Chapter: Principles of Management : Directing
Organization Culture: Elements and types of culture
ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE
Organizational
culture is an idea in the field of organizational studies and management which
describes the psychology, attitudes, experiences, beliefs and values (personal
and cultural values) of an organization. It has been defined as "the
specific collection of values and norms that are shared by people and groups in
an organization and that control the way they interact with each other and with
stakeholders outside the organization."
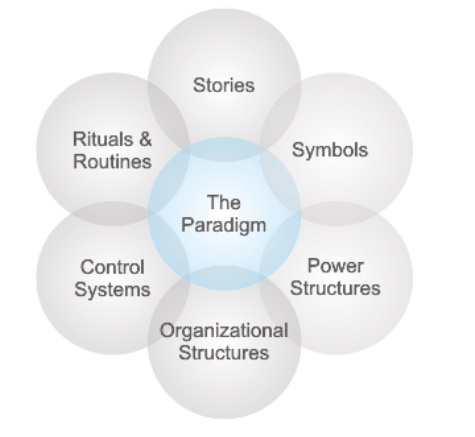
ELEMENTS OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE
Johnson
and Scholes described a cultural web, identifying a number of elements that can
be used to describe or influence Organizational Culture:
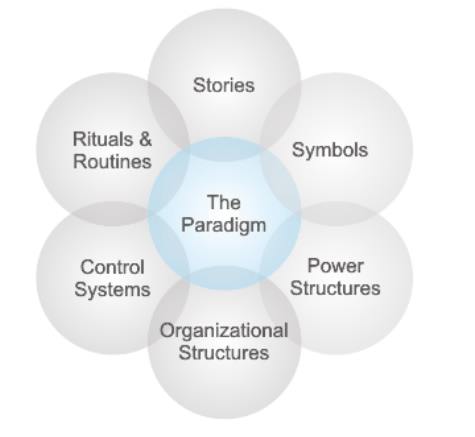
The six
elements are:
Stories: The past events and people talked about
inside and outside the company. Who and what the company chooses to immortalize
says a great deal about what it values, and perceives as great behavior.
Rituals and Routines: The daily behavior and
actions of people that signal acceptable behavior. This determines what is
expected to happen in given situations, and what is valued by management.
Symbols: The visual representations of the
company including logos, how plush the offices are, and the formal or informal
dress codes.
Organizational Structure: This includes both the
structure defined by the organization chart, and the unwritten lines of power
and influence that indicate whose contributions are most valued.
Control Systems: The ways that the organization
is controlled. These include financial systems, quality systems, and rewards
(including the way they are measured and distributed within the organization.)
Power Structures: The pockets of real power in
the company. This may involve one or two key senior executives, a whole group
of executives, or even a department. The key is that these people have the
greatest amount of influence on decisions, operations, and strategic direction.
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE
Deal and
Kennedy argue organizational culture is based on based on two elements:
Feedback
Speed: How quickly are
feedback and rewards provided (through which the people are told they are doing a good or a bad job).
Degree
of Risk: The level of risk
taking (degree of uncertainty).
The
combination of these two elements results in four types of corporate cultures:
Tough-Guy Culture or Macho Culture (Fast feedback and reward, high risk):
Stress
results from the high risk and the high potential decrease or increase of the
reward.
Focus on
now, individualism prevails over teamwork.
Typical
examples: advertising, brokerage, sports.
The most
important aspect of this kind of culture is big rewards and quick feedback.
This kind of culture is mostly associated with quick financial activities like
brokerage and currency trading. It can also be related with activities, like a
sports team or branding of an athlete, and also the police team. This kind of
culture is considered to carry along, a high amount of stress, and people
working within the organization are expected to possess a strong mentality, for
survival in the organization.
Work Hard/Play Hard (Fast feedback and reward, low risk):
Stress
results from quantity of work rather than uncertainty.
Focus on
high-speed action, high levels of energy.
Typical
examples: sales, restaurants, software companies.
This type
of organization does not involve much risk, as the organizations already
consist of a firm base along with a strong client relationship. This kind of
culture is mostly opted by large organizations which have strong customer
service. The organization with this kind of culture is
equipped
with specialized jargons and is qualified with multiple team meetings.
Bet Your Company Culture (Slow feedback and reward, high risk):
Stress
results from high risk and delay before knowing if actions have paid off.
Focus on
long-term, preparation and planning.
Typical
examples: pharmaceutical companies, aircraft manufacturers, oil prospecting
companies.
In this
kind of culture, the company makes big and important decisions over high stakes
endeavors. It takes time to see the consequence of these decisions. Companies
that postulate experimental projects and researches as their core business,
adopt this kind of culture. This kind of culture can be adopted by a company
designing experimental military weapons for example.
Process Culture (Slow feedback and reward, low risk):
Stress is
generally low, but may come from internal politics and stupidity of the system.
Focus on
details and process excellence.
Typical
examples: bureaucracies, banks, insurance companies, public services.
This type
of culture does not include the process of feedback. In this kind of culture,
the organization is extremely cautious about the adherence to laws and prefer
to abide by them. This culture provides consistency to the organization and is
good for public services.
One of the
most difficult tasks to undertake in an organization, is to change its work
culture. An organizational culture change requires an organization to make
amendments to its policies, its workplace ethics and its management system. It
needs to start right from its base functions which includes support functions,
operations and the production floor, which finally affects the overall output
of the organization. It requires a complete overhaul of the entire system, and
not many organizations prefer it as the process is a long and tedious one,
which requires patience and endurance. However, when an organization succeeds
in making a change on such a massive level, the results are almost always
positive and fruitful. The different types of organizational cultures mentioned
above must have surely helped you to understand them. You can also adopt one of
them for your own organization, however, persistence and patience is ultimately
of the essence.
Related Topics