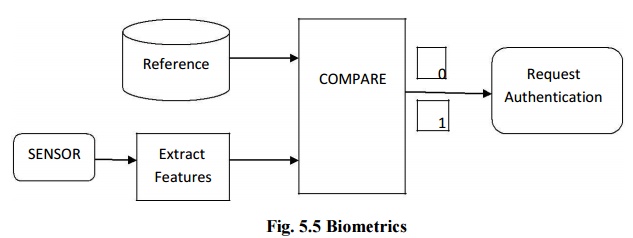
Biometrics
BIOMETRICS
1. Operating system
The core
functionality of every pervasive computing device is determined by its
operating system.
The major
differences of operating systems for pervasive devices from the user's point of
view are the human-machine interface, and the speed with which a task can be
performed.
For pervasive devices, there will likely be no equivalent to the Windows/Intel monopoly in the near future because pervasive devices do have a wide range of usages (from mobile phones to set-top boxes) with very constrained hardware
2. Palm OS:
Suitable
and easy to use operating system for PDAs, optimized restricted features are
available which leads to lower memory and CPU usage which results in longer
battery life.Features: Enhanced
Communication Support and Multimedia with Mobile Phones
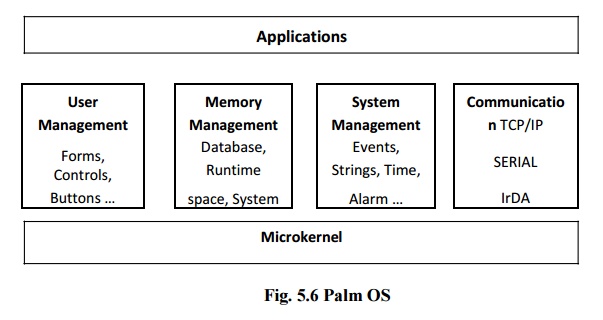
1.User
Management:
Single
user operating system
2.Task
Management:
One
application runs at a time and can call other applications.
3.Power
Management:
Power
modes (sleep, doze and running)
4.OS
size:
OS 3.5 is
about 1.4 MB.
User
Interface:
It
recognizes only the palm handwriting alphabets, one button access to
applications; minimize taps for often used operations.
Memory
Management:
Applications
should be well tested since if one application crashes then the system crashes.
Thus memory is divided into dynamic heap which is execution based and clears on
reset and storage is designed to hold permanent data.
Software
can be developed with both C and C++ in Palm OS.
3. EPOC:
The EPOC operating system was designed specifically
for phones. There are two versions: EPOC16 for 16-bit processors and EPOC32 for
32-bit processors.
Core operating system
functionality:
Heavily
Multitasking.
The base
layer provides the fundamental APIs.
The middleware
layer provides the
graphics, data, and
other components to
support
the graphical user interface and applications.
EIKON is
the system graphical user interface framework.
User
Management:
Single
user operating system
Task
management
Provides
multitasking with a pre-emptive, priority-driven scheduler.
User
interface
The EPOC user interface supports display, keyboard,
and sound. . It is also responsible for handling the data and command input.
Figure shows the EPOC user interface of an Ericsson device with a map
application.
Memory
management
EPOC has a memory management unit (MMU) concept to
provide separate address spaces for each application. These tools include
design patterns, stack clean-up heap failure, and heap-checking tools.
Programming languages supported by EPOC are C++,
Java and OPL. C++ used to develop system development and high performance application
programming.
4. Window
CE:
Windows
CE is an embedded operating system
developed by Microsoft.
Windows
CE 3.0 offers real-time support, a smart card subsystem for PC/SC compliant
readers, is Unicode based, and supports grayscale and color graphics up to
32-bit depth. Windows CE is a modular operating system that can be configured
by the device manufacturer. This is a result of the read-only memory
(ROM)-based design of Windows CE, in contrast to more desktop-oriented,
disk-based operating systems like Linux or BeOS. It can even be configured at
runtime.
The
kernel provides memory management, task scheduling, and interrupt handling.
