Chapter: Medical Physiology: Motor Functions of the Spinal Cord; the Cord Reflexes
Muscle Sensory Receptors- Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs-And Their Roles in Muscle Control
Muscle Sensory Receptors- Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs-And Their Roles in Muscle Control
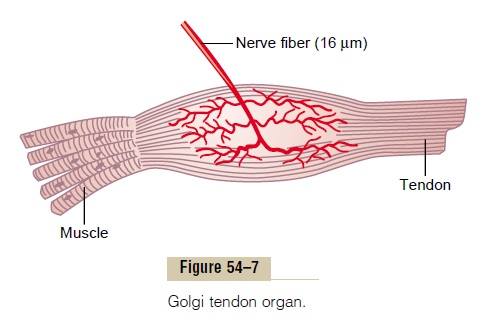
Proper control of muscle function requires not only excitation of the muscle by spinal cord anterior motor neurons but also continuous feedback of sensory information from each muscle to the spinal cord, indicating the functional status of each muscle at each instant. That is, what is the length of the muscle, what is its instantaneous tension, and how rapidly is its length or tension changing? To provide this informa-tion, the muscles and their tendons are supplied abun-dantly with two special types of sensory receptors: (1)muscle spindles (see Figure 54–2), which are distrib-uted throughout the belly of the muscle and send information to the nervous system about muscle length or rate of change of length, and (2) Golgitendon organs (see Figure 54–7), which are located inthe muscle tendons and transmit information about tendon tension or rate of change of tension.
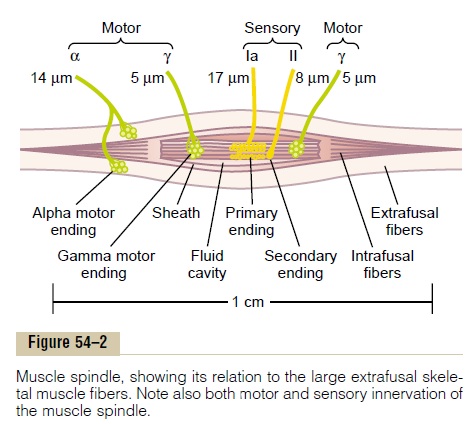
The signals from these two receptors are either entirely or almost entirely for the purpose of intrinsic muscle control. They operate almost completely at a subconscious level. Even so, they transmit tremendous amounts of information not only to the spinal cord but also to the cerebellum and even to the cerebral cortex, helping each of these portions of the nervous system function to control muscle contraction.
Related Topics