Chapter: Principles of Management : Directing
Hertzbergs Two Factor Theory or Hygeine Theory
Hertzbergs Two Factor Theory or
Hygeine Theory
In 1959,
Frederick Herzberg, a behavioural scientist proposed a two-factor theory or the
motivator-hygiene theory. According to Herzberg, there are some job factors
that result in satisfaction while there are other job factors that prevent
dissatisfaction.
According to Herzberg, the opposite
of “Satisfaction” is “No satisfaction” and the opposite of “Dissatisfaction” is
“No Dissatisfaction”.
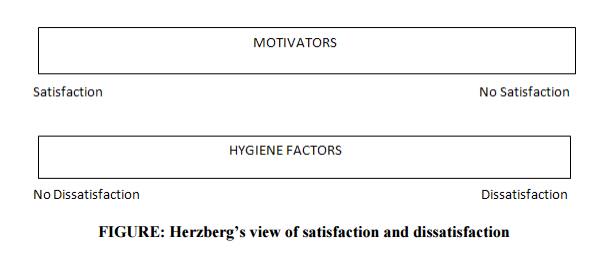
Herzberg classified these job
factors into two categories-
a.Hygiene factors- Hygiene factors are
those job factors which are essential for existence of motivation at workplace.
These do not lead to positive satisfaction for long-term. But if these factors
are absent / if these factors are non-existant at workplace, then they lead to
dissatisfaction. In other words, hygiene factors are those factors which when
adequate / reasonable in a job, pacify the employees and do not make them
dissatisfied. These factors are extrinsic to work. Hygiene factors are also
called as dissatisfiers or maintenance
factors as they are required to avoid dissatisfaction. These factors
describe the job environment / scenario. The hygiene factors symbolized the
physiological needs which the individuals wanted and expected to be fulfilled.
Hygiene factors include:
Pay-
The pay or salary structure should be appropriate and reasonable. It must be
equal and competitive to those in the same industry in the same domain.
Company
Policies and administrative policies- The company policies should not be too
rigid. They should be fair and clear. It should include flexible working hours,
dress code, breaks, vacation, etc.
Fringe
benefits- The employees should be offered health care plans (mediclaim),
benefits for the family members, employee help programmes, etc.
Physical
Working conditions- The working conditions should be safe, clean and hygienic.
The work equipments should be updated and well-maintained.
Status-
The employees’ status within the organization should be familiar and retained.
Interpersonal
relations-The relationship of the employees with his peers, superiors and
subordinates should be appropriate and acceptable. There should be no conflict
or humiliation element present.
Job
Security- The organization must provide job security to the employees.
b.Motivational
factors- According to Herzberg, the hygiene factors cannot be regarded as
motivators. The motivational factors yield positive satisfaction. These factors
are inherent to work. These factors motivate the employees for a superior
performance. These factors are called satisfiers. These are factors involved in
performing the job. Employees find these factors intrinsically rewarding. The
motivators symbolized the psychological needs that were perceived as an
additional benefit. Motivational factors include:
Recognition-
The employees should be praised and recognized for their accomplishments by the
managers.
Sense
of achievement- The employees must have a sense of achievement. This depends on
the job. There must be a fruit of some sort in the job.
Growth
and promotional opportunities- There must be growth and advancement
opportunities in an organization to motivate the employees to perform well.
Responsibility-
The employees must hold themselves responsible for the work. The managers
should give them ownership of the work. They should minimize control but retain
accountability.
Meaningfulness of the work- The work itself should be
meaningful, interesting and challenging for the employee to perform and to get
motivated.
Limitations of Two-Factor Theory
The two factor theory is not free
from limitations:
The
two-factor theory overlooks situational variables.
Herzberg
assumed a correlation between satisfaction and productivity. But the research
conducted by Herzberg stressed upon satisfaction and ignored productivity.
The
theory’s reliability is uncertain. Analysis has to be made by the
raters.
The raters may spoil the findings by analyzing same response in different
manner.
No
comprehensive measure of satisfaction was used. An employee may find his job
acceptable despite the fact that he may hate/object part of his job.
The
two factor theory is not free from bias as it is based on the natural reaction
of employees when they are enquired the sources of satisfaction and
dissatisfaction at work. They will blame dissatisfaction on the external factors
such as salary structure, company policies and peer relationship. Also, the
employees will give credit to themselves for the satisfaction factor at work.
The theory ignores blue-collar workers. Despite these
limitations, Herzberg’s Two-Factor theory is acceptable broadly.
Implications
of Two-Factor Theory
ĂĽ The Two-Factor theory implies that the managers must stress
upon guaranteeing the adequacy of
the hygiene factors to avoid employee dissatisfaction. Also, the managers must
make sure that the work is stimulating and rewarding so that the employees are
motivated to work and perform harder
and better. This theory emphasize
upon job-enrichment so as to motivate the employees. The job must utilize the
employee’s skills and competencies to the
maximum. Focusing on the
motivational factors can improve work-quality.
Related Topics