The
graphics/window/event manager (GWE) integrates the user interface functions of
graphical output and user input.
The
object store is the persistent memory of Windows CE and includes files, the
registry, and a database.
Finally,
the communication interfaces include infrared communication via IrDA,
TCP/IP,
and serial drivers.
User
management:
Because
Windows CE is designed for PDAs, it supports only one user.
`Task
management:
The task manager supports 32 simultaneous processes
and an unlimited number of threads.
Operating
system size:
The Windows CE footprint can be as small as 400 kb
for the kernel, up to 3 MB with all modules, and up to 8 MB including Pocket
Word and Internet Explorer.
User
interface:
Windows CE provides menu controls, dialog boxes,
an: icons, and supports sound.
Memory
management:
A protected virtual memory system that supports up
to 32 MB memory per process protects applications against each other. There
exists a special heap for the file system, registry, and object store that has
a transaction service for ensuring data integrity. The object store can have a
size up to 256 MB.
Security: Windows CE has support for cryptography with a cryptographic library (Cryptographic Application Programming Interface, CAPI) to securely store information in memory. The kernel-loader authentication program can use public-key signatures to prevent unauthorized applications from running. Access to the data, however, will be slower because of the electrically erasable and programmable read-only memory (EEPROM) memory used instead of battery-backed RAM.
Software development for Windows CE
Since Windows CE is based on the Win32 API development tools, such as
Visual C++ or Visual Basic, available for this API.
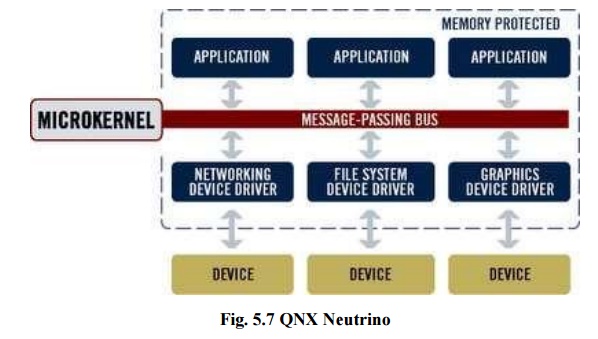
5. QNX Neutrino:
QNX is a
real time operating system consisting of microkernel surrounded by a collection
of optimal processes that provides UNIX based system services. Due to
microkernel architecture even if the file system driver or network driver
crashes, still the system will work which leads to stable system. QNX is very
well suitable for car devices.
User
management:
QNX
supports single user.
Task
management:
Supports
real multitasking.
User
interface:
Consist
of micro graphical user interfaces and widgets for easy interface.
Memory
management:
QNX has
an MMU concept for separation of address space of applications. Different
application runs on different threads.
Software
development for QNX is in C language.
6. Be OS:
Be OS is
highly optimized for multimedia application. It posses sound and graphic
processor. It deals with 64 bit file system
The architecture
is based on a symmetric multi processor model, allowing each processor full
access to resources and also it provides pre-emptive multitasking and pervasive
mulltithreading (rapind switching between several task).
User
management:
It
supports multiuser as like standard operating system.
Task
management:
Pre-emptive
multitasking by pervasive threads enables the task management much speeder.
Memory
management:
Provides
memory protection between applications and virtual memory support.
Software
development is done using C/C++.
7. Embedded Linux:
Embedded Linux is a stripped down operating system with special support
to pervasive devices. Mainly used for handheld devices.
The core
features are Configurable kernel, Scalability and Networking.
User
management:
It
supports multiuser as like standard operating system.
Task
management:
Preemptive
multitasking with optional real time scheduler is implemented.
Operating
System Size:
Depending
on the configuration, the size of the kernel can range from 200 KB to several
megabytes.
User
Interface:
x-Window
system for user interface and have striped down version to save memory.
Memory
management:
Supports
MMUs to provide memory protection between applications and virtual memory for
paging memory to hard disc.
Software
development is done using C/C++ and JAVA.
Related Topics