Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 2 : The Solar system and the Earth
Motions of the earth
Motions
of the earth
The
earth has two
basic movements:
1. Rotation
2. Revolution.
Galactic
movement:
This is
the movement of the earth with the sun
and the rest
of the solar system in an orbit around the centre of the MilkyWay
Galaxy. This, however, has little effect upon the changing environment of the
earth.
1. Rotation: The spinning of the earth around its axis is called the rotation of the earth. The axis is the imaginary line passing through the centre of the earth. The earth completes one rotation in 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4.09 seconds.
It rotates in an eastward direction opposite to the apparent movement of the sun. The
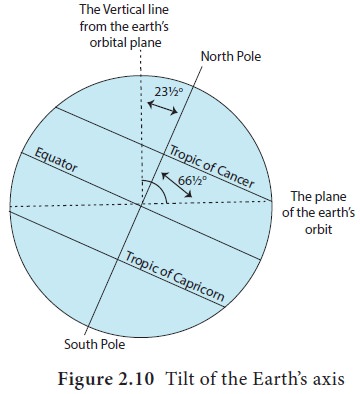
earth’s axis is inclined at an angle of 66½q to the orbital plane as it moves
around the sun. We can say, the earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 23½q
(Figure 2.10) from a perpendicular to the elliptic plane. The velocity of
earth’s rotation varies depending on the distance of a given place from the
equator.The rotational velocity at the poles is nearly zero. The greatest
velocity of the rotation is found at the equator. The velocity of rotation at
the equator is 1,670 km per hour.
Effects
of earth’s rotation: The
rotation of the earth causes the
following effects:
1. The apparent rising and setting of the sun is
actually caused by the earth’s rotation which results in the alternate
occurrence of day and night everywhere on the earth’s surface.
2. Rotation of the earth is also responsible for
the difference in time between different places on the earth. A 24 hour period divided
by 360 degrees gives a difference of 4 minutes for every degree of longitude
that passes the sun. The hour (60 minutes) is thus 1/24 of a day.
3. When you observe through a moving train, trees,
houses and fields on the other side of the track appear to move in the
direction opposite to that of the speeding train. The apparent movement of the
sun and the other heavenly bodies in relation to the rotating earth is
similar. As the earth rotates from west
to east, the sun, moon, planets and stars appear to rise in the east and set in
the west.
4. Rotation causes the working of the Coriolis force
which results in the
deflection of the winds and the ocean currents from their normal path.
5. Tide is caused by the rotation of the earth
apart from the gravitational pull of the sun and the moon.
Rotation causes a flattening of Earth at the two
poles and bulging at the Equator. Hence, there is a difference in diameter at
the poles and equator.
Circle
of Illumination: The
line around the earth separating the
light and dark is known as the circle of illumination (Figure 2.11).
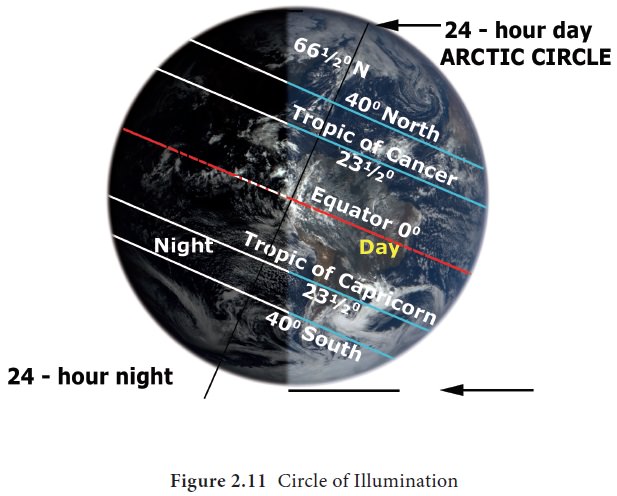
It passes through the poles and allows the entire
earth to have an equal amount of time during the daylight and night time hours.
This line can be seen from space, and the exact location of the line is
dependent on the various seasons.
Revolution of the Earth
The movement of the earth in its orbit around the sun in an anti-clockwise direction, that is, from west to east is called revolution of the earth. The earth revolves in an orbit at an average distance of 150 million km.
The distance of the earth from sun varies time to time due to the
elliptical shape of the orbit. About January 3rd the earth is closest to the
sun and it is said to be at Perihelion
(‘peri’ means close to and Helios
means sun). At Perihelion, the distance is 147 million km.
Around July 4th the earth is farthest from the sun
and it is said to be at Aphelion (Ap
means away and Helios means sun). At
Aphelion the distance of the earth is 152 million km away from the sun.
The period taken by the earth to complete one
revolution around the sun is 365 days and 6 hours (5 hours, 48 minutes and 45
seconds) or 365¼ days. The speed of the revolution is 1,07,000 km per hour. The
speed is 30 km per second. The bullet from a gun travels with a speed of 9 km
per second.
Period of Revolution and Leap year
The period of time the earth takes to make one
revolution around the sun determines the length of one year. The earth takes
365 days and 6 hours to complete one revolution. Earth takes 365.25 days to
complete one trip around the Sun .That extra quarter of a day presents a
challenge to our calendar system, which has one year as 365 days. To keep our
yearly calendars consistent with our orbit around the Sun once in, every four
years we add one day.
The extra day added to is called a leap day, and
the year the extra day is added to is called a leap year. The extra day is
added to the month of February which has 29 days in a leap year.
Brain
storming
How many birth days a person, whose life span
supposed to be 60 years, would have seen in his/ her life time, if born on 29th
February?
Effects of revolution of the earth
The revolution of the earth around the sun results
in the following
·
Cycle
of seasons,
·
Variation
in length of days and nights,
·
Variation
in distribution of solar energy over the earth and the temperature zones.
Let us
know!
How to calculate leap year? Take any year and
divide by 4 or 100 or 400. If it is divisible (whole number with no reminder),
it is a leap year.
Students’ activity: calculate and identify the leap
years from the following years 1992, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2008, 2010, 2012, 2014,
2017, 2020, 2024, 2030, 2035, 2040 and 2044.
Related Topics