Chapter: Linear Integrated Ciruits : IC Fabrication and Circuit Configuration for Linear ICs
Monolithic Capacitors
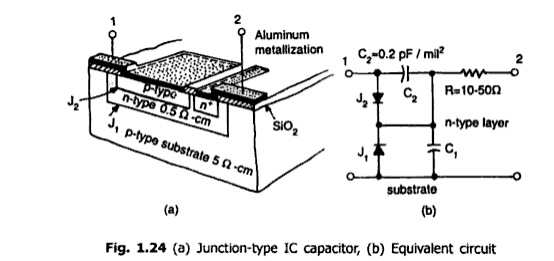
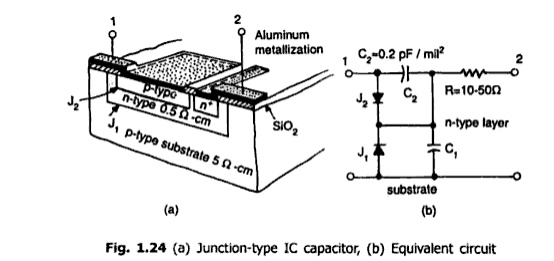
Monolithic Capacitors:
Monolithic
capacitors are not frequently used in integrated circuits since they are
limited in the range of values obtained and their performance. There are,
however, two types available, the junction capacitor is a reverse biased PN
junction formed by the collector-base or emitter-base diffusion of the
transistor. The capacitance is proportional to the area of the junction and
inversely proportional to the depletion thickness.
C α A, where a is the area of the junction and
C α T , where t is the thickness of the
depletion layer.
The
capacitance value thus obtainable can be around 1.2nF/mm2 .
The thin
film or metal oxide silicon capacitor uses a thin layer of silicon dioxide as
the dielectric. One plate is the connecting metal and the other is a heavily
doped layer of silicon, which is formed during the emitter diffusion. This
capacitor has a lower leakage current and is non-directional, since emitter
plate can be biased positively. The capacitance value of this method can be
varied between 0.3 and 0.8nF/mm2 .
Inductors:
No
satisfactory integrated inductors exist. If high Q inductors with inductance of
values larger than 5μH are required, they are usually supplied by a wound
inductor which is connected externally to the chip. Therefore, the use of
inductors is normally avoided when integrated circuits are used.
Related Topics