Chapter: Paediatrics: Practical procedures
Paediatrics: Capillary blood sampling
Capillary blood sampling is used
when small volumes of blood are neces-sary for analysis, e.g. FBC, blood gas,
blood glucose. An automated device to pierce the skin is preferred over a
lancet, as it causes less pain and punctures to a predetermined depth, thereby
reducing the risk of underly-ing bone damage or infection.
Equipment
•
Alcohol
impregnated swab.
•
Automated
device or sterile lancet.
•
Appropriate
sample bottles or capillary tubes.
•
Cotton
wool or gauze swab.
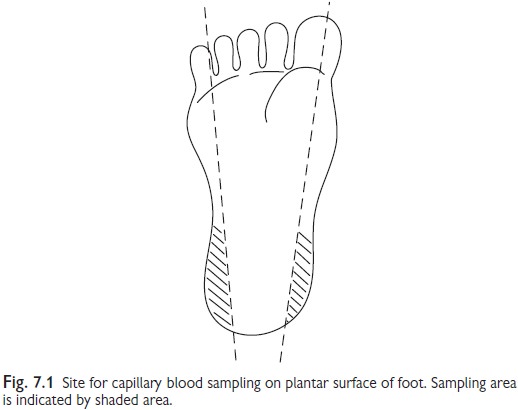
Site
•
Plantar
heel surface outside the medial and lateral limits of calcaneous bone in the
young infant (Fig. 7.1).
•
Finger
site in the older child.
Procedure
•
Warm
the heel or finger.
•
In the
case of foot, hold dorsiflexed.
•
Clean
with an alcohol impregnated swab.
•
Gently
massage area to improve blood flow and use your hand as a tourniquet.
•
Puncture
skin with an automated device or sterile lancet.
•
‘Scoop’
droplets of blood into an appropriate sample container or on to blood
glucose-measuring strip. Note that excessive squeezing leads to falsely high
serum potassium and haematocrit levels, and bruising.
•
Once
sample has been collected stop any residual bleeding by local pressure with a
cotton wool ball or gauze swab.
Related Topics